| Product Name | EX-527 |
| Description |
SIRT1 inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% (TLC); NMR (Conforms) |
| CAS No. | 49843-98-3 |
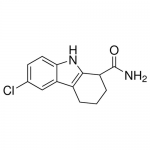
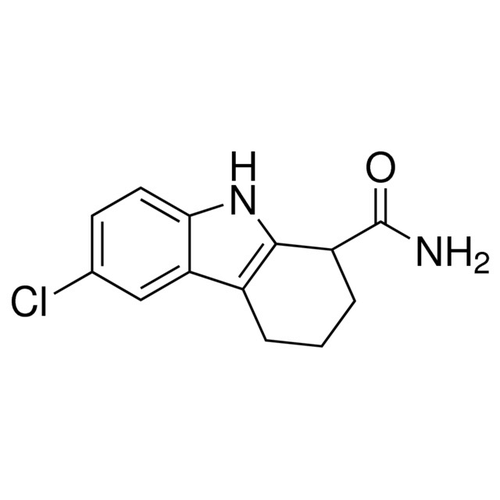
| Molecular Formula | C13H13ClN2O |
| Molecular Weight | 248.7 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in 18 mg/ml DMSO or 10 mg/ml Ethanol |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Light Yellow Solid |
| SMILES | C1CC(C2=C(C1)C3=C(N2)C=CC(=C3)Cl)C(=O)N |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C13H13ClN2O/c14-7-4-5-11-10(6-7)8-2-1-3-9(13(15)17)12(8)16-11/h4-6,9,16H,1-3H2,(H2,15,17) |
| InChIKey | FUZYTVDVLBBXDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Harmful- May be harmful if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection S24/25- Avoid contact with skin and eyes Hazard Statements: H301 – Toxic if swallowed H319 – Causes serious eye irritation Precautionary Statements: P301 + P310 – If swallowed: Immediately call a POSION Center P305 + P351 + P338: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. |
| Cite This Product | EX-527 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-353) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 6-Chloro-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1Hcarbazole-1-carboxamide (racemic) |
| Research Areas | Cell Signaling |
| PubChem ID | 5113032 |
| Scientific Background |
EX-527 is a potent and selective SIRT1 inhibitor (IC₅₀ = 98 nM) that does not affect other sirtuins or HDACs. It increases p53 acetylation following DNA damage and is fully cell permeable. In neuroscience, EX-527 has been shown to promote neuronal differentiation from pluripotent stem cells and modulate neurogenesis-related transcription factors. Its ability to influence cell fate decisions and epigenetic plasticity makes it a valuable probe for studying neurodevelopment, cellular reprogramming, and SIRT1-linked pathways in neurodegenerative disease models. |
| References |
1. Solomon J.M., et al., (2006) Mol. Cell. Biol. 26: 28. 2. Anderson J.L., et al., (2011) Mol.Cell 43: 834. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.