| Product Name | Ferrostatin-1 |
| Description |
Ferroptosis Inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% (TLC); NMR (Conforms) |
| CAS No. | 347174-05-4 |
| Molecular Formula | C15H22N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 262.4 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (100 mg/ml) or ethanol (100 mg/ml) |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Tan powder |
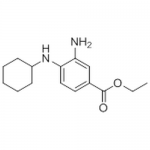
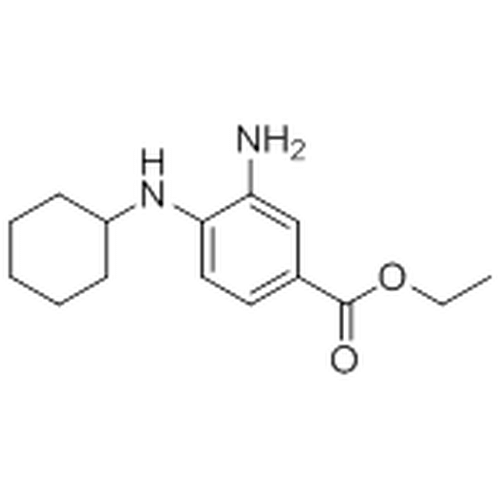
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)c1ccc(c(c1)N)NC2CCCCC2 |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Skin irritation (Category 2), H315 Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. Hazard statements: H315 Causes skin irritation. H319 Causes serious eye irritation. Precautionary statements: P260 Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray P264 Wash skin thoroughly after handling. P280 Wear protective gloves. P302 + P352 IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water. P304 + 340 If INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing P305 + 351+ + 338 IF IN EYES: Rinse continuously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do so- continue rinsing. P333 + 313 If skin irritation or a rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention |
| Cite This Product | Ferrostatin-1 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-525) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Ethyl 3-amino-4-(cyclohexylamino)benzoate |
| Research Areas | Apoptosis, Cancer, Cell Signaling, Neuroscience |
| Scientific Background | Ferrostatin-1 is a potent inhibitor of ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of regulated cell death characterized by lipid peroxidation. It has demonstrated neuroprotective effects in models of Parkinson’s disease, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. By preventing oxidative lipid damage, Ferrostatin-1 helps preserve neuronal integrity and function. Its ability to mitigate α-synuclein aggregation and reduce neuroinflammation positions it as a promising candidate for therapeutic development in neurodegenerative disease research. |
| References |
1. Dixon S.J., et al. (2012) Cell. 149: 1060. 2. Louandre C., et al. (2013) Int. J. Cancer. 133: 1732. 3. Skouta R., et al. (2014) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136: 4551. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.