| Product Name | Beta Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
Human Recombinant Beta Synuclein PFFs (Type 1) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | WB, SDS-PAGE, In vivo assay, In vitro assay | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conjugates |
No tag
StreptavidinProperties:
Biotin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nature | Recombinant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expression System | E. coli | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Purity | >95% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Resources | Sonication Protocol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Protein Length | Full Length | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Protein Size | 14.28 kDa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Properties
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH 7.4 |
| Storage Temperature | -80ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Dry Ice. Shipping note: Product will be shipped separately from other products purchased in the same order. |
| Purification | Ion-exchange Purified |
| Cite This Product | Human Recombinant Beta Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils (StressMarq Biosciences | Victoria, BC CANADA | Catalog# SPR-457) |
| Certificate of Analysis | Certified >95% pure using SDS-PAGE analysis. |
| Other Relevant Information | For best results, sonicate immediately prior to use. Refer to the Neurodegenerative Protein Handling Instructions on our website, or the product datasheet for further information. Monomer source is catalog# SPR-405. |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Beta-synuclein, Synuclein beta, SNCB, SYUB_HUMAN, PNP14, Phosphoneuroprotein 14, 14 kDa brain-specific, G Protein Beta1/Gamma2 Subunit-Interacting Factor 1, Beta Synuclein PFFs |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Parkinson's Disease, Synuclein, Tangles & Tau |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm |
| Accession Number | NP_001001502.1 |
| Gene ID | 6620 |
| Swiss Prot | Q16143 |
| Scientific Background |
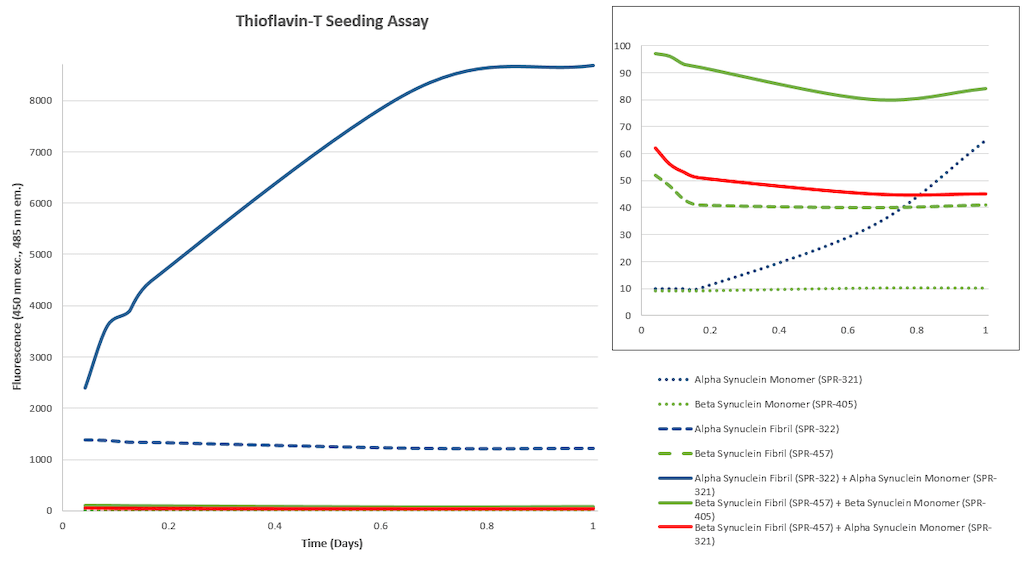
Beta-synuclein, a member of the synuclein protein family, plays a nuanced role in neuronal function and pathology. Unlike its counterpart alpha-synuclein, which is heavily implicated in Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies, beta-synuclein has traditionally been considered neuroprotective. However, emerging evidence suggests that beta-synuclein can form pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) under pathological conditions, contributing to neurodegenerative processes. Beta-synuclein PFFs exhibit distinct biophysical properties and aggregation dynamics that influence synaptic integrity and neuronal survival. These fibrils can disrupt synaptic vesicle trafficking, interfere with SNARE-complex assembly, and promote neuroinflammation—hallmarks of neurodegeneration. Recent studies indicate that beta-synuclein PFFs may act synergistically or antagonistically with alpha-synuclein aggregates, modulating disease progression in disorders such as dementia with Lewy bodies and multiple system atrophy. In vivo models demonstrate that beta-synuclein fibrillization correlates with age-dependent synaptic dysfunction and neuronal loss, underscoring its relevance in aging-related neurodegenerative diseases. The ability to generate and study beta-synuclein PFFs in controlled experimental systems provides a powerful tool for dissecting the molecular mechanisms of protein aggregation, toxicity, and intercellular propagation. As research advances, beta-synuclein PFFs are emerging as both biomarkers and therapeutic targets, offering new avenues for early diagnosis and intervention in neurodegenerative disorders. |
| References |
1. www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/facts-figures 2. Alzheimer, A. Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg. Z. Psychiatr. Psych.-Gerichtl. Med. 64, 146–148 (1907). 3. Taschenberger G., et al. (2013) Ann Neurol. 74(1): 109-118. |





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.