| Product Name | Nitric Oxide Detection Kit (Discontinued) |
| Description |
Colorimetric detection of nitrate and nitrite |
| Species Reactivity | Species Independent |
| Platform | Microplate |
| Sample Types | Buffer, Cell lysates, Plasma, Saliva, Serum, Tissue Culture Media, Urine, Water |
| Detection Method | Colorimetric Assay |
| Assay Type | Indirect Quantitative Assay |
| Utility | Colorimetric assay used to quantitatively measure Nitrate and Nitrite present in a variety of samples. |
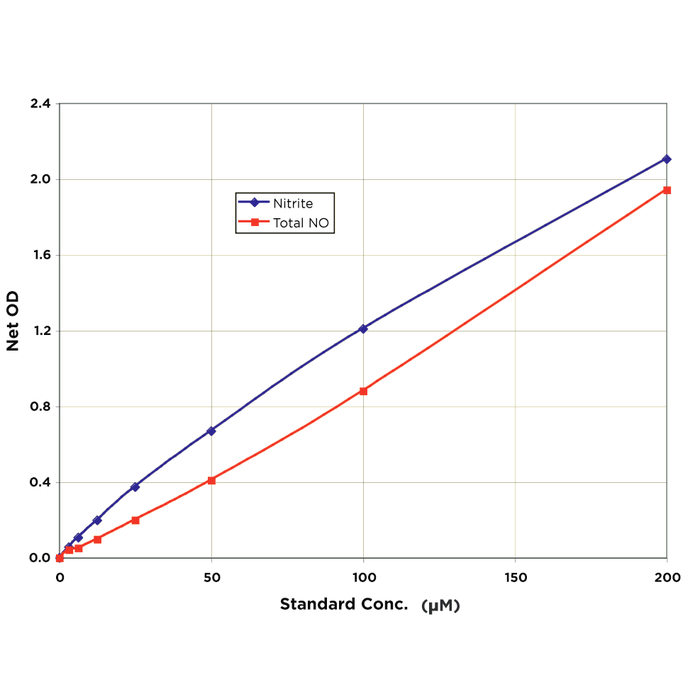
| Sensitivity | 2.63 µM in the Nitrite and 1.02 µM in the Total Nitric Oxide |
| Assay Range | 3.125 - 200 µM |
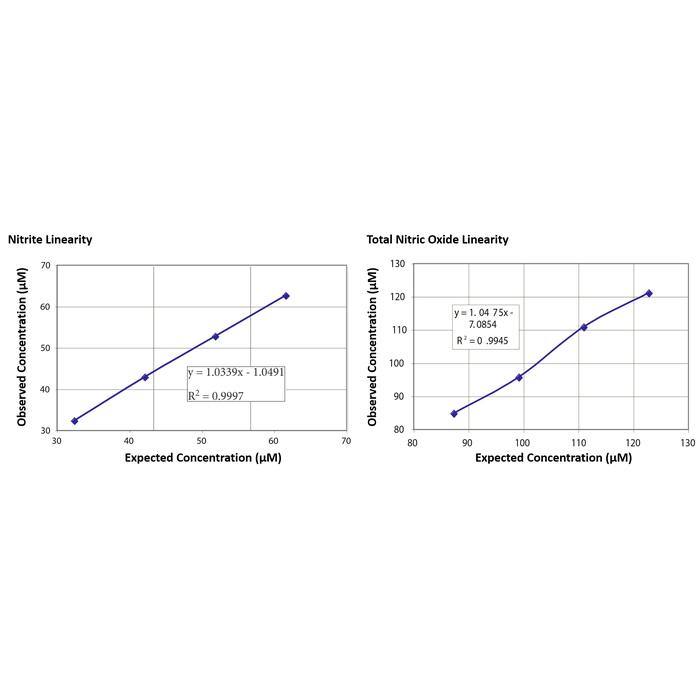
| Precision | Intra Assay Precision: Three samples were further diluted in Assay Buffer and run in replicates of 20 in an assay. The mean and precision of the calculated Nitrite or Total NO concentrations were: Sample 1 (Nitrite Concentration)- 45.1 µM, 4.4% CV, Sample 1 (Total NO Concentration)- 70.5 µM, 6.8% CV Sample 2 (Nitrite Concentration)- 73.3 µM, 9.1% CV, Sample 1 (Total NO Concentration)- 107.4 µM, 4.4% CV Sample 3 (Nitrite Concentration)- 132.7 µM, 1.3% CV, Sample 1 (Total NO Concentration)- 157.8 µM, 1.8% CV Inter Assay Precision: Three samples were further diluted in Assay Buffer and run in duplicates in twenty assays run over multiple days by three operators. The mean and precision of the calculated Nitrite or Total NO concentrations were: Sample 1 (Nitrite Concentration)- 44.1 µM, 3.1% CV, Sample 1 (Total NO Concentration)- 68.8 µM, 7.4% CV Sample 2 (Nitrite Concentration)- 66.4 µM, 4.0% CV, Sample 1 (Total NO Concentration)- 112.1 µM, 5.7% CV Sample 3 (Nitrite Concentration)- 126.7 µM, 6.3% CV, Sample 1 (Total NO Concentration)- 154.48 µM, 4.1% CV |
| Incubation Time | 30 minutes |
| Number of Samples | 88 samples in duplicate |
| Other Resources | Kit Booklet , MSDS |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | 4ºC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Product Type | Detection Kits | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assay Overview | The Nitric Oxide Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure Nitrate and Nitrite present in a variety of samples. Nitric Oxide content is derived from the sum of Nitrate (-NO3) and Nitrite (-NO2). Both Nitrate and Nitrite standards are provided to generate standard curves for the assay and all samples should be read off the appropriate standard curve. For Nitrite detection, samples are mixed with the Color Reagents A and B and incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes. The colored product is read at 550 – 570 nm. The concentration of Nitrite in the sample is calculated, after making a suitable correction for any dilution of the sample, using software available with most plate readers. Total Nitric Oxide content is measured after the sample is incubated with Nitrate Reductase and NADH. The reductase in combination with NADH reduces Nitrate to Nitrite. After a 20 minute incubation at room temperature, Color Reagents A and B are added and incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes. The colored product is read and calculated as with the Nitrite determination above. The concentration of Nitrate in the sample is calculated by subtracting the measured Nitrite concentration from the Total Nitric Oxide concentration for the sample. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kit Overview |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cite This Product | Nitric Oxide Detection Kit (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SKT-212) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Nitrogen monoxide; Nitrogen(II) oxide Detection Kit |
| Research Areas | Cell Signaling, Neuroscience, Post-translational Modifications |
| Scientific Background |
Nitric oxide (NO) is a diffusible, transient, reactive molecule that has physiological effects in the picomolar-to-micromolar range. Acting through soluble guanylate cyclase activation, NO is an important physiological regulator of the cardiovascular, nervous, and immunological systems (1). NO is bio-available by two routes. It can be endogenously generated by constitutive or induced enzymes like Nitric Oxide Synthase or it can be orally ingested as nitrates / nitrites for rapid uptake into circulation and subsequent conversion (2). The reactive nature of nitric oxide allows it to act as a cytotoxic factor when released during an immune response by cells such as macrophages. The reactivity also allows NO to be easily converted to a toxic radical that can produce nitrosative damage to cells, organelles and molecules such as DNA. Nitrosaylation however can be a regulated post-translational modification in cell signaling (3). The balance and dynamics of the regulatory/damage facets of NO are major forces in mitochondrial signaling and dysfunction (4). NO is linked not only to coronary heart disease, endothelial dysfunctions, erectile dysfunction, and neurological disorders, but also diabetes, chronic periodontitis, autism, cancer, and assorted age-related diseases (5-9). The physical properties of Nitric Oxide make it challenging for direct detection methods. However, colorimetric methods can be applied to measure its stable break-down products nitrate (-NO3) and nitrite (-NO2) (10). |
| References |
1. Moncada, S and EA Higgs. (1991) Eur. J. Clin. Invest., 21:361-374. 2. Kapil, V. et al. (2010) Heart, 96:1703-1709. 3. Seth, D and Stamler, JS. (2007) Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 15:1-8. 4. Eursalimsky, JD and Moncada, S. (2007) ATVB 27:2524-2531. 5. Knott, AB and Bossy-Wetzel, E. (2010) Diab.Obes.Metab. 12(Suppl2):126-133. 6. Van Dyke, K. et al. (2010) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1203:138-145. 7. Reher, VSG. et al. (2007) J. Oral Sci. 49(4):271-276. 8. Sogut, S. et al. (2003) Clin. Chim. Acta 331:111-117. 9. Balam. E. et al. (2002) Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 32(5):162-166. 10. Moshage, H. (1997) Clin.Chem. 43(4):553-556. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.