| Product Name | 5-Azacytidine |
| Description |
DNA hypomethylation agent |
| Purity | >98% (TLC); NMR (Conforms) |
| CAS No. | 320-67-2 |
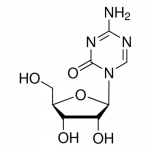
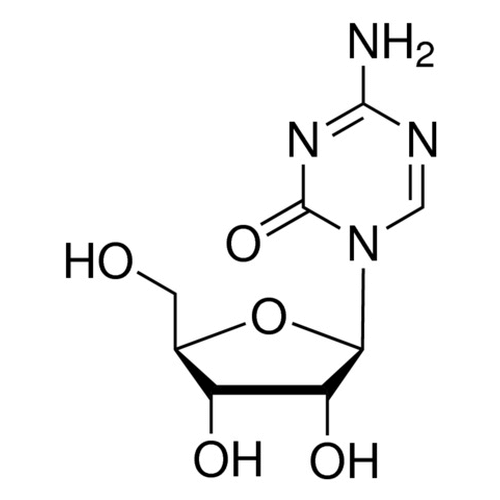
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N4O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 244.2 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in 25 mg/ml DMSO or 12 mg/ml Water |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White Solid |
| SMILES | C1=NC(=NC(=O)N1[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)O)N |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C8H12N4O5/c9-7-10-2-12(8(16)11-7)6-5(15)4(14)3(1-13)17-6/h2-6,13-15H,1H2,(H2,9,11,16)/t3-,4-,5-,6-/m1/s1 |
| InChIKey | NMUSYJAQQFHJEW-KVTDHHQDSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Harmful- May be harmful if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection S24/25- Avoid contact with skin and eyes Hazard Statements: H302- Harmful if swallowed H350 – May cause cancer Precautionary Statements: P201 – Obtain special instructions before use. P308 + P313 – If exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention |
| Cite This Product | 5-Azacytidine (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-345) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 4-Amino-1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1,3,5-triazin-2(1H)-one; Ladakamycin; U-18496; NSC-102816; 5-AzaC |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cell Signaling |
| PubChem ID | 9444 |
| Scientific Background | 5-Azacytidine is a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor that incorporates into DNA and forms covalent adducts with DNMT1, leading to enzyme depletion and global DNA demethylation. This reactivates silenced genes and alters epigenetic landscapes. In neurodegenerative disease research, 5-Azacytidine is used to study the role of epigenetic regulation in neuronal differentiation, plasticity, and disease progression. It has also been shown to enhance the efficiency of stem cell reprogramming and promote differentiation into neuronal lineages, making it a valuable tool in regenerative neuroscience and epigenetic therapy development. |
| References |
1. Schneider-Stock R., et al. (2005) J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 312(2): 525-536. 2. Mikkelsen T.S., et al., (2008) Nature. 454(7200): 49-55. 3. Qian Q., et al., (2012) Stem Cells Dev. 21(1): 67-75. |

StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.