Properties
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% Sodium azide *Storage buffer may change when conjugated |
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC, Conjugated antibodies should be stored according to the product label |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Number | 10A10 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Specificity | Specific for Acrolein modified proteins. Does not detect free acrolein. Does not cross-react with Crotonaldehyde, Hexanoyl Lysine, 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal, 4-Hydroxy nonenal, Malondialdehyde, or Methylglyoxal modified proteins. |
| Cite This Product | Acrolein Antibody (StressMarq Biosciences | Victoria, BC CANADA, Catalog# SMC-505, RRID: AB_2702729) |
| Certificate of Analysis | A 1:1000 dilution of SMC-505 was sufficient for detection of Acrolein in 2 µg of Acrolein conjugated to BSA by ECL immunoblot analysis using Goat Anti-Mouse IgG:HRP as the secondary Antibody. |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Acraldehyde, Acrylaldehyde, Acrylic aldehyde, Allyl aldehyde, Propenal, 2-Propenal, Prop-2-enal, Prop-2-en-1-al, Acroleine, Paracetaldehyde, Acquinite, Aqualin, Aqualine, Biocide |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Cancer, Lipid peroxidation, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Oxidative Stress |
| Scientific Background |
Lipid peroxidation, a hallmark of oxidative stress, occurs when reactive oxygen species (ROS) attack unsaturated lipids in cellular membranes. This process not only compromises membrane integrity but also generates toxic byproducts that disrupt cellular homeostasis. Among these, acrolein—a highly reactive α,β-unsaturated aldehyde—has emerged as a critical factor in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acrolein is a terminal product of lipid peroxidation and is significantly more reactive than other aldehydes. It forms stable adducts with nucleophilic sites in DNA and proteins, particularly targeting cysteine, histidine, and lysine residues. These modifications impair protein function, alter signaling pathways, and contribute to mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal death. Elevated levels of acrolein have been consistently observed in the brains and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and other neurodegenerative conditions. Its presence correlates with markers of inflammation, synaptic loss, and cognitive decline, positioning acrolein as both a biomarker of disease progression and a potential therapeutic target. In neuroscience research, acrolein is increasingly recognized for its role in amplifying oxidative damage and neuroinflammation. Understanding its molecular interactions and downstream effects is essential for developing antioxidant-based therapies and early diagnostic tools aimed at mitigating neurodegeneration. |
| References | 1. Takabe, W. et al. (2001) Carcinogenesis. 22 (6): 935-941 |
Product Images
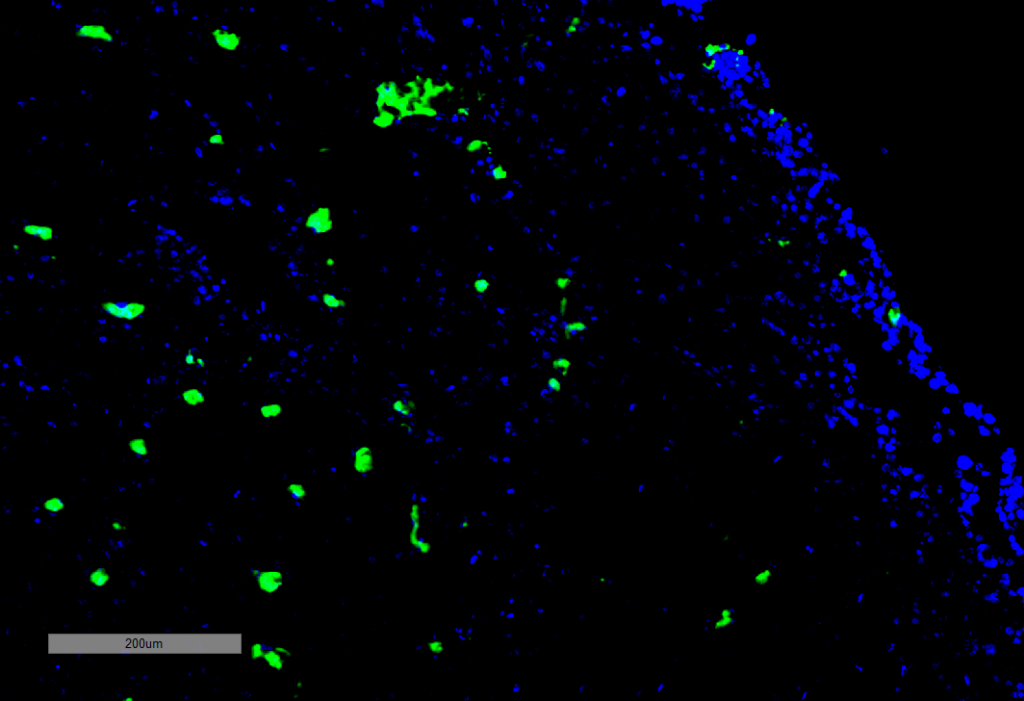
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 10A10 (SMC-505). Tissue: Adrenal Carcinoma. Species: Human. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-505) at 1:100 for Overnight at 4C, then 30 min at 37C. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L): FITC for 45 min at 37C. Counterstain: DAPI for 3 min at RT. Magnification: 5X.
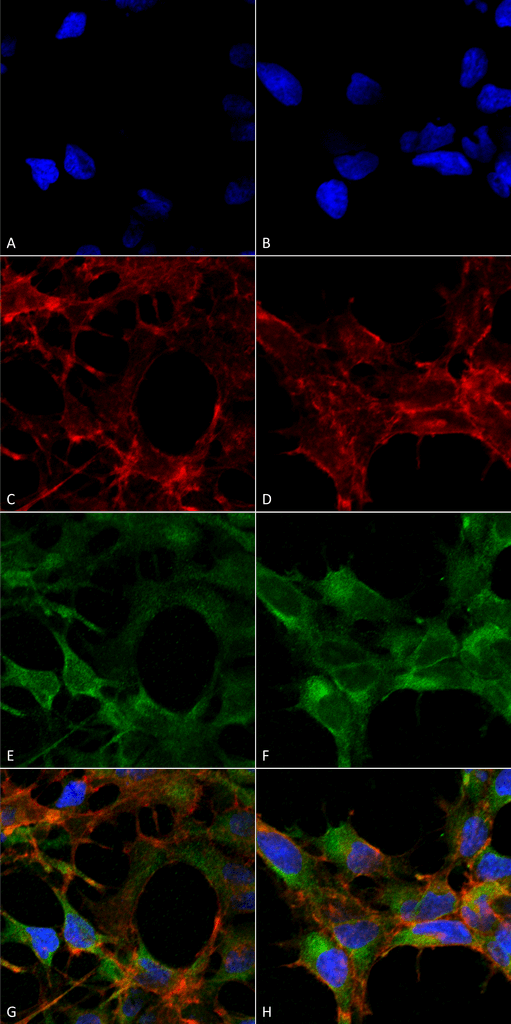
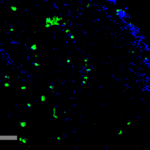
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 10A10 (SMC-505). Tissue: Embryonic kidney epithelial cell line (HEK293). Species: Human. Fixation: 5% Formaldehyde for 5 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-505) at 1:50 for 30-60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 488 at 1:1500 for 30-60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:250, 1:50000 for 30-60 min at RT. Magnification: 20X (2X Zoom). (A,C,E,G) – Untreated. (B,D,F,H) – Cells cultured overnight with 50 µM H2O2. (A,B) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (C,D) Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain. (E,F) Acrolein Antibody. (G,H) Composite. Courtesy of: Dr. Robert Burke, University of Victoria.
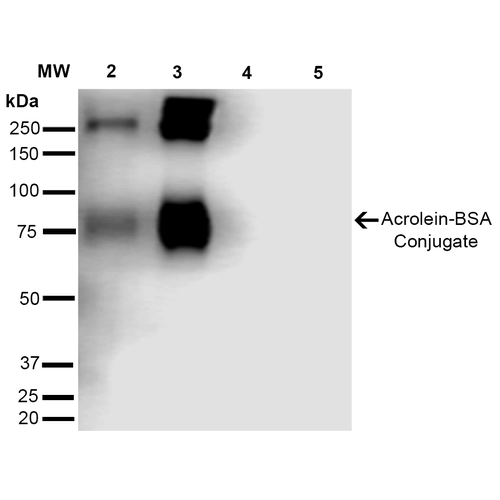
Western Blot analysis of Acrolein-BSA Conjugate showing detection of 67 kDa Acrolein protein using Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 10A10 (SMC-505). Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: AcroleinBSA (0.5 µg). Lane 3: AcroleinBSA (2.0 µg). Lane 4: BSA (0.5 µg). Lane 5: BSA (2.0 µg). Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-505) at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: 67 kDa.
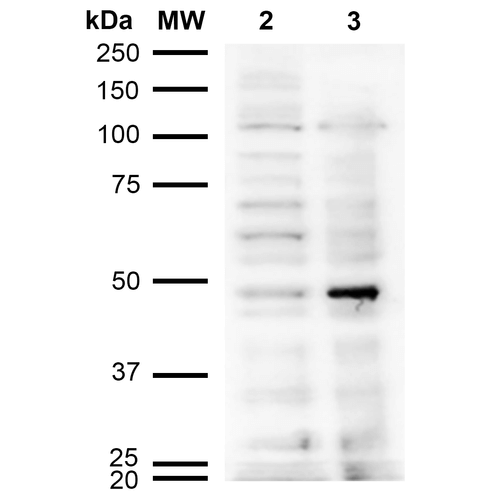
Western Blot analysis of Human Cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) lysate showing detection of Acrolein protein using Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 10A10 (SMC-505). Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: HeLa cell lysate. Lane 3: H2O2 treated HeLa cell lysate. Load: 12 µg. Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-505) at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT.
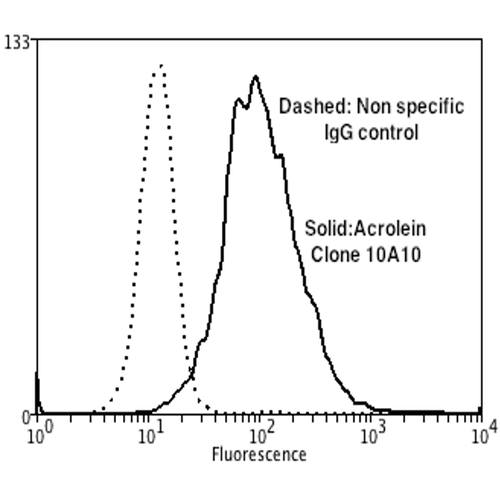
Flow Cytometry analysis using Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 10A10 (SMC-505). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 90% Methanol. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Acrolein Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-505) at 1:50 for 30 min on ice. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse: PE at 1:100 for 20 min at RT. Isotype Control: Non Specific IgG. Cells were subject to oxidative stress by treating with 250 µM H2O2 for 24 hours.

![Mouse Anti-Acrolein Antibody [10A10] used in Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence (ICC/IF) on Embryonic kidney epithelial cell line (HEK293) (SMC-505)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-505_Acrolein_Antibody_10A10_ICC-IF_Human_Embryonic-kidney-cells-HEK293_Composite_1-100x100.png)
![Mouse Anti-Acrolein Antibody [10A10] used in Western Blot (WB) on Acrolein-BSA Conjugate (SMC-505)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-505_Acrolein_Antibody_10A10_WB_Acrolein-BSA-Conjugate_1-100x100.png)
![Mouse Anti-Acrolein Antibody [10A10] used in Flow Cytometry (FCM) on Human Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y) (SMC-505)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-505_Acrolein_Antibody_10A10_FCM_Human_Neuroblastoma-cells-SH-SY5Y_1-100x100.png)
![Mouse Anti-Acrolein Antibody [10A10] used in Western Blot (WB) on Cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) lysate (SMC-505)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-505_Acrolein_Antibody_10A10_WB_Human_Cervical-Cancer-cell-line-HeLa_1-100x100.png)
Seth :
We switched to the StressMarq antibody from another company and are very happy with it. I have used it for multiple applications. The first is use in rat spinal cord contusion injury, where we are trying novel approaches to remove acrolein as a therapeutic intervention post injury. Tissue is fixed for 1-2 days in 4% PFA then frozen in OCT and stored at -80C. I haven’t done an IF stain, but shows up nicely using DAB and amplifying the signal with an ABC kit. Also works very nicely with western blot, seeing bands in the 75kDa to 250kDa range, in brain and spinal cord lysates.