| Product Name | NSC-66811 |
| Description |
p53/mdm2 inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 6964-62-1 |
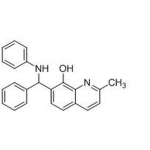
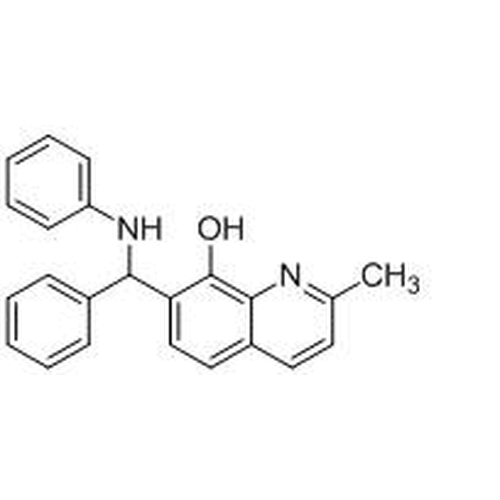
| Molecular Formula | C23H20N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 340.4 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in 25 mg/ml DMSO |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White Solid |
| SMILES | CC1=NC2=C(C=C1)C=CC(=C2O)C(C3=CC=CC=C3)NC4=CC=CC=C4 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C23H20N2O/c1-16-12-13-18-14-15-20(23(26)22(18)24-16)21(17-8-4-2-5-9-17)25-19-10-6-3-7-11-19/h2-15,21,25-26H,1H3 |
| InChIKey | WEENRMPCSWFMTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution – Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection S24/25- Avoid contact with skin and eyes |
| Cite This Product | NSC-66811 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-338) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 2-Methyl-7-[Phenyl(phenylamino)methyl]-8-quinolinol, 7-[Anilino(phenyl)methyl]-2-methylquinolin-8-ol |
| Research Areas | Apoptosis, Cancer, Cancer Growth Inhibitors, p53/mdm2 Inhibitors |
| PubChem ID | 248986 |
| Scientific Background | NSC-66811 is a novel small-molecule inhibitor that disrupts the MDM2-p53 interaction, a key regulatory axis in cell cycle control and apoptosis. By mimicking three critical p53 residues, NSC-66811 binds to MDM2 with high affinity (Ki = 120 nM), preventing MDM2-mediated degradation of p53. This leads to stabilization and activation of p53, promoting transcription of downstream genes involved in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. While primarily studied in oncology, the p53 pathway is increasingly recognized for its role in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, where dysregulated apoptosis and impaired DNA repair contribute to neuronal loss. NSC-66811 may offer a mechanistic tool to explore p53-mediated neuroprotection and cellular stress responses in neural models. |
| References | 1. Lu Y., et al. (2006) J. Med.Chem. 49: 3759. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.