| Product Name | BRD 7389 |
| Description |
p90 RSK kinase inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% (HPLC) |
| CAS No. | 376382-11-5 |
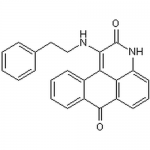
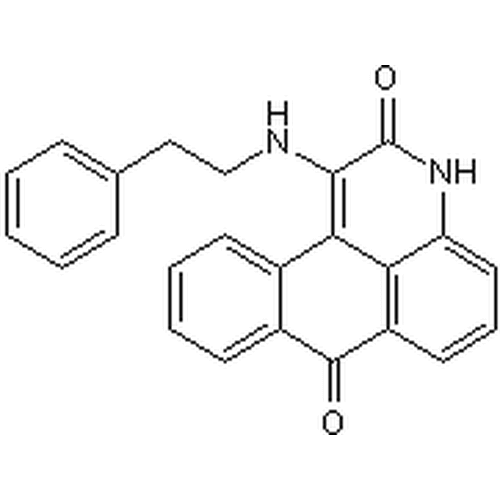
| Molecular Formula | C24H18N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 366.4 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Orange powder |
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CCNC2=C3C4=CC=CC=C4C(=O)C5=C3C(=CC=C5)NC2=O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C24H18N2O2/c27-23-17-10-5-4-9-16(17)21-20-18(23)11-6-12-19(20)26-24(28)22(21)25-14-13-15-7-2-1-3-8-15/h1-12,20,25H,13-14H2 |
| InChIKey | QVEVXIXBUORVGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Not a hazardous substance or mixture. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. |
| Cite This Product | BRD 7389 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-497) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | BRD7389, BRD-7389, 1-[(2-Phenylethyl)amino]-3H-naphtho[1,2,3-de]quinoline-2,7-dione, 1-Phenethylamino-3H-naphtho[1,2,3-de]quinoline-2,7-dione |
| Research Areas | Apoptosis, Cancer, Cancer Growth Inhibitors, Cell Signaling, Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors |
| PubChem ID | 24870634 |
| Scientific Background | BRD 7389 is a selective inhibitor of p90 ribosomal S6 kinases (RSK1, RSK2, and RSK3), key effectors in the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Although initially studied for its role in regulating insulin expression in pancreatic alpha-cells, BRD 7389’s modulation of RSK activity has implications for neuroscience. RSK signaling influences neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and memory formation. Dysregulation of this pathway has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive disorders. By targeting RSKs, BRD 7389 may serve as a tool for dissecting the molecular mechanisms underlying neuronal function and resilience, offering potential leads for therapeutic development in neurodegeneration. |
| References | 1. Fomina-Yadlin D., et al. (2010) Pro. Nat. Acad.Sci. USA. 107(34): 15099–15104. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.