| Product Name | BIX-01294 |
| Description |
HMT inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 935693-62-2 |
| Molecular Formula | C28H38N6O2*3HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 600.02 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | May be dissolved in DMSO (100 mM) or Water (100 mM) |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Cream solid |
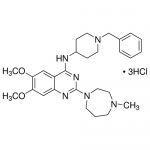
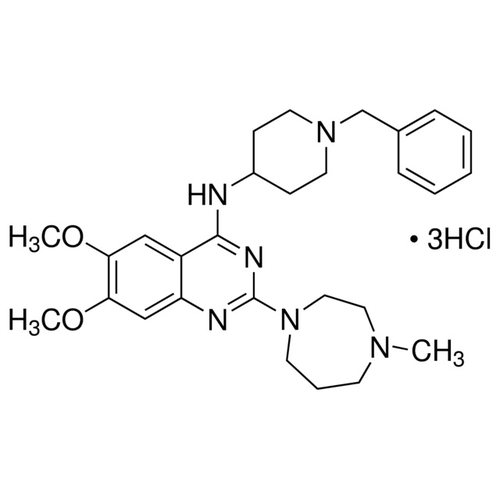
| SMILES | CN1CCCN(CC1)C2=NC3=CC(=C(C=C3C(=N2)NC4CCN(CC4)CC5=CC=CC=C5)OC)OC.Cl.Cl.Cl |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C28H38N6O2/c1-32-12-7-13-34(17-16-32)28-30-24-19-26(36-3)25(35-2)18-23(24)27(31-28)29-22-10-14-33(15-11-22)20-21-8-5-4-6-9-21/h4-6,8-9,18-19,22H,7,10-17,20H2,1-3H3,(H,29,30,31) |
| InChIKey | OSXFATOLZGZLSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution – Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection S24/25- Avoid contact with skin and eyes |
| Cite This Product | BIX-01294 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-347) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 2-(Hexahydro-4-methyl-1H-1,4-diazepin-1-yl)-6,7-dimethoxy-N-[1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl]-4-quinazolinamine trihydrochloride; N-(1-Benzyl-4-piperidinyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-2-(4-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl)-4-quinazolinamine trihydrochloride |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cell Signaling |
| PubChem ID | 25150857 |
| Scientific Background | BIX-01294 is a selective inhibitor of G9a and G9a-like protein histone lysine methyltransferases, with IC50 values of 0.7 and 1.7 µM, respectively. It modulates H3K9me2 levels in mammalian cells and has been instrumental in studies of epigenetic regulation and cellular reprogramming. In neuroscience, BIX-01294’s ability to alter chromatin states and gene expression profiles makes it a valuable tool for investigating neurodevelopmental processes and neuroplasticity. Its role in facilitating the induction of pluripotent stem cells also opens avenues for regenerative medicine and modeling of neurological diseases. Although primarily used in stem cell and cancer research, its epigenetic effects are increasingly relevant to understanding and potentially treating neurodegenerative disorders. |
| References |
1. Kubicek S., et al. (2007) Mol Cell. 25(3): 473-481. 2. Shi Y., et al. (2008) Cell Stem Cell. 3(5): 568-574. 3. Chang Y., et al. (2009) Nat Struct Mol Biol. 16(3): 312-317. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.