The Epichaperome in Cancer Therapy: Using Protein Interaction Networks to Optimize Drug Delivery
StressMarq’s HSP70/HSC70, HSP90 and HSP110 antibodies were recently cited in a research publication in Cancer Cell journal by Pillarsetty et al. The researchers introduce a theranostic platform for precision medicine where the protein networks properties are used for cancer therapy. In precision medicine, scientists identify the genetic changes responsible for cancer growth in order to develop targeted therapies.
What is the Epichaperome?
It is well known that the “chaperome” is a family of proteins that regulates cellular homeostasis. Under cellular stress conditions, chaperomes form a stable protein network known as “epichaperome” which is found only in cancer cells and it is vital for tumor growth and survival. Chaperones of the Heat Shock proteins HSP90 and HSC70 play a critical role in the epichaperome formation.
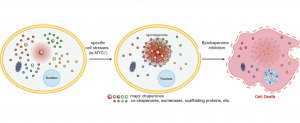
Schematic showing the re-wiring of the chaperome into the epichaperome network, following a specific cell stress. Inhibition of one of the epichaperome components dismantles the network. When the network is key to maintain viability in such cancer cell, epichaperome dismantling results in cell death. Source: http://www.impactjournals.com/oncoscience/index.php?abs=321
PU-PET Assay for Epichaperome Analysis
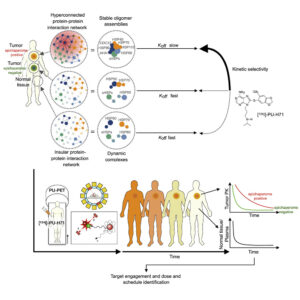
Researchers at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center developed the synthetic purine-scaffold inhibitor PU-H71, selective for the HSP90, which works only in tumors where an epichaperome has formed. They also developed a radiolabeled [124 I] PU-H71 inhibitor to study the distribution and pharmacokinetic properties of PU-H71 in living subjects using PET (positron emission tomography) imaging.
The PU-PET diagnostic assay is used to detect and quantify the epichaperome positivity in solid tumors. The radioactive probe binds to the HSP90 in the epichaperome and the PET scan shows the location of the tumor that carries the epichaperome. The advantage of this method is that we can quantify in real-time how much of the drug reaches the tumor and how long it stays in it. Furthermore, it can give real-time tumor pharmacometric data that can be used in determining the best drug dose and schedule for an individual.
[124I]PU-H71 dissociates from epichaperomes much more slowly than it does from other HSP90 pools. This difference in the dissociation constant (koff ) provides this probe with epichaperome selectivity. The PU-PET assay is used to measure and visualize the epichaperome, its inhibitor engagement and collect pharmacometric data that can be used to optimize the dose and schedule selection. Source: https://www.cell.com/cancer-cell/fulltext/S1535-6108(19)30427-1
The results of this paper present a paradigm for precision medicine and can be used for the development of other drugs and radioactive agents that also target the epichaperome.
The original research paper was published in Cancer Cell journal (October 2019).
“Paradigms for Precision Medicine in Epichaperome Cancer Therapy”


Leave a Reply