Properties
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide. *Storage buffer may change when conjugated |
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC, Conjugated antibodies should be stored according to the product label |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Number | 2F11 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Specificity | This antibody binds a 3-dimensional fibrillar epitope of alpha synuclein (including AA101-120, AA61-80), present in MSA (Multiple System Atrophy) aggregates in human brain samples. It does not appear to detect PD (Parkinson's disease) or PDLB (Parkinson's disease with Lewy Bodies) aggregate structures in human brain samples. It can, however, bind recombinant human PFFs and mouse PFFs. |
| Cite This Product | Alpha Synuclein Antibody (Aggregate-Specific) (StressMarq Biosciences | Victoria, BC CANADA, Catalog# SMC-617, RRID: AB_3716711) |
| Certificate of Analysis | A 1:1000 dilution of SMC-617 was sufficient for detection of Alpha Synuclein aggregates in 15 µg of human brain cell lysate by ECL immunoblot analysis using goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP as the secondary antibody. |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Alpha Synuclein, α-Synuclein, SNCA, Snca, SYN, alphaSYN, NACP, Non-A beta component of AD amyloid, Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor, Parkinson disease familial 1, PARK1, PARK 1, PARK4, PARK 4, Parkinson disease (autosomal dominant, Lewy body) 4, Lewy body 4, Synuclein-alpha, PD1 |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Synuclein, Tangles & Tau, Multiple System Atrophy |
| Cellular Localization | Cell Junction, Cytoplasm, Cytosol, Membrane, Nucleus, Synapse |
| Accession Number | NP_001035916.1 |
| Gene ID | 20617 |
| Swiss Prot | O55042 |
| Scientific Background |
Alpha-synuclein (SNCA) is a presynaptic neuronal protein abundantly expressed in the brain, particularly within the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, striatum, and thalamus (1,2). Localized to both synaptic terminals and mitochondria, alpha-synuclein plays a critical role in synaptic vesicle regulation and cytoskeletal dynamics through its interaction with tubulin (3), suggesting a potential function as a microtubule-associated protein. It is also essential for cognitive development, with SNCA inactivation linked to deficits in spatial learning and working memory (4). Pathologically, alpha-synuclein aggregates are a defining feature of several neurodegenerative diseases. These fibrillar inclusions constitute the major non-Aβ component of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease and are the principal constituents of Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease (PD). In PD, progressive accumulation of alpha-synuclein and ubiquitin-positive inclusions in dopaminergic neurons is closely associated with motor and cognitive decline (5,6). Alpha-synuclein aggregation is not merely a byproduct of disease but a driver of neurotoxicity, mitochondrial dysfunction, and synaptic failure. Its central role in disease pathogenesis has made it a high-priority target for biomarker development and therapeutic intervention. Covered by US patent family US11,098,108B2 (7). |
| References |
1. “Genetics Home Reference: SNCA”. US National Library of Medicine. (2013). 2. Zhang L., et al. (2008) Brain Res. 1244: 40-52. 3. Alim M.A., et al. (2002) J Biol Chem. 277(3): 2112-2117. 4. Kokhan V.S., Afanasyeva M.A., Van'kin G. (2012) Behav. Brain. Res. 231(1): 226-230. 5. Spillantini M.G., et al. (1997) Nature. 388(6645): 839-840. 6. Mezey E., et al. (1998) Nat Med. 4(7): 755-757. 7. Louwrier, A. US Patent family US11,098,108 B2 |
Product Images
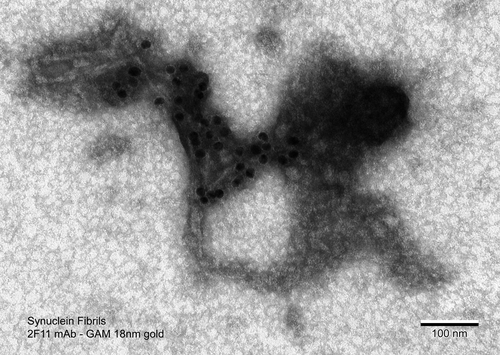
Immuno-gold electron micrograph of sonicated α-Syn Fibrils (SPR-322) stained with 2F11 antibody (1:400 dilution) and visualized using goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated with 18 nm gold particles. The sample was then placed on a transmission electron microscopy metallic grid and stained with uranyl acetate.
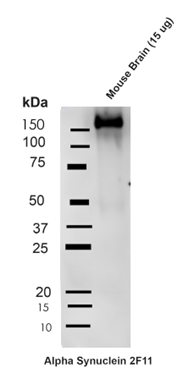
Western blot on 15ug mouse brain lysate from Fmr1 KO mice (FXS mice) with C57Bl/6J genetic background. Block: 5% Skim Milk in 1X TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Alpha Synuclein Monoclonal Antibody clone 2F11 at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse HRP:IgG at 1:3000 for 1 hour at RT. Color Development: ECL solution (Super Signal West Pico) for 5 min in RT. Band clearly identifies large molecular weight oligomeric band (monomeric band predicted at 14kD).
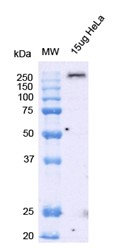
Western blot on 15ug Hela lysate. Block: 5% Skim Milk in 1X TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Alpha Synuclein Monoclonal Antibody clone 2F11 at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse HRP:IgG at 1:3000 for 1 hour at RT. Color Development: ECL solution (Super Signal West Pico) for 5 min in RT. Band clearly identifies large molecular weight oligomeric band (monomeric band predicted at 14kD).
![<p>SPR binding analysis of 2F11 antibody and human alpha synuclein type 1 fibrils (SPR-322), type 2 (SPR-317) fibrils and monomeric protein (SPR-321). Buffer (top left), alpha synuclein monomers (top right), alpha synuclein fibrils type1 (bottom left), and alpha synuclein fibrils type 2 (bottom right). Data: KD[nM] for SPR-322 = 42.5, SPR-317 = 365.3; 2F11 binds SPR-322 with 8.6 x greater affinity than SPR-317. 2F11 does not bind monomeric alpha synuclein (SPR-321).</p>](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-617_Alpha-Synuclein-Aggregate-Specific_Antibody_2F11_SPR-Binding-Analysis_1-2.png)
SPR binding analysis of 2F11 antibody and human alpha synuclein type 1 fibrils (SPR-322), type 2 (SPR-317) fibrils and monomeric protein (SPR-321). Buffer (top left), alpha synuclein monomers (top right), alpha synuclein fibrils type1 (bottom left), and alpha synuclein fibrils type 2 (bottom right). Data: KD[nM] for SPR-322 = 42.5, SPR-317 = 365.3; 2F11 binds SPR-322 with 8.6 x greater affinity than SPR-317. 2F11 does not bind monomeric alpha synuclein (SPR-321).
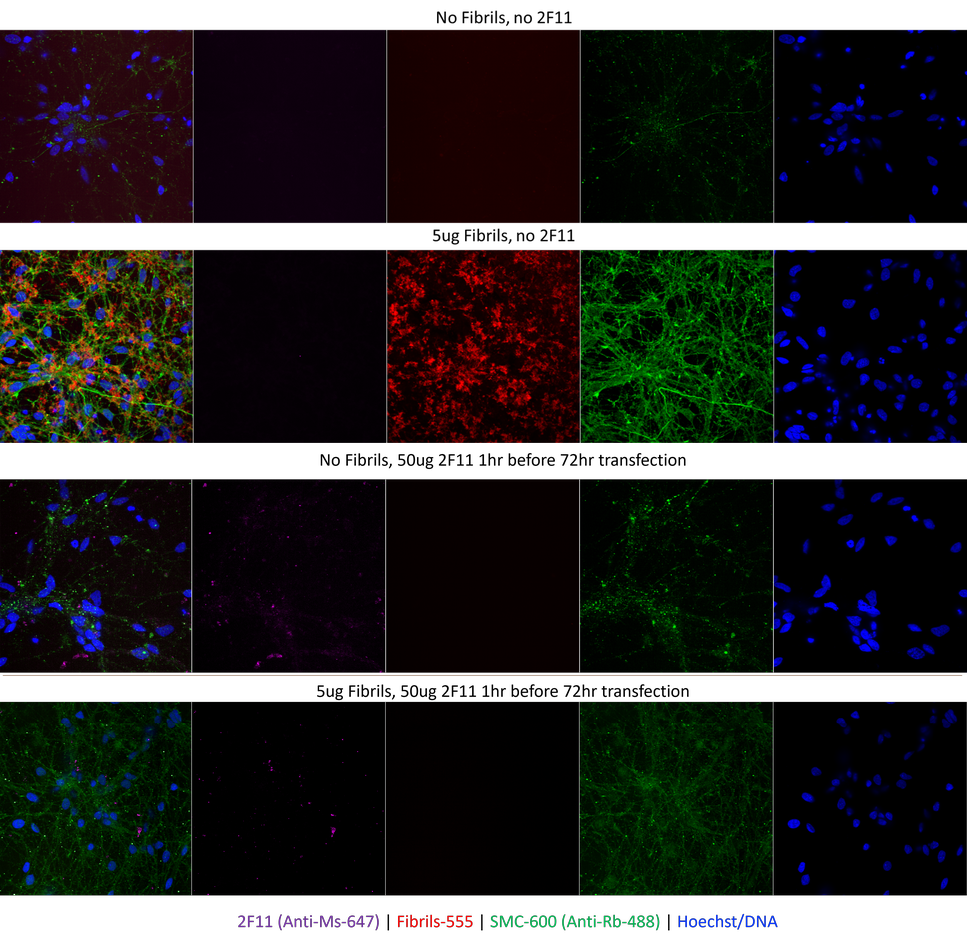
8 Day differentiated iPSCs with added alpha synuclein fibrils (SPR-322), conjugated to Alexa Fluor 555 with or without 1h prior 2F11 addition. SPR-322 Alexa Fluor 555 added at 5µg/well for 48h, 2F11 (50ug/well added 1h before fibrils where applicable). Cells were subsequently washed 48h after addition and imaged a following 24h later. Imaging and channels: 2F11 antibody: 647nm (using an anti-mouse-647 conjugate); Fibrils: 555nm, phosph-ser129 (SMC-600) 488nm, and Hoechst stain for DNA. Top two images: no fibrils, no 2F11 added; fibrils added, no 2F11 antibody. Fibrils are clearly visible in the cells as is enhanced phosph-ser129 signal. Bottom two images: no fibrils, 2F11 antibody added; fibrils and 2F11 antibody added. The image clearly shows 2F11 antibody addition stops cell entry of the 555-labelled fibrils.
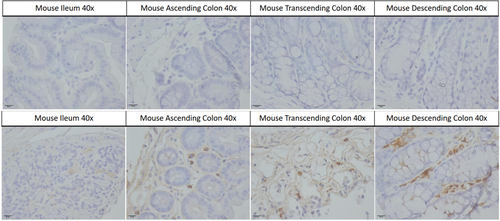
Mouse gut samples stained with 2F11 at 1:1000 dilution with overnight incubation at 4°C in PBS with 0.1% BSA, Secondary biotinylated anti-mouse antibody for 1 hour at RT also in 0.1% BSA PBS. VECTASTAIN ABC reagent kit was added after secondary incubation. Peroxidase HRP substrate was left on the gut tissue for 6 minutes. H&E staining of all tissue was performed at 1:1 with dH20, rinsed, then stained with blueing solution prior to dehydration. Imaging at 40 x magnification. Mouse tissue used from a mouse Parkinson’s disease (PD) seeding model based on C57BLJ/6 mice with brain injections of Human PD patient alpha-synuclein fractions. Mouse gut sections were used at a thickness of 3µm. Top panel shows (in biological order of mouse gut from ileum to descending colon) control secondary staining. Bottom panel shows gut samples from mice injected with human PD patient brain-derived alpha synuclein, also in biological order (ileum to descending colon). There is clear aggregate staining visible in the lower panel.
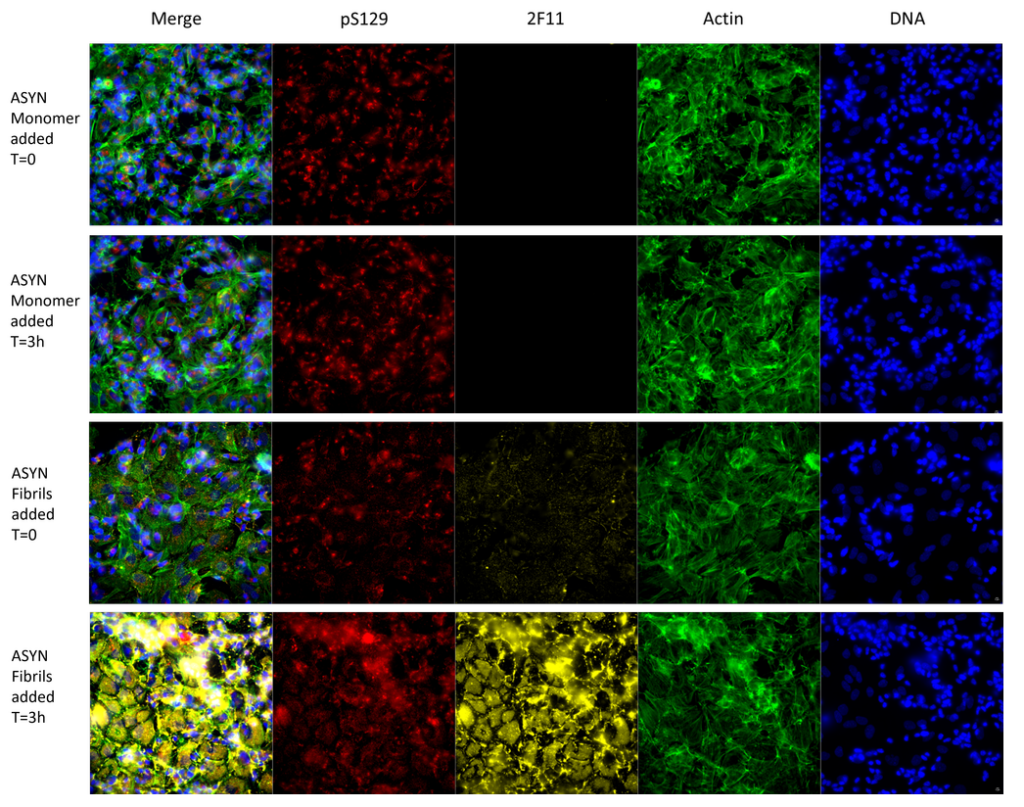
8 Day differentiated SH-SY5Y cells with added alpha synuclein monomers (SPR-321; 5µg) or fibrils (SPR-322; 5µg) at time zero and 3h time points. Staining and channels phospho-ser129 (ab51253) and secondary DaRb-647; 2F11 (1:1000 dilution, DaMs-555); Actin stain (Phalloidin dye: 488nm); DNA (Hoechst dye, 405nm). Top two images: T=0, T=3h, no signal change from 2F11 showing that alpha synuclein monomers do not bind the antibody. Bottom two images: T=0, T=3h. 2F11 channel clearly shows a large increase in fibril signal entering the cells by 3h, with a concomitant increase in phspho-Ser129 signal.

![Mouse Anti-Alpha Synuclein Antibody (Aggregate-Specific) [2F11] used in Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence (ICC/IF) on Human SH-SY5Y (SMC-617)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-617_Alpha-Synuclein-Aggregate-Specific_Antibody_2F11_ICC-IF_Human_SH-SY5Y_1-1.png)
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.