DNA Damage
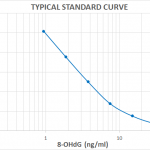
8-hydroxy-2-deoxy Guanosine (8-OHdG) is produced by the oxidative damage of DNA by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and serves as an established marker of oxidative stress. Hydroxylation of guanosine occurs in response to both normal metabolic processes and a variety of environmental factors (i.e., anything that increases reactive oxygen and nitrogen species). Increased levels of 8-OHdG are associated with the aging process as well as with a number of pathological conditions including cancer, diabetes, and hypertension.
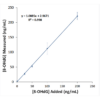
DNA damage can be measured by competitive ELISA, which allows for the quantification of 8-OHdG in cell lysates, plasma, sample matrices, and urine. DNA and RNA damage can also be detected with our monoclonal antibody, which is species independent and has been validated for IHC, ICC/IF, ELISA, IP, FCM, and functional assays. Both the monoclonal antibody and ELISA kit have been cited extensively.