Properties
| Storage Buffer | 25mM Tris buffer pH7.2, 150mM NaCl, 0.1 mM DTT, 50% glycerol |
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Purification | Affinity Purified |
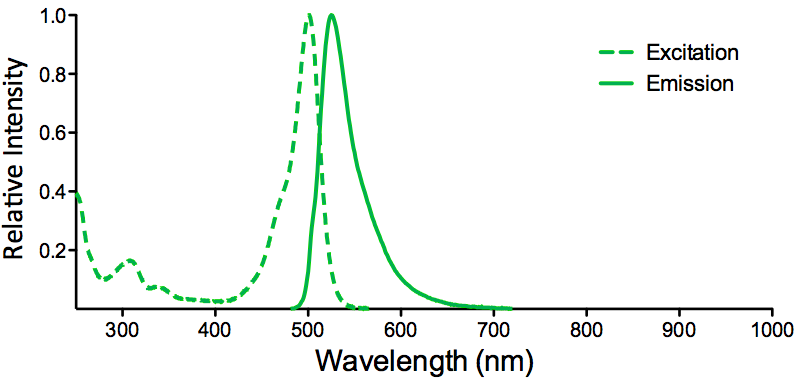
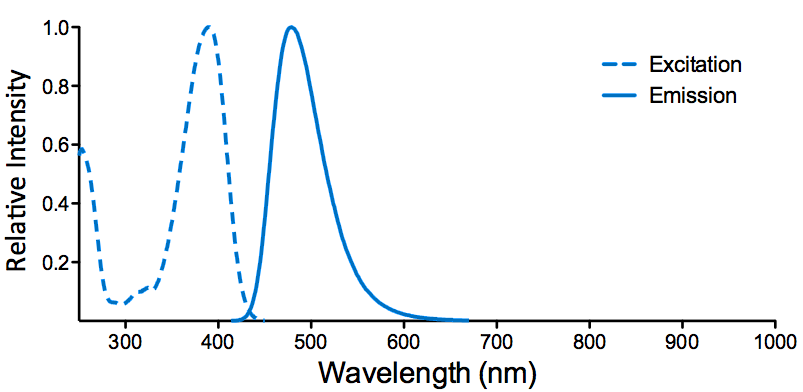
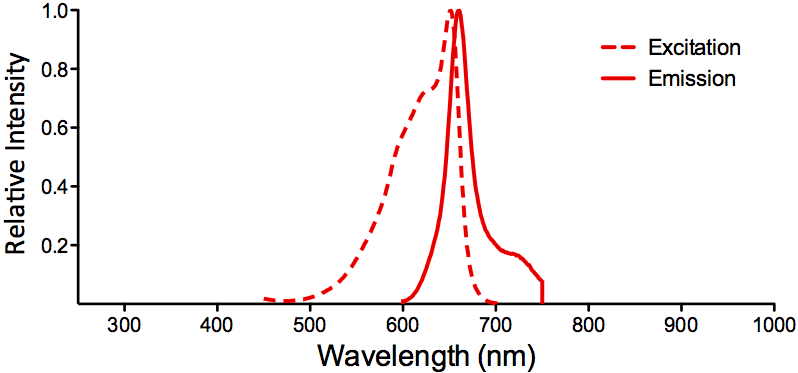
| Cite This Product | Human Recombinant CDC37 Protein (StressMarq Biosciences | Victoria, BC CANADA | Catalog# SPR-304) |
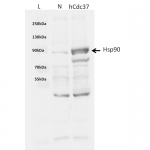
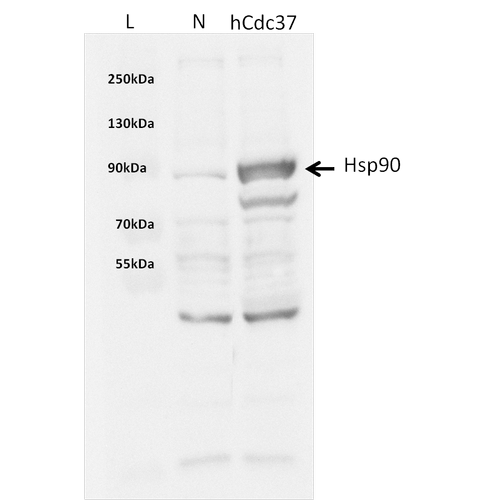
| Certificate of Analysis | This product has been certified >90% pure using SDS PAGE analysis. 4uM SPR-303, when added to 2uM SPR-300 (Aha1)-activated HSP90 (2uM; His-tagged HSP90 beta) in 33mM Hepes pH7.2, 30mM NaCl, 5mM MgCl2, 1mM DTT, 1.5mM ATP in a 100ul reaction at 37 degrees C, eliminated all Aha1-mediated ATPase stimulation as well as intrinsic HSP90 ATPase activity. (This is an enzyme-linked ATP regeneration assay tracking loss of NADH absorbance at 340nm). |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | CDC37, Cell division cycle 37 homolog, p50cdc37, Cdc37L1 |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cell Signaling, Heat Shock |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm |
| Accession Number | NP_008996.1 |
| Gene ID | 11140 |
| Swiss Prot | Q16543 |
| Scientific Background |
CDC37 is a co-chaperone that specifically targets protein kinases for folding and stabilization by the HSP90 complex. It acts as a kinase-specific adaptor, guiding client proteins into the chaperone system and regulating their maturation and activity. In the nervous system, CDC37 is essential for the stability of kinases involved in neuronal signaling, synaptic plasticity, and cell survival. Dysregulation of CDC37 can impair kinase function, contributing to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, where aberrant kinase signaling and protein aggregation are common features. CDC37’s interaction with HSP90 influences the fate of key neurodegenerative disease-related proteins, including tau kinases and stress-activated kinases. Targeting CDC37 may offer a strategy to modulate kinase-driven pathways and restore signaling balance in neurodegeneration. |
| References |
1. Dai K., Kobayashi R., Beach D. (1996) J Biol Chem. 271(36): 22030-22034. 2. Stepanova L., Leng X., Parker S.B., Harper J.W. (1996) Genes Dev. 10(12): 1491-1502. 3. Kimura Y., et al. (1997) Genes Dev. 11(14): 1775-1185. 4. Gray P.J., et al. (2008) Nat Rev Cancer. 8(7): 491-495. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.