| Product Name | CID 2011756 |
| Description |
PKD kinase inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% (HPLC) |
| CAS No. | 638156-11-3 |
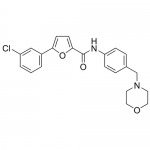
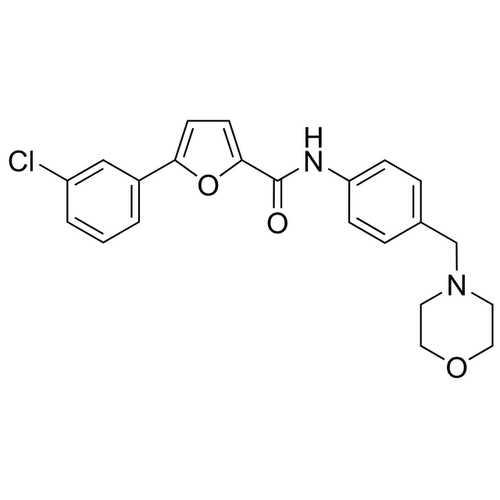
| Molecular Formula | C22H21ClN2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 396.9 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in DMSO |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White to beige solid |
| SMILES | C1COCCN1CC2=CC=C(C=C2)NC(=O)C3=CC=C(O3)C4=CC(=CC=C4)Cl |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C22H21ClN2O3/c23-18-3-1-2-17(14-18)20-8-9-21(28-20)22(26)24-19-6-4-16(5-7-19)15-25-10-12-27-13-11-25/h1-9,14H,10-13,15H2,(H,24,26) |
| InChIKey | XQJWTJLJEYIUDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Acute toxicity, Oral(Category 4) Eye irritation(Category 2A) Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. Hazard statements: H302 Harmful if swallowed. H319 Causes serious eye irritation. Precautionary statements: P305 + P351 + P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiousl y with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. |
| Cite This Product | CID 2011756 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-438) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | CID-2011756, 5-(3-Chlorophenyl)-N-[4-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)phenyl]furan-2-carboxamide |
| Research Areas | Apoptosis, Cancer, Cancer Growth Inhibitors, Cell Signaling, Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors |
| PubChem ID | 2011756 |
| Scientific Background | CID 2011756 is a specific, ATP-competitive inhibitor of protein kinase D (PKD), a family of serine/threonine kinases involved in signal transduction, vesicle trafficking, and cell survival. In neuroscience, PKD signaling has been linked to synaptic plasticity, neuroinflammation, and axonal transport. CID 2011756 is used to explore the role of PKD in neuronal function and to investigate its potential as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases characterized by disrupted intracellular signaling and transport. |
| References | 1. Sharlow E.R., et al. (2011) PloS One 6(10): e25134. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.