Properties
| Storage Buffer | PB pH 7.4 (10 mM KH2PO4, 7.5 mM NaOH, pH 7.4) |
| Storage Temperature | -80ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Dry Ice. Shipping note: Product will be shipped separately from other products purchased in the same order. |
| Purification | Ion-exchange Purified, monomer removed with 100K MWCO filter |
| Cite This Product | Human Recombinant Alpha Synuclein Oligomers (StressMarq Biosciences | Victoria, BC CANADA | Catalog# SPR-484) |
| Certificate of Analysis | Certified >95% pure using SDS-PAGE analysis. Low endotoxin <5 EU/mL @ 2mg/mL. |
| Other Relevant Information | Kinetically stable alpha synuclein oligomers are generated from monomer without an inducer/inhibitor, remain soluble oligomers for at least two weeks at 37 degrees, and are toxic to dopaminergic neurons. |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Alpha-synuclein, Alpha synuclein, Asyn, SNCA, NACP, PARK1, PARK4, PD1, Synuclein alpha, Non-A beta component of AD amyloid, Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor, Synuclein Alpha-140, SYN, Parkinson's disease familial 1 Protein Protein |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Parkinson's Disease, Synuclein, Tangles & Tau, Multiple System Atrophy |
| Cellular Localization | Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Presynaptic Termini |
| Accession Number | NP_000336.1 |
| Gene ID | 6622 |
| Swiss Prot | P37840 |
| Scientific Background |
Our kinetically stable oligomers of alpha-synuclein are generated without an inducer or inhibitor and remain stable for at least 2 weeks at 37oC. They present as globular structures under TEM, demonstrate toxicity in rat primary dopaminergic neurons and induce Parkinson’s-associated alpha synuclein phosphoserine 129 pathology. These oligomers have been previously characterized as globular, cylindrical structures with a beta-sheet structure intermediate between monomers and fibrils, and were demonstrated to have a higher toxicity to neurons than alpha-synuclein fibrils (1,2). Alpha-Synuclein (SNCA) is expressed predominantly in the brain, where it is concentrated in presynaptic nerve terminals (3). Alpha-synuclein is highly expressed in the mitochondria of the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, striatum and thalamus (4). Functionally, it has been shown to significantly interact with tubulin (5), and may serve as a potential microtubule-associated protein. It has also been found to be essential for normal development of the cognitive functions; inactivation may lead to impaired spatial learning and working memory (6). SNCA fibrillar aggregates represent the major non A-beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid plaque, and a major component of Lewy body inclusions, and Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive accumulation in selected neurons of protein inclusions containing alpha-synuclein and ubiquitin (7, 8). |
| References |
1. Chen, S.W., et. al. (2015). PNAS. E1994-E2003. 2. Lorenzen, N., et. al. (2014). JACS. 136: 3859-3868. 3. “Genetics Home Reference: SNCA”. US National Library of Medicine. (2013). 4. Zhang L., et al. (2008) Brain Res. 1244: 40-52. 5. Alim M.A., et al. (2002) J Biol Chem. 277(3): 2112-2117. 6. Kokhan V.S., Afanasyeva M.A., Van'kin G. (2012) Behav. Brain. Res. 231(1): 226-230. 7. Spillantini M.G., et al. (1997) Nature. 388(6645): 839-840. 8. Mezey E., et al. (1998) Nat Med. 4(7): 755-757. |
Product Images
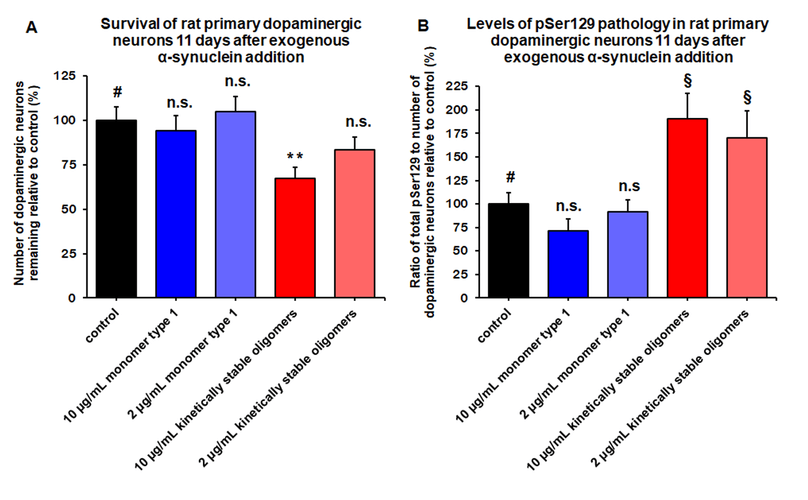
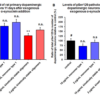
Kinetically stable alpha-synuclein oligomers (SPR-484) are toxic to dopaminergic neurons and induce phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein Ser129, a pathology associated with Parkinson’s disease. Survival of rat primary dopaminergic neurons 11 days after treatment quantified by anti-MAP2 antibody and expressed as a percentage of control (A). Levels of alpha-synuclein pSer129 present in rat primary dopaminergic neurons 11 days after treatment quantified by ratio of anti-alpha-synuclein pSer129 antibody to anti-MAP2 antibody expressed as a percentage of control (B). Mean +/- s.e.m; ** p<0.01 stats vs control, one-way Anova followed by Dunnett’s test; § p<0.05, stats vs control, Student’s t-test. Data is representative of n=6 experimental repeats for each condition; # represents control, n.s. indicates not significant p>0.05.
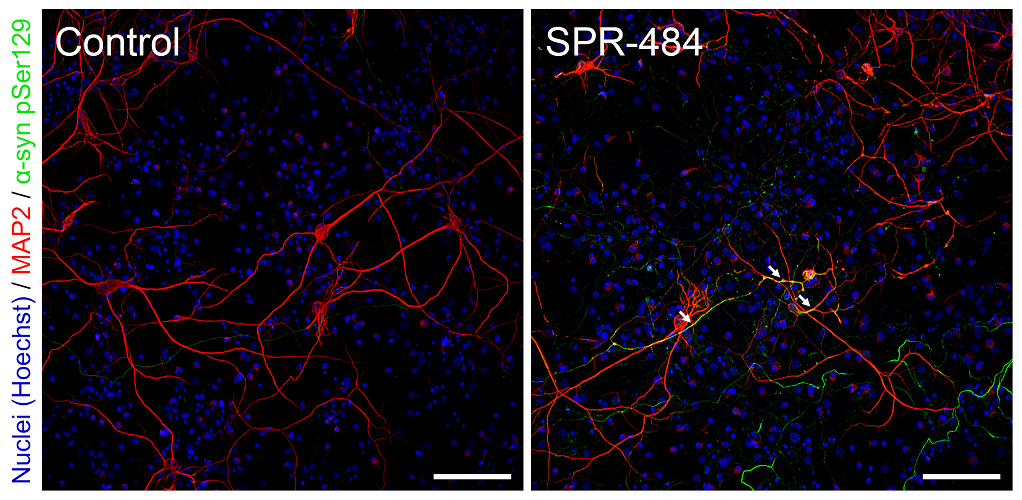
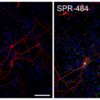
Representative immunohistochemistry images of Parkinson’s-associated pSer129 pathology induced in rat primary dopaminergic cells by kinetically stable alpha-synuclein oligomers (SPR-484). Primary rat dopaminergic neurons 11 days after treatment with control PBS buffer (A). Primary rat dopaminergic neurons 11 days after treatment with 10 µg/mL SPR-484 (B). Nuclei appear blue (Hoechst), dopaminergic neurons appear red (MAP2) and pathology appears green (α-syn pSer129). Both cultures treated with chicken polyclonal anti-MAP-2 antibody, mouse monoclonal anti-αsyn pSer129-specific antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse IgG, Alexa Fluor 647 goat anti-chicken IgG, and fluorescent marker Hoechst in the same solution. White arrows emphasize several regions of strong presence of pSer129 pathology in MAP2 positive neurons. Scale bar represents 100 μm. Note: SPR-484 is generated recombinantly in E.coli and is non-phosphorylated prior to addition on neurons.
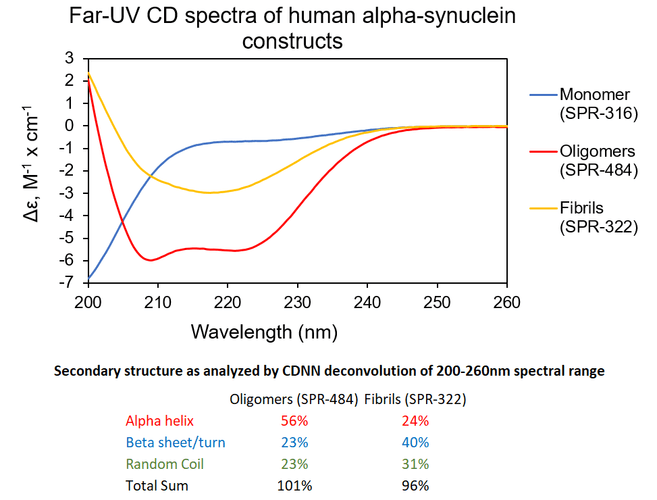
Αlpha Synuclein Oligomers Have Distinct Secondary Structure Differences Compared to Fibrils. UV-CD data suggests that StressMarq’s Alpha Synuclein Oligomers have distinct secondary structure differences compared to our monomers and fibrils. More specifically, StressMarq’s Kinetically Stable Alpha Synuclein Oligomers (SPR-484) show a significantly higher alpha helix content and lower beta sheet/turn content than our Alpha Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils (Type 1) (SPR-322). StressMarq’s Alpha Synuclein Monomers (SPR-316) show a strong negative signal at 200 nm indicative of a disordered protein state (low secondary structure content).
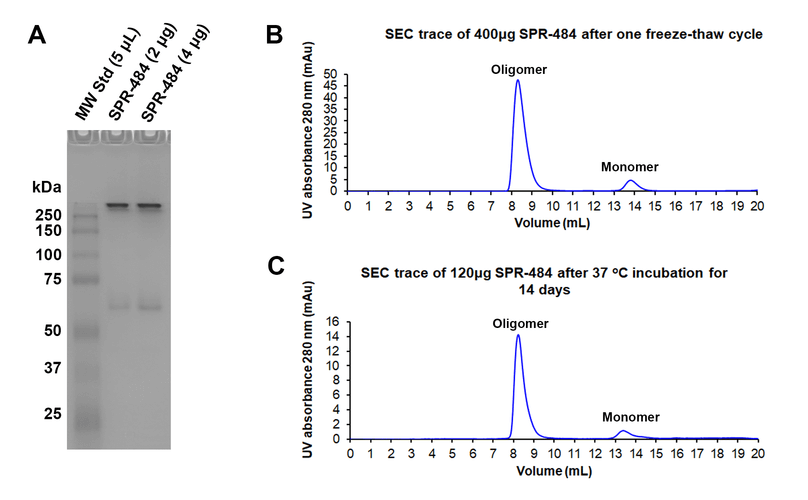
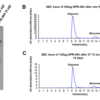
Kinetically stable alpha-synuclein oligomers (SPR-484) are stable after a freeze-thaw cycle and when incubated at 37 oC for 2 weeks. Tris-Gylcine Native PAGE migration of kinetically stable alpha-synuclein oligomers after a freeze-thaw cycle (A). Size-exclusion chromatography of SPR-484 after a freeze-thaw cycle (B) and 37oC incubation for 14 days (C). By peak area, approximately 90% of SPR-484 remains oligomeric after freeze-thaw and 37oC treatments. SEC was performed on Superdex 200 10/300 GL Increase column in phosphate buffer pH 7.4. Note: Monomeric alpha-synuclein is an intrinsically disordered 14 kDa protein. Due to its extended conformation in solution, migration of free monomeric alpha-synuclein is similar to that of a globular 60 kDa protein on Native PAGE and SEC.
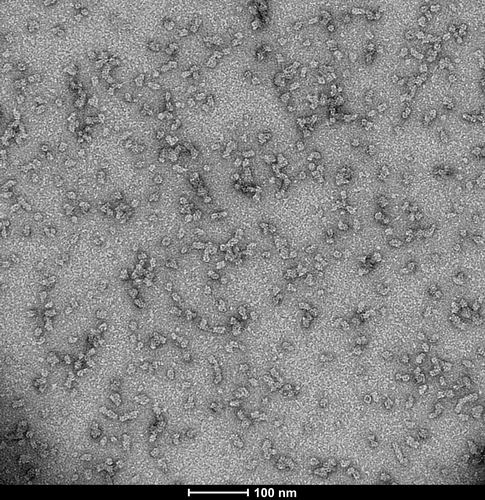


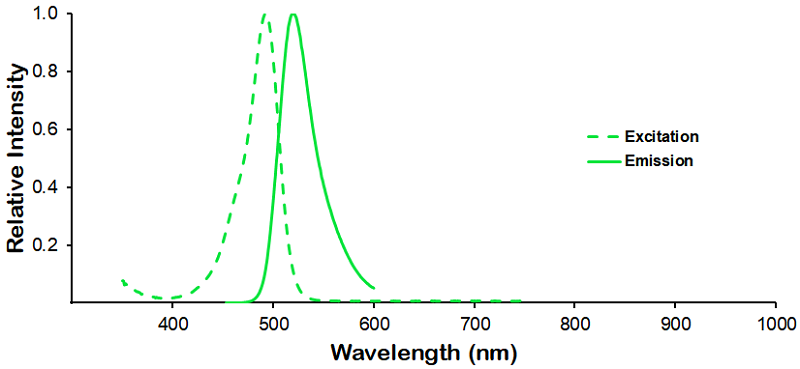
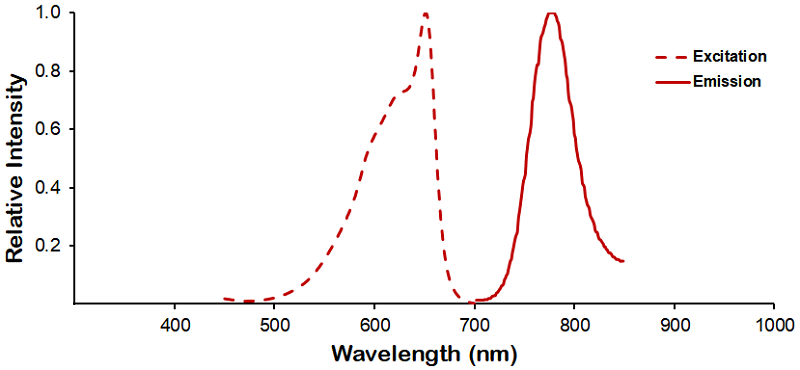
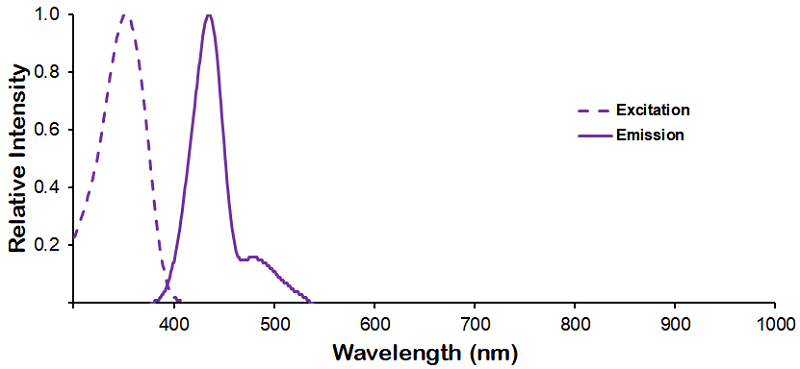
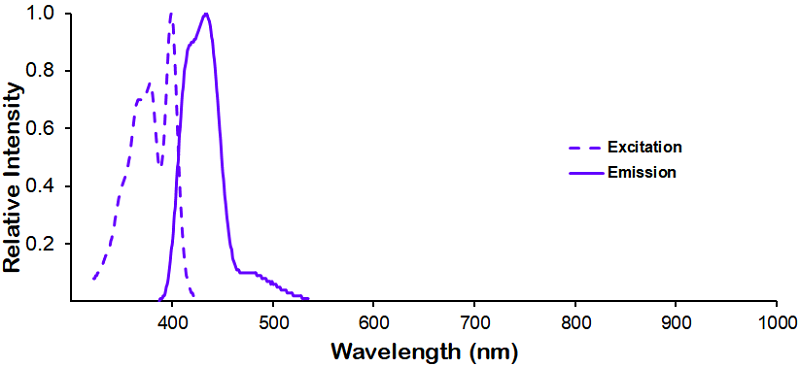
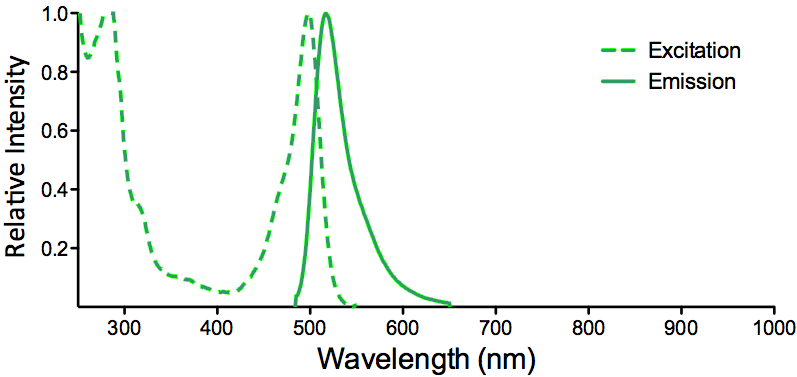
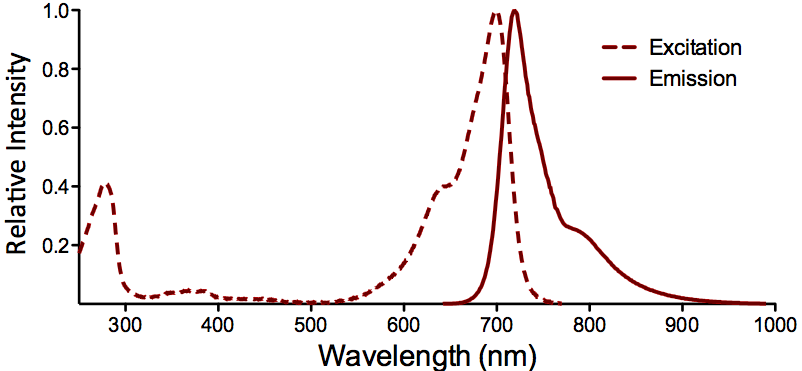
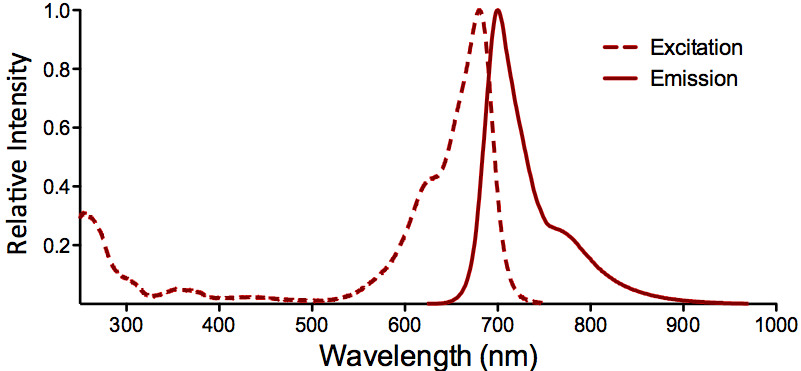
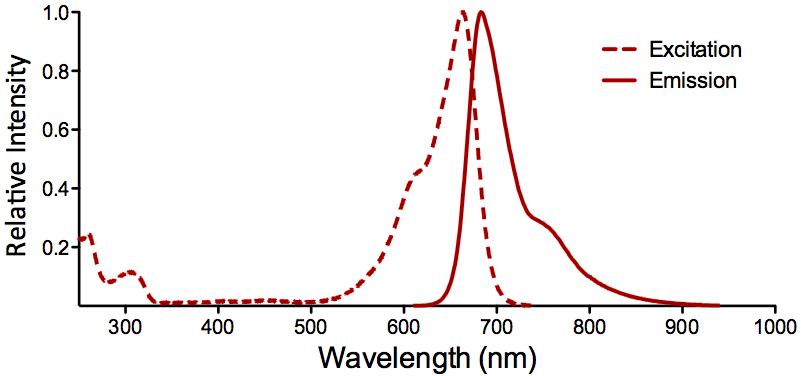
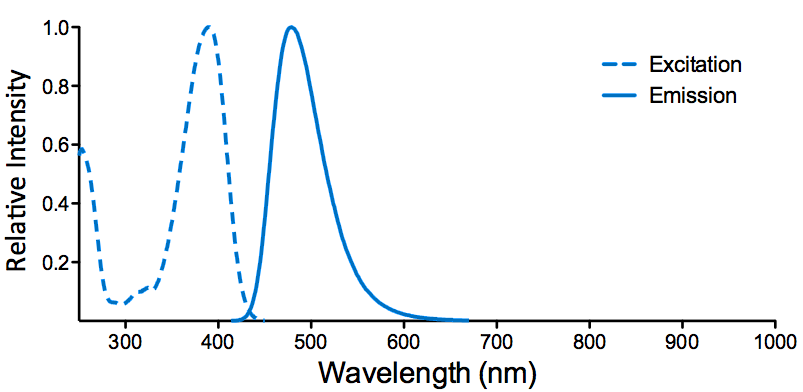
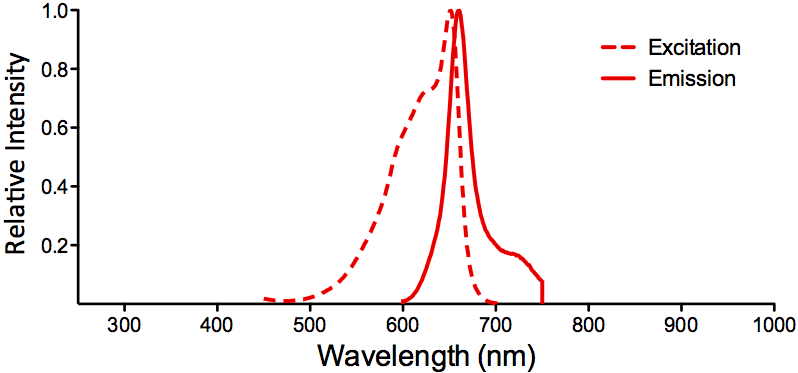
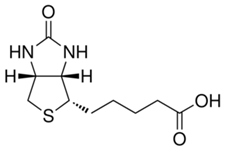
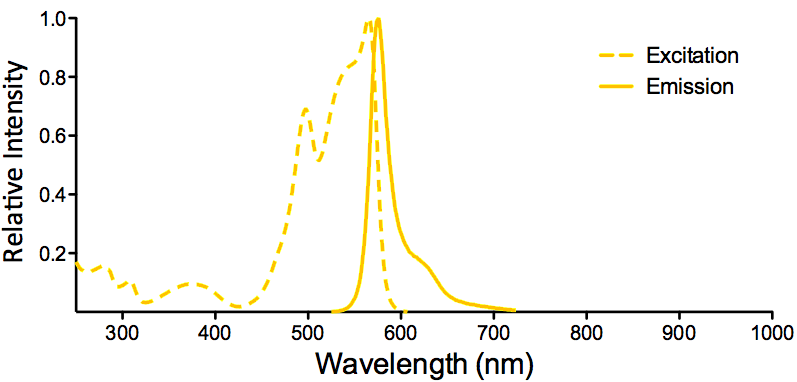

StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.