Properties
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide *Storage buffer may change when conjugated |
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC, Conjugated antibodies should be stored according to the product label |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Number | N43/6 (Formerly sold as S43-6) |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Specificity | Detects ~77kDa. |
| Cite This Product | KCNQ4 Antibody (StressMarq Biosciences | Victoria, BC CANADA, Catalog# SMC-309, RRID: AB_2131718) |
| Certificate of Analysis | 1 µg/ml of SMC-309 was sufficient for detection of KCNQ4 in 10 µg of COS-1 cell lysate transiently expressing KCNQ4 by colorimetric immunoblot analysis using Goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP as the secondary antibody. |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | KCNQ4, Kv7.4, KVLQT4, Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 4, Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv7.4, KQT-like 4, Potassium channel subunit alpha KvLQT4, Potassium voltage-gated channel KQT-like subfamily member 4, DFNA2, KCNQ4_HUMAN, Kcnq4, KCNQ 4, Potassium channel KQT like 4, Potassium voltage gated channel KQT like protein 4, Voltage gated potassium channel subunit Kv7.4 |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Ion Channels, Neuroscience, Potassium Channels, Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels |
| Cellular Localization | Basal Cell Membrane, Plasma Membrane |
| Accession Number | NP_004691.2 |
| Gene ID | 9132 |
| Swiss Prot | P56696 |
| Scientific Background |
KCNQ4 encodes a voltage-gated potassium channel subunit that plays a vital role in regulating neuronal excitability, particularly in sensory systems. Predominantly expressed in the outer hair cells of the cochlea, KCNQ4 contributes to potassium ion efflux, maintaining the resting membrane potential and enabling precise auditory signal transduction. This channel is modulated by key signaling pathways: it is inhibited by M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and activated by retigabine, a potassium channel opener with anticonvulsant properties. These regulatory mechanisms highlight KCNQ4’s importance in maintaining excitatory-inhibitory balance in neurons. Mutations or dysfunction in KCNQ4 are strongly associated with progressive sensorineural hearing loss (DFNA2), but emerging evidence suggests broader implications in neurodegenerative disease. Disrupted potassium channel activity can lead to chronic neuronal hyperexcitability, oxidative stress, and eventual neurodegeneration—mechanisms shared across conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and age-related hearing loss. Given its pharmacological responsiveness and role in sensory neuron stability, KCNQ4 is gaining attention as a potential therapeutic target. Enhancing its function may offer neuroprotective benefits by restoring ionic homeostasis and preventing excitotoxic damage in vulnerable neural circuits. As research into ion channelopathies expands, KCNQ4 stands out as a key player in both auditory neuroscience and the broader landscape of neurodegenerative disease research. |
| References |
1. Hernandez C.C., Zaiko O., Tolstykh G.P., Shapiro M.S. (2008) J Physiol. 586(7): 1811-1821. 2. Kharkovets T., et al. (2006) EMBO J. 25(3): 642-652. 3. Tatulian L., Delmas P., Abogadie F.C., Brown D.A. (2001) J Neuroscience. 21(15): 5535-5545. |
Product Images
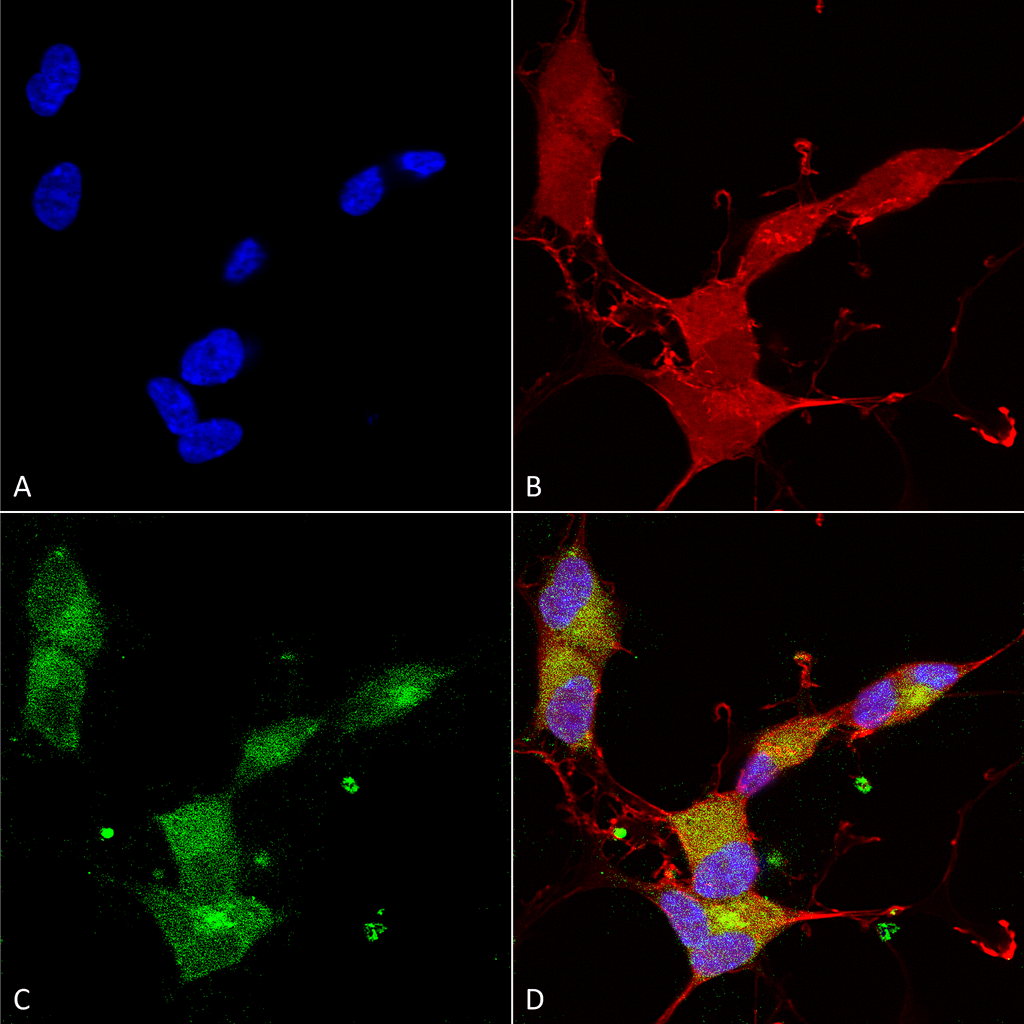
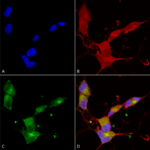
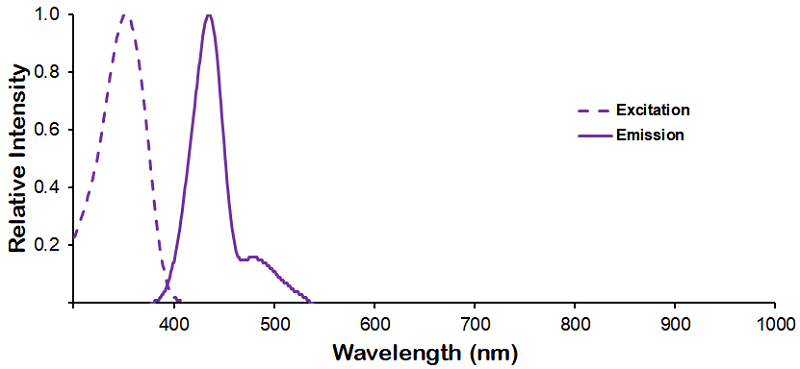
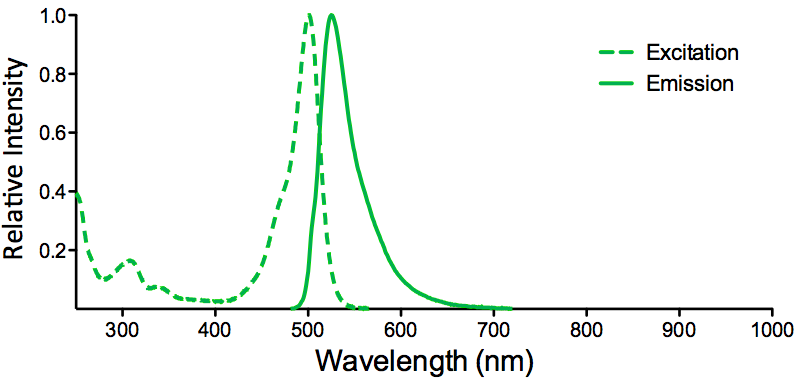
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNQ4 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N43/6 (SMC-309). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ4 Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-309) at 1:100 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) KCNQ4 Antibody (D) Composite.
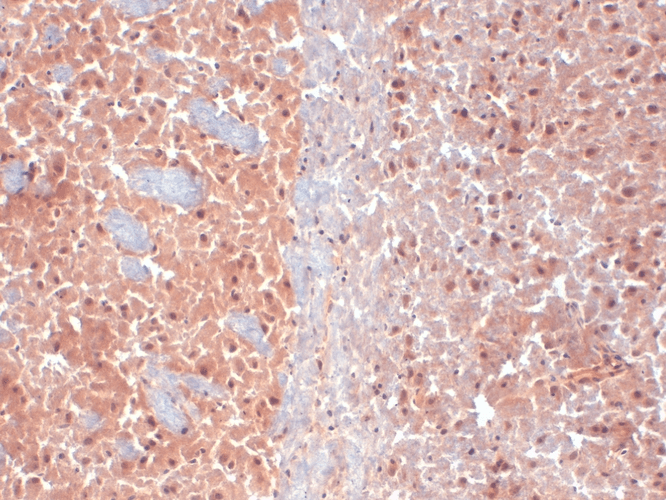
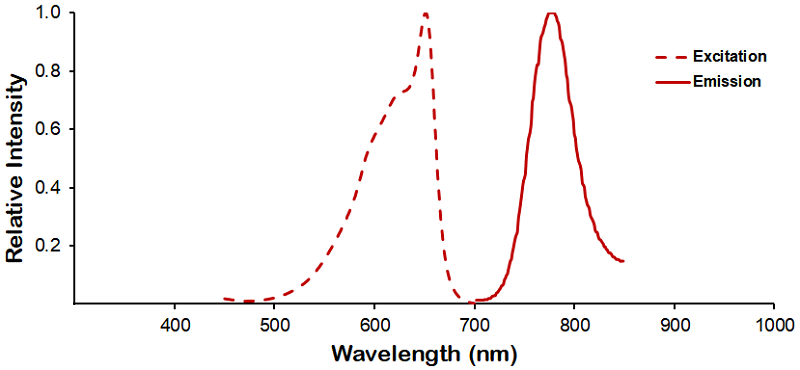
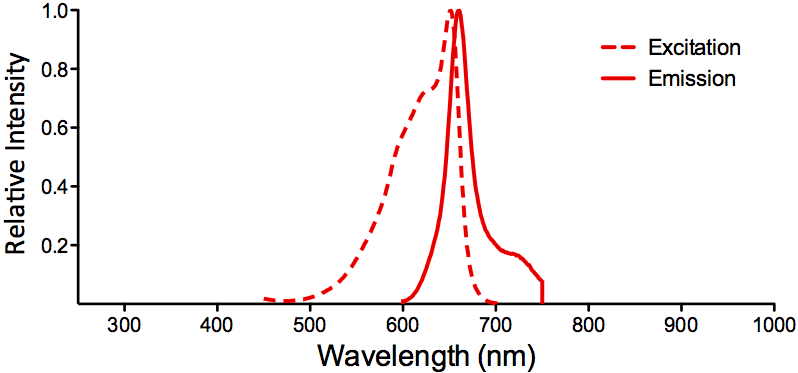
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNQ4 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N43/6 (SMC-309). Tissue: frozen brain section. Species: Mouse. Fixation: 10% Formalin Solution for 12-24 hours at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ4 Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-309) at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Secondary Antibody: HRP/DAB Detection System: Biotinylated Goat Anti-Mouse, Streptavidin Peroxidase, DAB Chromogen (brown) for 30 minutes at RT. Counterstain: Mayer Hematoxylin (purple/blue) nuclear stain at 250-500 µl for 5 minutes at RT.
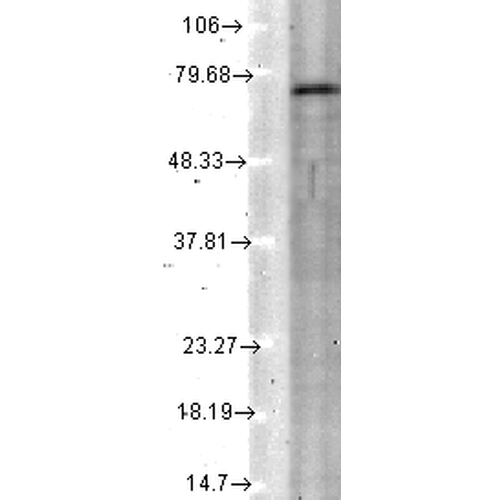
Western Blot analysis of Rat tissue lysate showing detection of KCNQ4 protein using Mouse Anti-KCNQ4 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N43/6 (SMC-309). Load: 15 µg. Block: 1.5% BSA for 30 minutes at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ4 Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-309) at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Sheep Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP for 1 hour at RT.
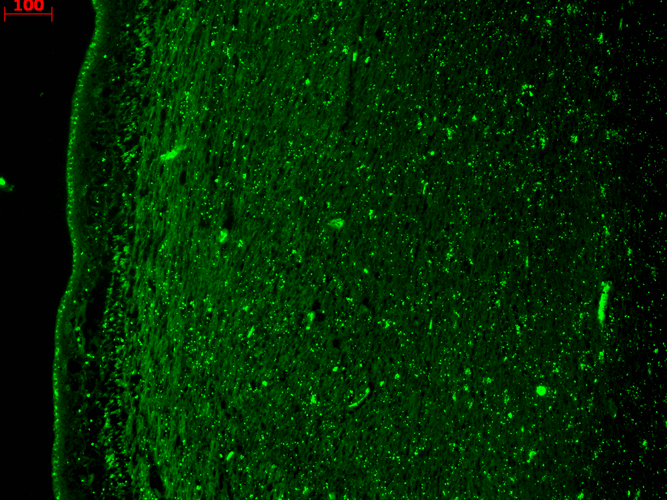
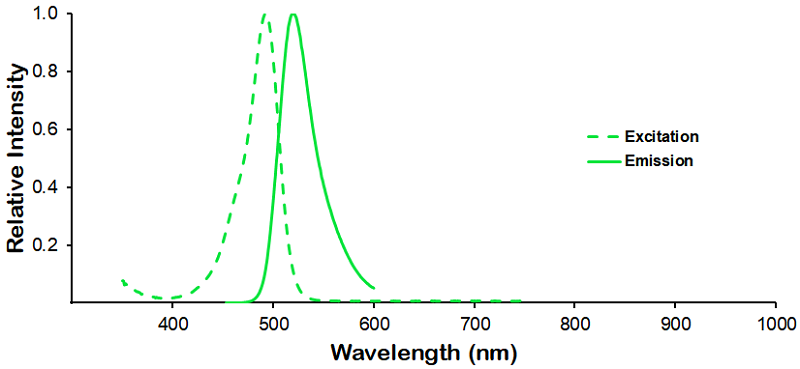
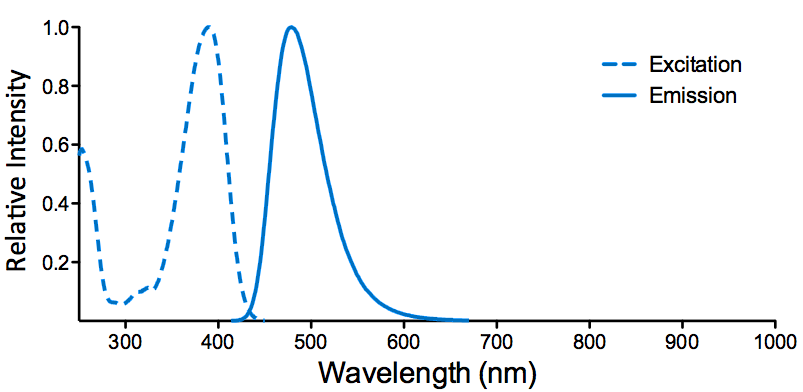
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNQ4 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N43/6 (SMC-309). Tissue: hippocampus. Species: Human. Fixation: Bouin’s Fixative and paraffin-embedded. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ4 Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-309) at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Secondary Antibody: FITC Goat Anti-Mouse (green) at 1:50 for 1 hour at RT.

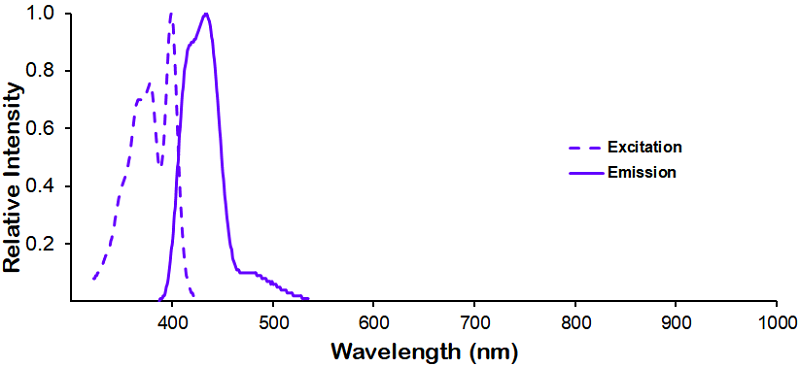
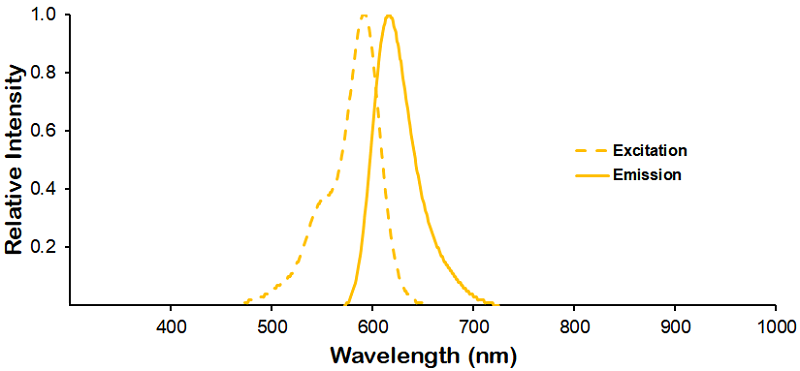
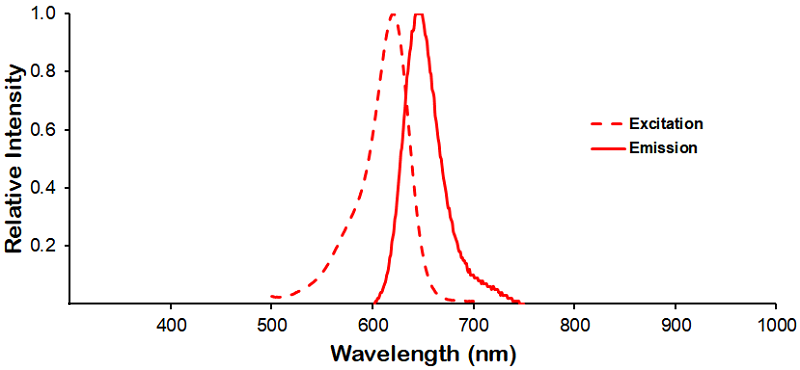
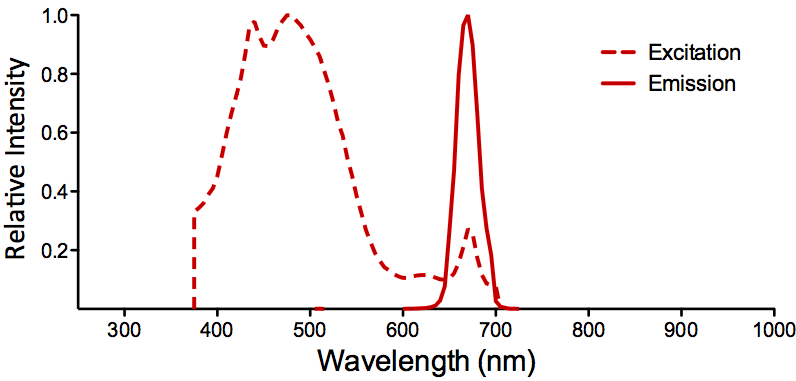
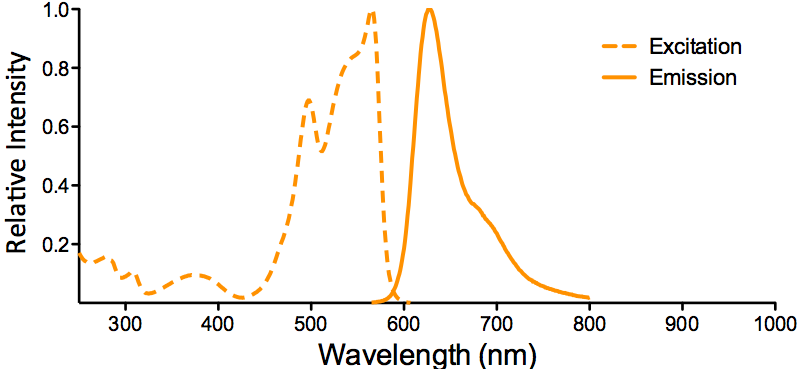
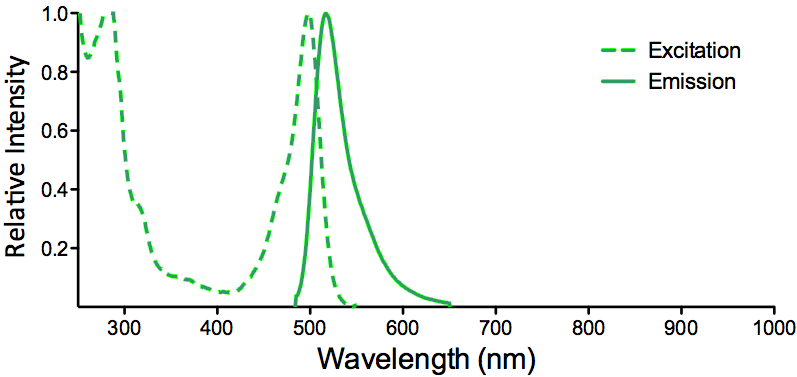
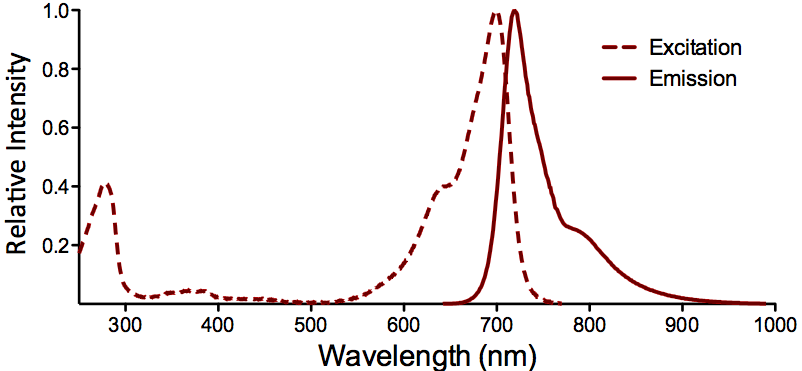
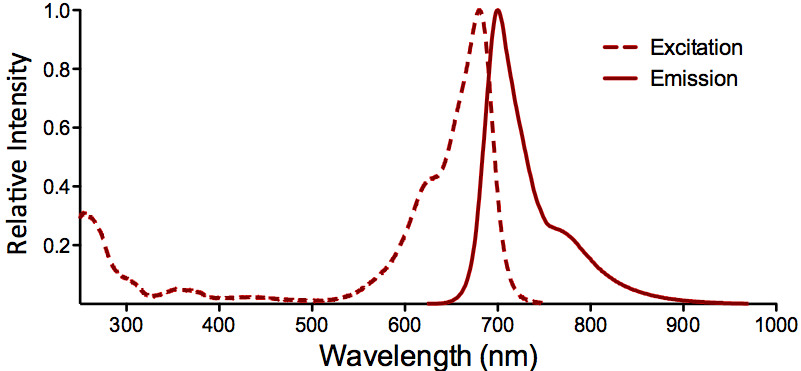
StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.