| Product Name | Radicicol |
| Description |
Hsp90 inhibitor |
| Purity | 97% by TLC |
| CAS No. | 12772-57-5 |
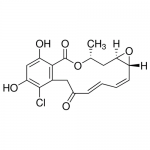
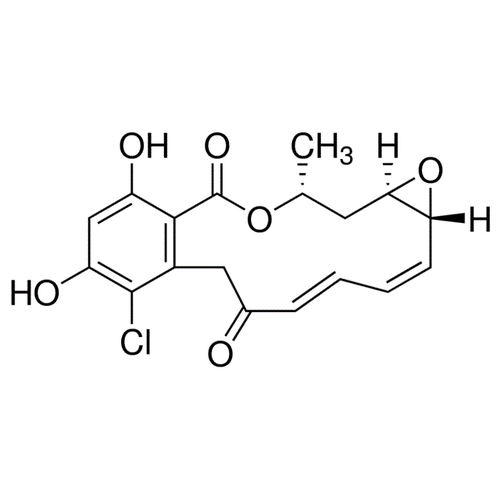
| Molecular Formula | C18H17CIO6 |
| Molecular Weight | 364.8 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Source | Produced by fermentation |
| Appearance | White to Yellow Solid |
| SMILES | COc1ccc2c(=O)c(coc2c1OC)c3cc(c(cc3I)OC)OC |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C18H17ClO6/c1-9-6-15-14(25-15)5-3-2-4-10(20)7-11-16(18(23)24-9)12(21)8-13(22)17(11)19/h2-5,8-9,14-15,21-22H,6-7H2,1H3/b4-2+,5-3-/t9-,14-,15-/m1/s1 |
| InChIKey | WYZWZEOGROVVHK-GTMNPGAYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution: Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection |
| Cite This Product | Radicicol (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-117) |
Biological Description
| Research Areas | Cancer, Heat Shock |
| PubChem ID | 6323491 |
| Scientific Background | Radicicol is a macrocyclic antifungal compound that functions as a potent inhibitor of HSP90, a molecular chaperone involved in protein folding and stability. In neuroscience, Radicicol’s ability to bind HSP90 and disrupt its interaction with client proteins offers a mechanism for modulating neurodegenerative disease pathways. It selectively depletes kinases such as Raf and inhibits src-like kinases, contributing to the regulation of cellular stress responses and apoptosis. Radicicol also exhibits anti-angiogenic properties and induces morphological reversion in transformed cells, which may be relevant in neuro-oncology. Its strong binding affinity to HSP90 across species, including yeast and bacterial homologs, underscores its utility in translational research models. By targeting chaperone-mediated proteostasis, Radicicol holds promise for therapeutic intervention in disorders characterized by protein misfolding and aggregation. |
| References |
1. Kwon H.J., et al. (1992) Cancer Res. 52: 6929. 2. Yen A., et al. (1994) Exp.Cell Res. 214: 163. 3. Kwon H.J., et al. (1995) J.Biochem.(Tokyo) 118: 221. 4. Soga S., et al. (1998) J.Biol.Chem. 273: 822. 5. Oikawa T., et al. (1993) Eur.J.Pharmacol. 241: 221. 6. Roe S.M. et al. (1999) J.Med.Chem. 42: 260. |

StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.