| Product Name | Hexyl Pentynoic Acid (HPA) |
| Description |
HDAC inhibitor |
| Purity | >97% (TLC), NMR conforms |
| CAS No. | 96017-59-3 |
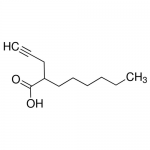
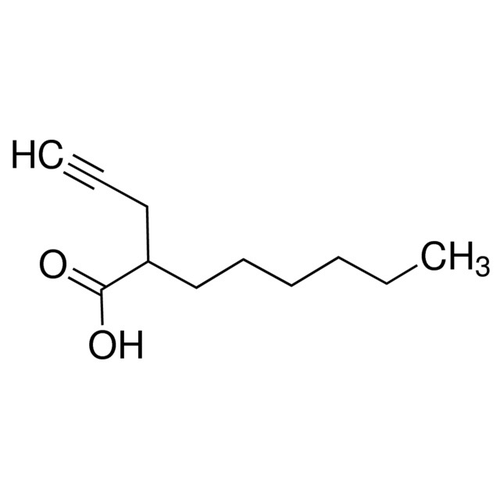
| Molecular Formula | C11H11O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 182.3 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in 25 mg/ml DMSO or 25 mg/ml Ethanol |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Colorless Oil |
| SMILES | O=C(O)C(CCCCCC)CC#C |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C11H18O2/c1-3-5-6-7-9-10(8-4-2)11(12)13/h2,10H,3,5-9H2,1H3,(H,12,13) |
| InChIKey | DUQSBRQHALCSLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution- Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection S24/25- Avoid contact with skin and eyes |
| Cite This Product | HPA (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-356) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 2-(2-propynyl)octanoic acid, HPA |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cell Signaling |
| PubChem ID | 175664 |
| Scientific Background | HPA (Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal axis) refers to a complex neuroendocrine system that regulates stress responses through the release of cortisol and other glucocorticoids. Dysregulation of the HPA axis is associated with chronic stress, depression, and neurodegenerative diseases. In neuroscience, HPA axis activity is studied to understand its impact on hippocampal function, neurogenesis, and neuroinflammation. Elevated glucocorticoid levels can exacerbate neuronal damage and cognitive impairment, making HPA axis modulation a target for therapeutic intervention in brain disorders. |
| References |
1. Eikel D., et al. (2006) Chem. Res. Toxicol. 19: 272. 2. Leng Y., et al. (2010) Neurosci. Lett. 476: 127. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.