| Product Name | Cystatin C EIA Kit (Discontinued) |
| Description |
Colorimetric measurement of human cystatin C levels |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Platform | Microplate |
| Sample Types | EDTA Plasma, Heparin Plasma, Serum, Tissue Culture Media, Urine |
| Detection Method | Colorimetric Assay |
| Assay Type | Sandwich EIA (Enzyme Immunoassay) |
| Utility | EIA kit used to measure cystatin C levels in samples. |
| Sensitivity | 0.058 ng/ml |
| Assay Range | 0.156 - 10 ng/ml |
| Precision | Intra Assay Precision: Four human samples were diluted with Assay Buffer and run in replicates of 20 in an assay. The mean and precision of the calculated Cystatin C concentrations were: Sample 1- 7.72 ng/mL, 9.1% CV Sample 2- 5.08 ng/mL, 10.3% CV Sample 3- 4.42 ng/mL, 7.6% CV Sample 4- 0.88 ng/mL, 10.3% CV Inter Assay Precision: Four human samples were diluted with Assay Buffer and run in duplicates in ten assays run over multiple days by three operators. The mean and precision of the calculated Cystatin C concentrations were: Sample 1- 7.79 ng/mL, 8.4% CV Sample 2- 5.48 ng/mL, 10.2% CV Sample 3- 4.97 ng/mL, 11.1% CV Sample 4- 1.04 ng/mL, 12.40% CV |
| Incubation Time | 2 hours |
| Number of Samples | 40 samples in duplicate |
| Other Resources | Kit Booklet , MSDS |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | 4ºC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Product Type | EIA Kits | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
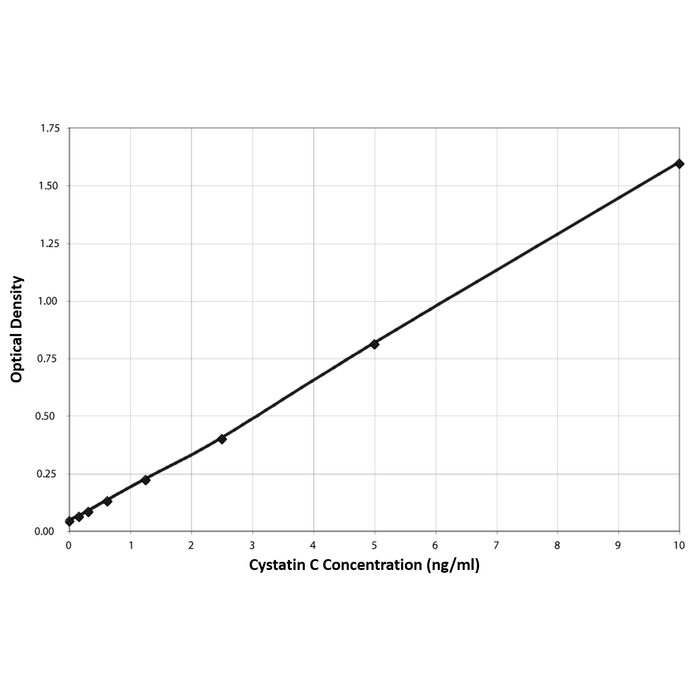
| Assay Overview | The Cystatin C EIA kit is designed to quantitatively measure human Cystatin C present in biological samples and tissue culture media. A human Cystatin C standard is provided to generate a standard curve for the assay and all samples should be read off the standard curve. Standards or diluted samples are pipetted into a clear microtiter plate coated with a monoclonal antibody to capture the Cystatin C present. After a 60 minute incubation, the plate is washed and a peroxidase conjugated Cystatin C monoclonal antibody is added. The plate is again incubated for 30 minutes and washed. Substrate is then added to the plate, which reacts with the bound Cystatin C Antibody Conjugate. After a third incubation, the reaction is stopped and the intensity of the generated color is detected in a microtiter plate reader capable of measuring 450 nm wavelength. The concentration of the Cystatin C in the sample is calculated, after making suitable correction for dilution, using software available with most plate readers. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kit Overview |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cite This Product | Cystatin C EIA Kit (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SKT-219) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Cystatin 3 EIA Kit, gamma trace EIA Kit, post-gamma-globulin or neuroendocrine basic polypeptide EIA Kit |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Cancer, Cell Signaling, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience |
| Scientific Background |
Cystatin C is a non-glycosylated protein of low molecular weight (13kDa) in the cystatin superfamily. Cystatin C is produced at a constant rate in all nucleated cells, secreted from cells and thus found in detectable amounts in most body fluids (1,2). Cystatin C belongs to the cysteine proteinase inhibitor group and is associated with several pathological conditions. Imbalance between Cystatin C and cysteine proteinases is associated with diseases such as inflammation, renal failure, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis and hereditary Cystatin C amyloid angiopathy (1,3,4). Increased levels have been found in autoimmune diseases, with colorectal tumors and metastases, patients with inflammation and in patients on dialysis (5,6,7). Cystatin C is removed from blood plasma by glomerular filtration in the kidneys. It is reabsorbed by the proximal tubular cells and degraded. There is a linear relationship between the reciprocal Cystatin C concentration in plasma and the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Cystatin C is suggested to be a better marker for GFR than the ubiquitous serum creatinine marker as its serum concentration is not affected by other factors such as age, gender and body mass and Cystatin C has higher sensitivity to detect a reduced GFR than creatinine determination (2,5). Low levels of Cystatin C are found with the breakdown of the elastic laminae and atherosclerosis and abdominal aortic aneurysm (8). There is evident association of Cystatin C levels with the incidence of myocardial infarction, coronary death and angina pectoris, presenting a risk factor for secondary cardiovascular events (9). |
| References |
1. Pergande M. and Jung K. Clin Chem. 1993 39(9):1885-90. 2. Newman D, et al. Kidney Int’l. 1995 Jan;47(1):312-8. 3. Levy E. Expert Rev. Neurotherapeutics 2008 May;8(5):687-9. 4. Nakashima I, et al. Ann Neurol. 2007 Aug;62(2):197-200. 5. Uchida K. and Gotoh, A. Clin Chim Acta. 2002 Sep;323:121-8. 6. Pucci L, et al. Clin Chem. 2007 Mar;53(3):480-8. 7. Stabuc B, et al. Clin Chem. 2000 Feb;46(2):193-7. 8. Shlipak M, et al. NEJM 2005 May;352(20):2049-60. 9. Koenig W, et al. Clin Chem. 2005 Feb;51(2):321-7. |
Product Images
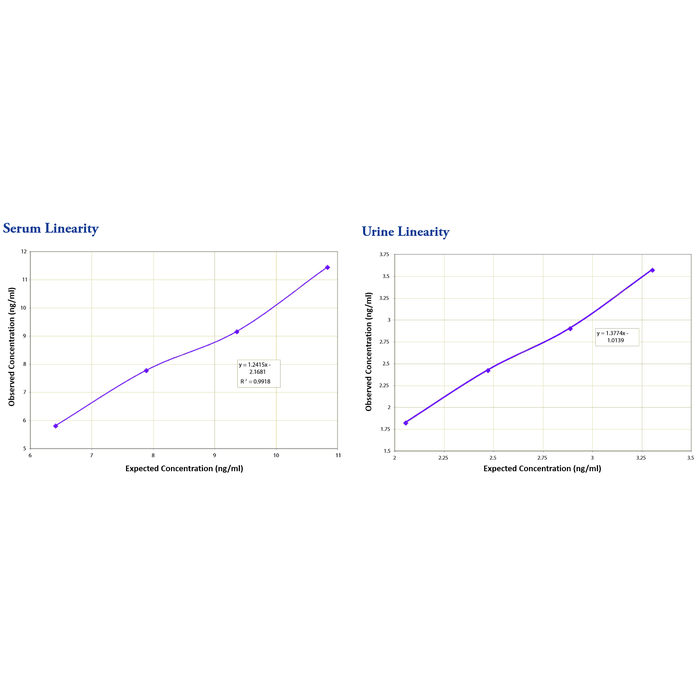
Serum linearity was determined by taking two human serum samples diluted 1:100, one with a low diluted Cystatin C level of 4.94 ng/mL and one with a higher diluted level of 12.31 ng/mL and mixing them in the ratios given below. Urine linearity samples were diluted 1:16. One sample with a value of 1.64 ng/mL was mixed in ratios with a sample of 3.72 ng/mL. The diluted serum and urine samples were mixed 4:1, 3:2, 2:3 and 1:4 and run in the assay. The measured concentrations were compared to the values previously determined.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.