| Product Name | Hinokitiol |
| Description |
Iron Chelator antioxidant |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 499-44-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 164.2 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Antioxidant |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or ethanol (25 mg/ml) |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White Solid |
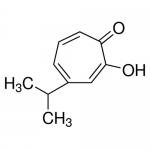
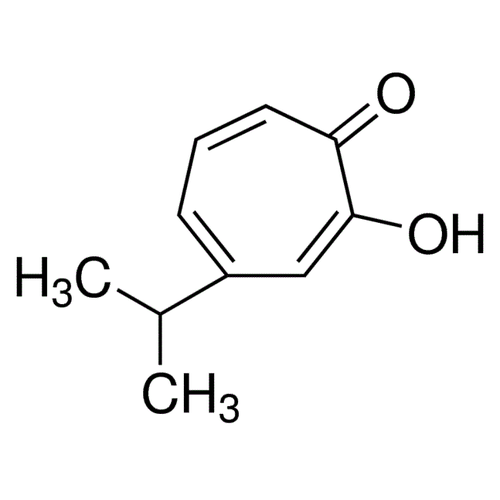
| SMILES | CC(C)C1=CC=CC(=O)C(=C1)O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C10H12O2/c1-7(2)8-4-3-5-9(11)10(12)6-8/h3-7H,1-2H3,(H,11,12) |
| InChIKey | FUWUEFKEXZQKKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution: Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection Hazard Phrases: H302 |
| Cite This Product | Hinokitiol (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-151) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 2-Hydroxy-4-isopropyl-2,4,6-cycloheptatrien-1-one |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Oxidative Stress |
| PubChem ID | 3611 |
| Scientific Background | Hinokitiol is a natural monoterpenoid known for its potent metal-chelating properties. In neurodegenerative disease research, hinokitiol has shown promise due to its ability to modulate metal ion homeostasis, a critical factor in the pathogenesis of disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. By chelating excess metal ions, hinokitiol may reduce oxidative stress and prevent metal-induced aggregation of neurotoxic proteins. Additionally, its pro-apoptotic and differentiation-inducing effects in cellular models suggest potential for modulating neural cell fate. These properties position hinokitiol as a candidate for therapeutic strategies targeting metal dysregulation and oxidative damage in the brain. |
| References |
1. Tanaka T., et al. (1999) Cell Biol Int. 23(8): 541-550. 2. Ido Y., et al. (1999) Cell Prolif. 32(1): 63-73 3. Kim D.S., et al. (2004) Arch Pharm Res. 27(3): 334-339. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.