Properties
| Storage Buffer | 20mM HEPES buffer pH7.2, 80mM NaCl, 10% glycerol |
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Purification | Affinity Purified |
| Cite This Product | Human Recombinant AHA1 Protein (StressMarq Biosciences | Victoria, BC CANADA | Catalog# SPR-309) |
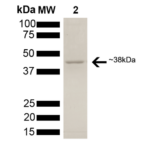
| Certificate of Analysis | This product has been certified >90% pure using SDS PAGE analysis. 2uM SPR-309 generated a 9-fold ATPase activation of 2uM HSP90 (His-tagged HSP90 beta) in 33mM Hepes pH7.2, 30mM NaCl, 5mM MgCl2, 1mM DTT, 1.5mM ATP in a 100ul reaction at 37 degrees C. (This is an enzyme-linked ATP regeneration assay tracking loss of NADH absorbance at 340nm.) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | AHSA1, AHA1, HSPC322, p38, C14orf3, LOC10598, Activator of Hsp90 ATPase activity 1, Activator of 90 kDa heat shock protein ATPase homolog 1 |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cell Signaling, Chaperones, Heat Shock |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm |
| Accession Number | NP_036243.1 |
| Gene ID | 10598 |
| Swiss Prot | O95433 |
| Scientific Background |
AHA1 (Activator of HSP90 ATPase 1) is a co-chaperone that enhances the ATPase activity of HSP90, accelerating its chaperone cycle and modulating the folding of client proteins. In the nervous system, AHA1 plays a critical role in regulating the stability and function of proteins involved in synaptic signaling, neuronal development, and stress responses. In neurodegenerative diseases, AHA1 has been implicated in the processing of aggregation-prone proteins such as tau and huntingtin. By stimulating HSP90 activity, AHA1 can influence the folding and degradation of these proteins, potentially affecting their accumulation and toxicity. Dysregulation of AHA1 expression or function may contribute to proteostasis imbalance, a hallmark of disorders like Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease. AHA1’s role in modulating the chaperone machinery makes it a promising target for therapeutic strategies aimed at restoring protein homeostasis in neurodegeneration. Its activity may also serve as a biomarker for cellular stress and chaperone system dynamics in the aging brain. |
| References |
1. Hainzl O., Lapina M.C., Buchner J., Richter K. (2009) J Biol Chem. Epub. 2. Harst A., Lin H., Obermann W.M. (2005) Biochem J. 387 (pt.3): 789-796. 3. Lotz G.P., Brychzy A., Heinz S., Obermann W.M. (2008) J Cell Sci. 121(pt.5): 717-723. 4. Holmes J.L., Sharp S.Y., Hobbs S., Workman P. (2008) Cancer Res. 68(4): 1188-1197. |


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.