| Product Name | Geldanamycin |
| Description |
Hsp90 inhibitor |
| Purity | >95% |
| CAS No. | 30562-34-6 |
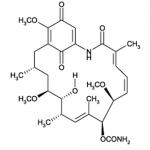
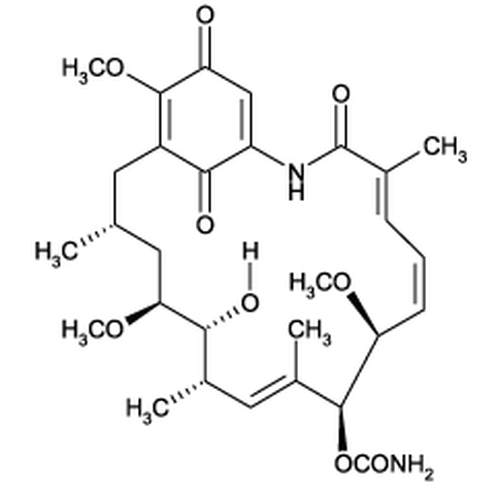
| Molecular Formula | C29H40N2O9 |
| Molecular Weight | 560.6 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in methanol, chloroform or DMSO (10 mg/ml); insoluble in water |
| Source | Produced by fermentation |
| Appearance | Yellow Solid |
| SMILES | C[C@H]1C[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](/C=C(/[C@@H]([C@H](/C=CC=C(C(=O)NC2=CC(=O)C(=C(C1)C2=O)OC)/C)OC)OC(=O)N)C)C)O)OC |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C29H40N2O9/c1-15-11-19-25(34)20(14-21(32)27(19)39-7)31-28(35)16(2)9-8-10-22(37-5)26(40-29(30)36)18(4)13-17(3)24(33)23(12-15)38-6/h8-10,13-15,17,22-24,26,33H,11-12H2,1-7H3,(H2,30,36)(H,31,35) |
| InChIKey | QTQAWLPCGQOSGP-KSRBKZBZSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Harmful. May be harmful if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through skin. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection Risk Phrases: R68- Possible risk of irreversible effects |
| Cite This Product | Geldanamycin (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-111) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | (4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-8,14,19-trimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1] docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Heat Shock |
| PubChem ID | 5288382 |
| Scientific Background | Geldanamycin is a benzoquinone ansamycin antibiotic that targets HSP90, disrupting its chaperone function and leading to the degradation of oncogenic and neurotoxic client proteins. While extensively studied in oncology, geldanamycin has demonstrated neuroprotective effects in models of Parkinson’s disease. It reduces alpha-synuclein toxicity in dopaminergic neurons and destabilizes mutant p53, a protein linked to neuronal apoptosis. Geldanamycin also inhibits c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling and suppresses hypoxia-induced stress responses, both of which are implicated in neurodegeneration. By modulating protein folding, stress signaling, and autophagy, geldanamycin offers a mechanistic framework for targeting neurodegenerative pathways. Despite its therapeutic potential, clinical use is limited by hepatotoxicity and poor solubility, prompting the development of safer analogs such as 17-AAG and 17-DMAG. |
| References |
1. Whitesell L., et al. (1994) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:8324. 2. Neckers L. (2002) Trends Mol. Med. 8: S55. 3. Mabjeesh N.J., et al. (2002) Cancer Res. 62: 2478. 4. Chavany C., et al. 1996) Amer. Society Biochem Mol Bio. 9: 4974-4977. 5. Villa R., et al. (2003) Carcinogenesis. 24(5): 851-9. 6. Yamaki H., Iguchi-Ariga S.M., and Ariga H. (1989) J Antibiot (Tokyo). 42(4): 604-10. |

StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.