Properties
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% Sodium azide *Storage buffer may change when conjugated |
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC, Conjugated antibodies should be stored according to the product label |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Number | 5D9 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Specificity | Specific for Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct (HEL) modified peptides and proteins. Does not detect free Hexanoyl-Lysine. Does not cross-react with Acrolein, Crotonaldehyde, 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal, 4-Hydroxy nonenal, Malondialdehyde, or Methylglyoxal modified proteins. |
| Cite This Product | Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody (StressMarq Biosciences | Victoria, BC CANADA, Catalog# SMC-508, RRID: AB_2702783) |
| Certificate of Analysis | A 1:1000 dilution of SMC-508 was sufficient for detection of Hexanoyl Lysine adduct in 0.5 µg of Hexanoyl Lysine conjugated to BSA by ECL immunoblot analysis using Goat Anti-Mouse IgG:HRP as the secondary Antibody. |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct, HEL (Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct), HEL, HEL Adduct, Hexanoyl-Lys adduct, Hexanoyl-Lys, Hexanoyl-Lysine (HEL) adduct, Hexanoyl-Lys (HEL), Hexanoyl Lysine adduct, Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct-modified protein, Hexanoyl-Lysine Adduct (HEL) |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Lipid peroxidation, Oxidative Stress |
| Scientific Background |
Hexanoyl-lysine adduct (HEL) is a lipid peroxidation marker formed by the reaction of oxidized fatty acids with lysine residues on proteins. It serves as an early indicator of oxidative stress, a central feature in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. In the brain, HEL accumulation reflects damage to neuronal membranes and proteins caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Elevated levels of HEL have been detected in models of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurodegenerative conditions, correlating with disease progression and cognitive decline. HEL is particularly valuable as a biomarker due to its stability and specificity for lipid peroxidation. Its presence indicates oxidative damage at an early stage, often preceding overt neurodegeneration. This makes HEL a promising candidate for early diagnosis, disease monitoring, and evaluating the efficacy of antioxidant therapies. By highlighting the oxidative component of neurodegeneration, HEL contributes to a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms and supports the development of targeted interventions aimed at reducing oxidative injury in the nervous system. |
| References | 1. Sakai, K et al. (2014) Subcell. Biochem. 77:61-72. |
Product Images
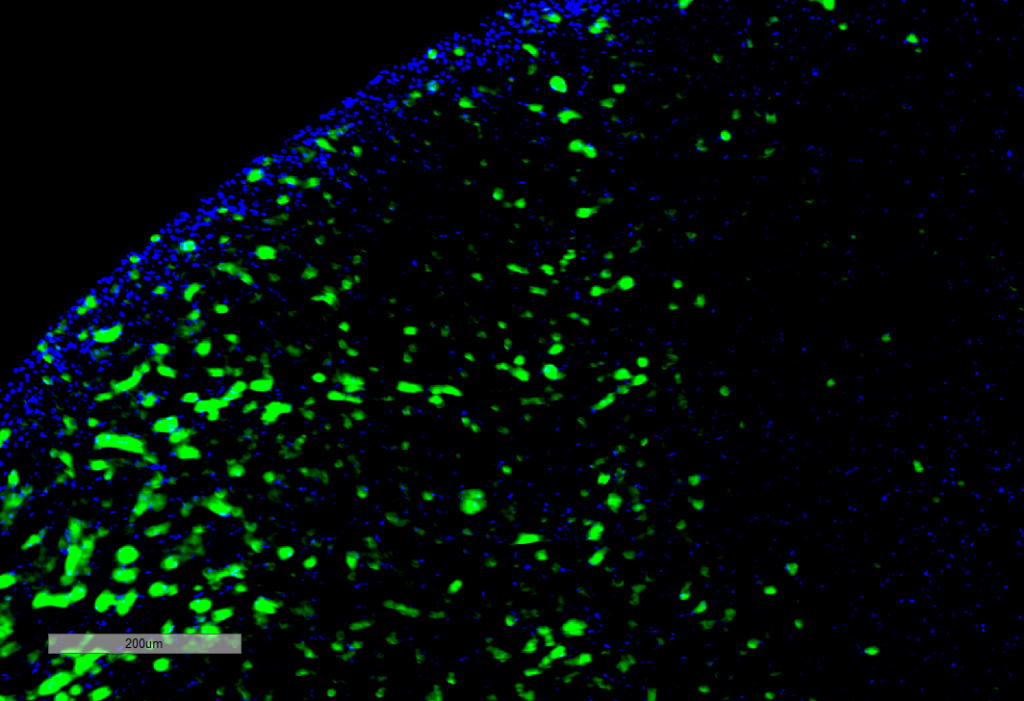
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5D9 (SMC-508). Tissue: Kidney. Species: Rat. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-508) at 1:100 for Overnight at 4C, then 30 min at 37C. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L): FITC for 45 min at 37C. Counterstain: DAPI for 3 min at RT. Magnification: 10X.
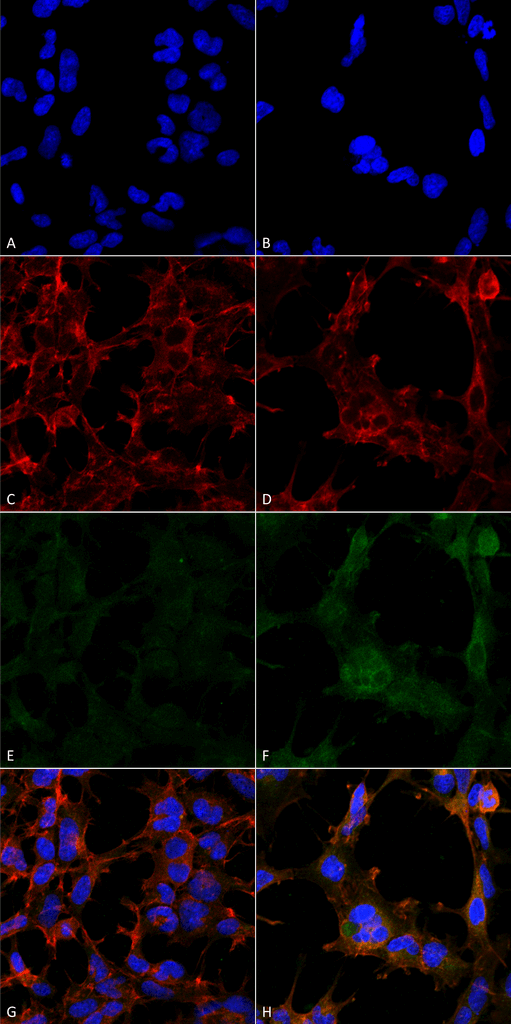
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5D9 (SMC-508). Tissue: Embryonic kidney epithelial cell line (HEK293). Species: Human. Fixation: 5% Formaldehyde for 5 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-508) at 1:50 for 30-60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 488 at 1:1500 for 30-60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:250, 1:50000 for 30-60 min at RT. Magnification: 20X (2X Zoom). (A,C,E,G) – Untreated. (B,D,F,H) – Cells cultured overnight with 50 µM H2O2. (A,B) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (C,D) Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain. (E,F) Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody. (G,H) Composite. Courtesy of: Dr. Robert Burke, University of Victoria.
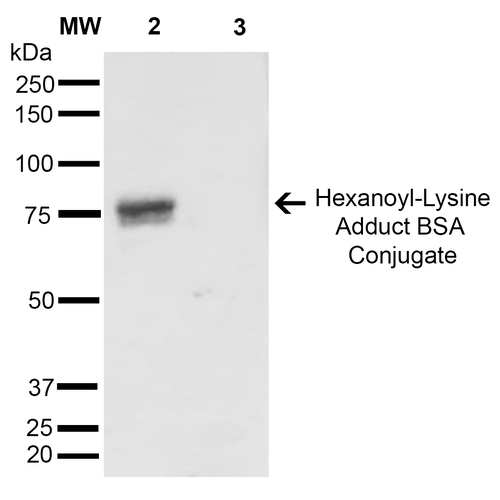
Western Blot analysis of Hexanoyl Lysine-BSA Conjugate showing detection of 67 kDa Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct protein using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5D9 (SMC-508). Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: Hexanoyl Lysine-BSA. Lane 3: BSA. Load: 0.5 µg. Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-508) at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: 67 kDa.
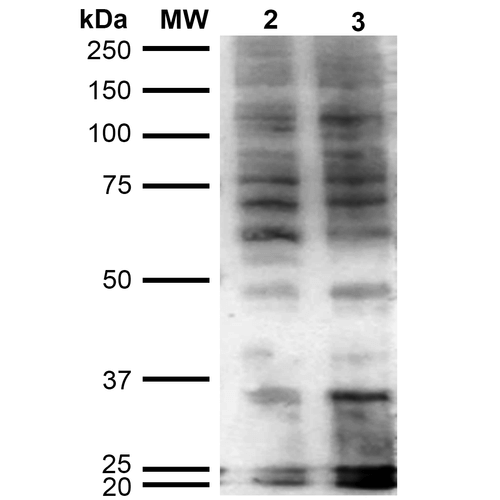
Western Blot analysis of Human Cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) lysate showing detection of Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct protein using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5D9 (SMC-508). Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: HeLa cell lysate. Lane 3: H2O2 treated HeLa cell lysate. Load: 12 µg. Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-508) at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT.
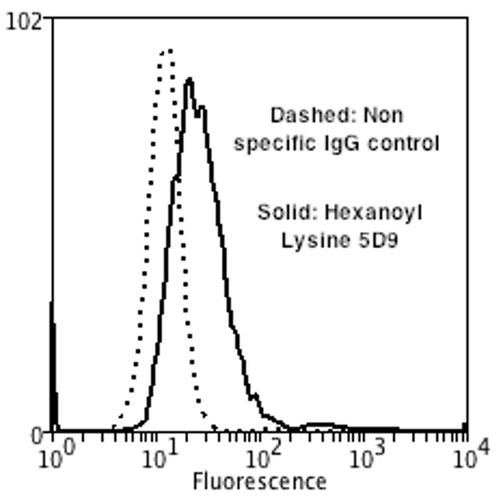
Flow Cytometry analysis using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5D9 (SMC-508). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 90% Methanol. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-508) at 1:50 for 30 min on ice. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse: PE at 1:100 for 20 min at RT. Isotype Control: Non Specific IgG. Cells were subject to oxidative stress by treating with 250 µM H2O2 for 24 hours.
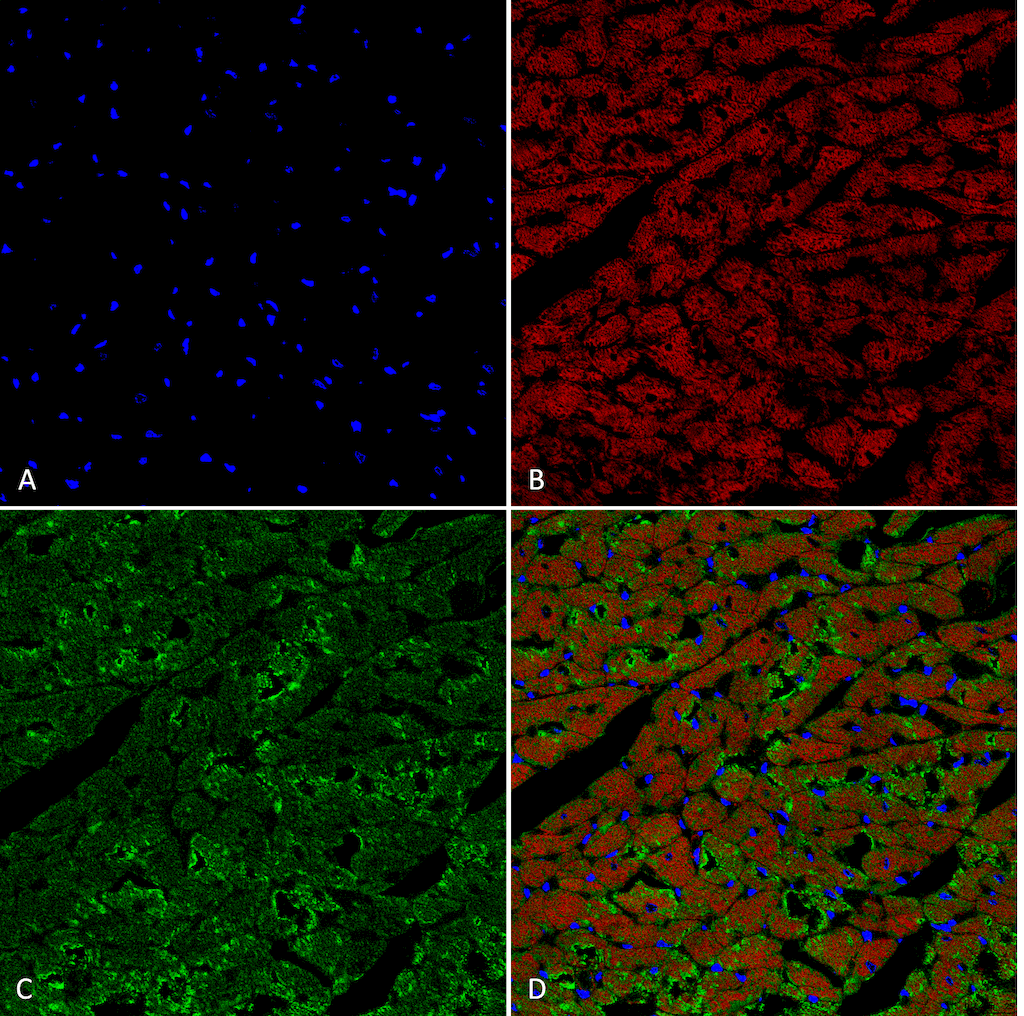
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5D9 (SMC-508). Tissue: Heart. Species: Rat. Fixation: Formalin fixed, paraffin embedded. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-508) at 1:25 for 1 hour at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: Alexa Fluor 488. Counterstain: DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. Magnification: 63X. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Actin (C) Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody (D) Composite.

![Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody [5D9] used in Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence (ICC/IF) on Embryonic kidney epithelial cell line (HEK293) (SMC-508)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-508_Hexanoyl-Lysine-adduct_Antibody_5D9_ICC-IF_Human_Embryonic-kidney-cells-HEK293_Composite_1-100x100.png)
![Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody [5D9] used in Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on Rat Heart (SMC-508)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-508_Hexanoyl-Lysine-adduct_Antibody_5D9_IHC_Rat_Heart_1-100x100.png)
![Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody [5D9] used in Western Blot (WB) on Hexanoyl Lysine-BSA Conjugate (SMC-508)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-508_Hexanoyl-Lysine_Antibody_5D9_WB_Hexanoyl-Lysine-BSA-Conjugate_1-100x100.png)
![Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody [5D9] used in Flow Cytometry (FCM) on Human Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y) (SMC-508)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-508_Hexanoyl-Lysine-adduct_Antibody_5D9_FCM_Human_Neuroblastoma-cells-SH-SY5Y_1-100x100.png)
![Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody [5D9] used in Western Blot (WB) on Cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) lysate (SMC-508)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-508_Hexanoyl-lysine_Antibody_5D9_WB_Human_Cervical-Cancer-cell-line-HeLa_1-100x100.png)
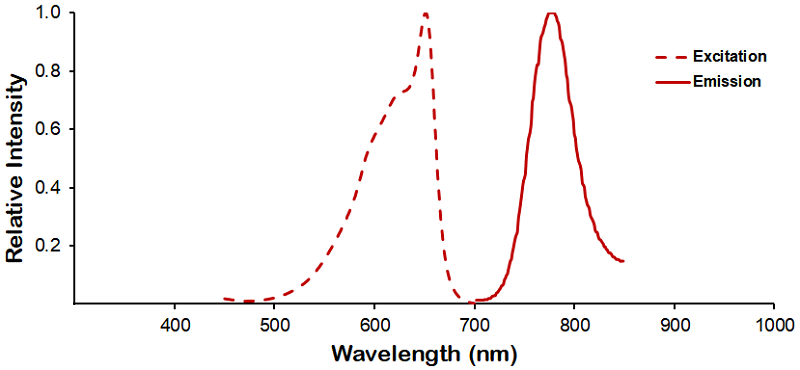
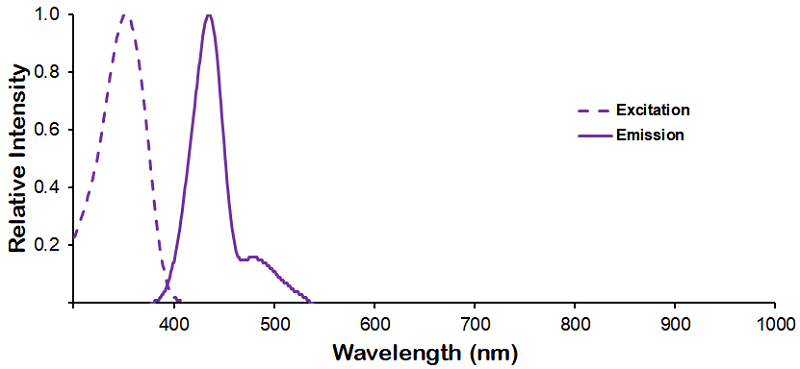
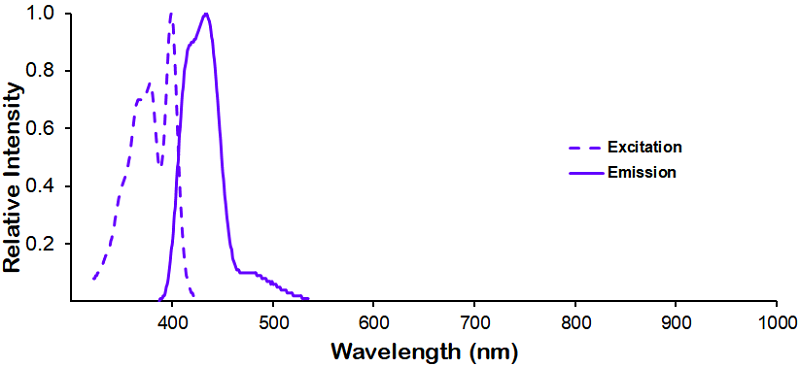
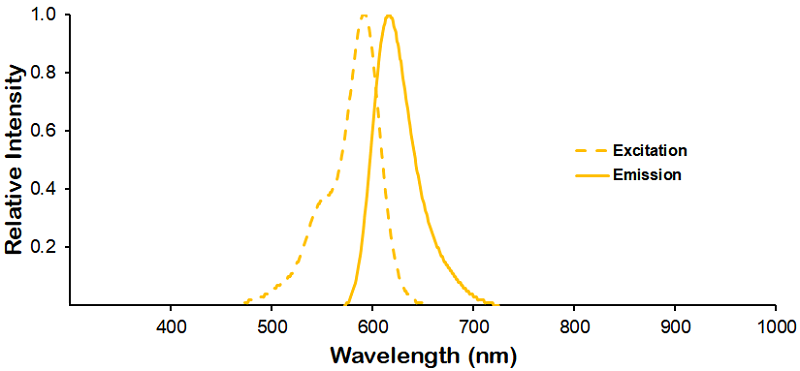
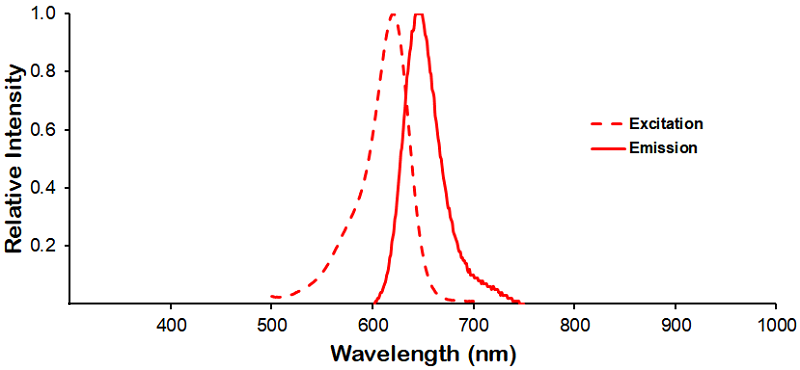
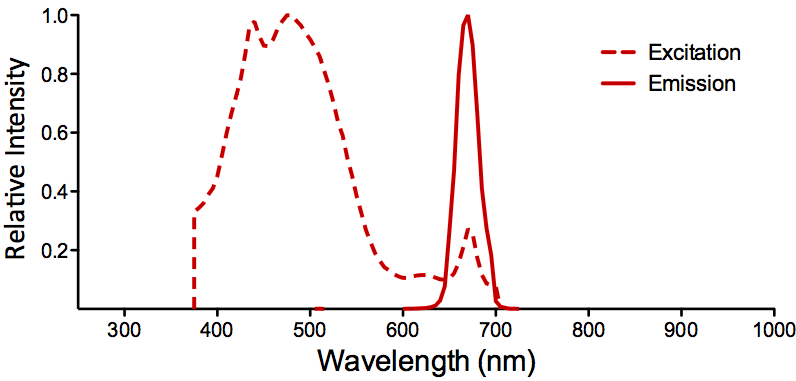
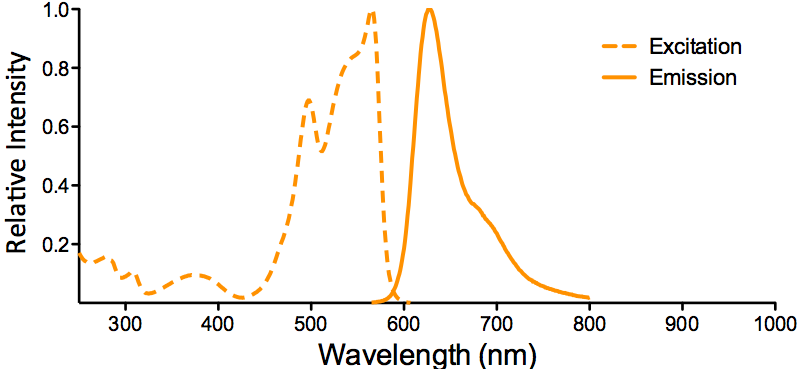
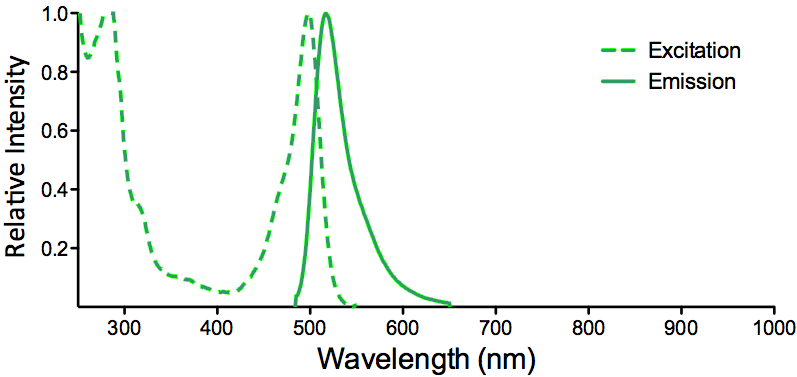
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.