| Product Name | HSP27 ELISA Kit (Discontinued) |
| Description |
Colorimetric detection of HSP27 |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Platform | Microplate |
| Sample Types | Cell lysates, Plasma, Serum, Tissue |
| Detection Method | Colorimetric Assay |
| Assay Type | Sandwich ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay) |
| Utility | ELISA kit used to quantitate HSP27 concentration in samples. |
| Sensitivity | 0.04 ng/ml |
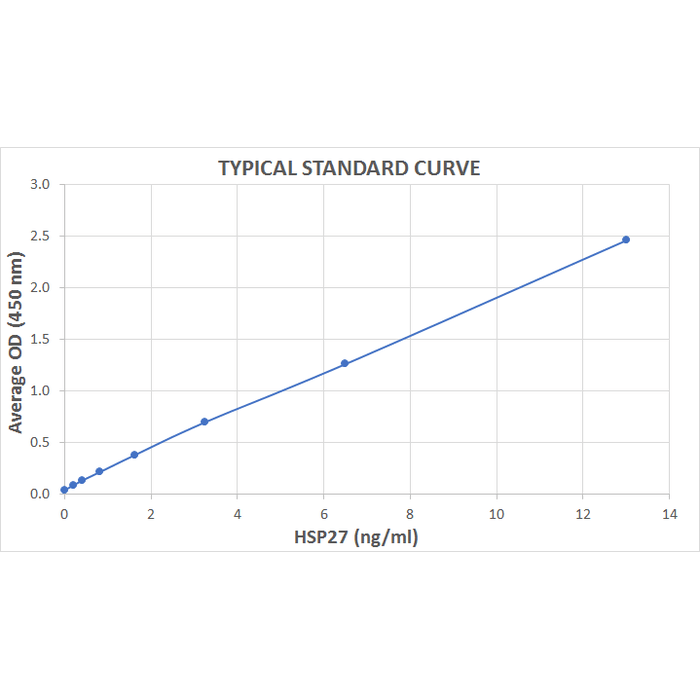
| Assay Range | 0.2 - 13 ng/ml |
| Incubation Time | 30 minutes |
| Number of Samples | 40 samples in duplicate |
| Other Resources | Kit Booklet Lot No. 1102 , Kit Booklet Lot No. SK192626 , Kit Booklet Lot No. SH588516 , MSDS |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | 4ºC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Product Type | ELISA Kits | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assay Overview | 1. Prepare Standard and samples in Standard and Sample Diluent. 2. Add 100 µL of Standard or sample to appropriate wells. 3. Cover plate with Plate Sealer and incubate at room temperature (20-25°C) for 1 hour. 4. Wash plate four times with 1X Wash Buffer. 5. Add 100 µL of Biotinylated Antibody Working Solution to each well. 6. Cover plate with Plate Sealer and incubate at room temperature for 1 hour. 7. Wash plate four times with 1X Wash Buffer. 8. Add 100 µL of Streptavidin-HRP Working Solution to each well. 9. Cover plate with Plate Sealer and incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes. 10. Wash plate four times with 1X Wash Buffer. 11. Add 100 µL of TMB Substrate to each well. 12. Develop the plate in the dark at room temperature for 30 minutes. 13. Stop reaction by adding 100 µL of Stop Solution to each well. 14. Measure absorbance on a plate reader at 450 nm. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kit Overview |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cite This Product | HSP27 ELISA Kit (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SKT-109) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 28kDa heat shock protein ELISA Kit, CMT2F ELISA Kit, HSP25 ELISA Kit, HSP27 ELISA Kit, HSP28 ELISA Kit, HSPB1 ELISA Kit, SRP27 ELISA Kit |
| Research Areas | Actin, Actin Assembly, Atherosclerosis, Cancer, Cardiovascular System, Cell Signaling, Chaperone Proteins, Contractility, Cytoskeleton, Heart, Microfilaments, Microtubules, Protein Trafficking, Tumor Biomarkers |
| Scientific Background | HSP27s belong to an abundant and ubiquitous family of small heat shock proteins (sHSP). It is an important HSP found in both normal human cells and cancer cells. The basic structure of most sHSPs is a homologous and highly conserved amino acid sequence, with an alpha-crystallin-domain at the C-terminus and the WD/EPF domain at the less conserved N-terminus. This N-terminus is essential for the development of high molecular oligomers (1, 2). HSP27-oligomers consist of stable dimers formed by as many as 8-40 HSP27 protein monomers (3). The oligomerization status is connected with the chaperone activity: aggregates of large oligomers have high chaperone activity, whereas dimers have no chaperone activity (4). HSP27 is localized to the cytoplasm of unstressed cells but can redistribute to the nucleus in response to stress, where it may function to stabilize DNA and/or the nuclear membrane. Other functions include chaperone activity (as mentioned above), thermotolerance invivo, inhibition of apoptosis, and signal transduction. Specifically, in vitro, it acts as an ATP-independent chaperone by inhibiting protein aggregation and by stabilizing partially denatured proteins, which ensures refolding of the HSP70 complex. HSP27 is also involved in the apoptotic signaling pathway because it interferes with the activation of cytochrome c/Apaf-1/dATP complex, thereby inhibiting the activation of procaspase-9. It is also hypothesized that HSP27 may serve some role in cross-bridge formation between actin and myosin (5). And finally, HSP27 is also thought to be involved in the process of cell differentiation. The up-regulation of HSP27 correlates with the rate of phosphorylation and with an increase of large oligomers. It is possible that HSP27 may play a crucial role in termination of growth (6). Looking for more information on HSP27? Visit our new HSP27 Scientific Resource Guide at http://www.HSP27.com. |
| References |
1. Kim K.K., Kim R., and Kim, S. (1998) Nature 394(6693): 595-599. 2. Van Montfort R., Slingsby C., and Vierling E. (2001) Addv Protein Chem. 59: 105-56. 3. Ehrnsperger M., Graber S., Gaestel M. and Buchner J. (1997) EMBO J. 16: 221-229. 4. Ciocca D.R., Oesterreich S., Chamness G.C., McGuire W.L., and Fugua S.A. (1993) J Natl Cancer Inst. 85 (19):1558-70. 5. Sarto C., Binnz P.A., and Mocarelli P. (2000) Electrophoresis. 21(6): 1218-26. 6. Arrigo A.P. (2005) J Cell Biochem. 94(2): 241-6. |

StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.