| Product Name | Tranilast |
| Description |
Angiogenesis inhibitor |
| Purity | >95% (HPLC) |
| CAS No. | 53902-12-8 |
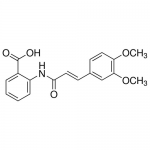
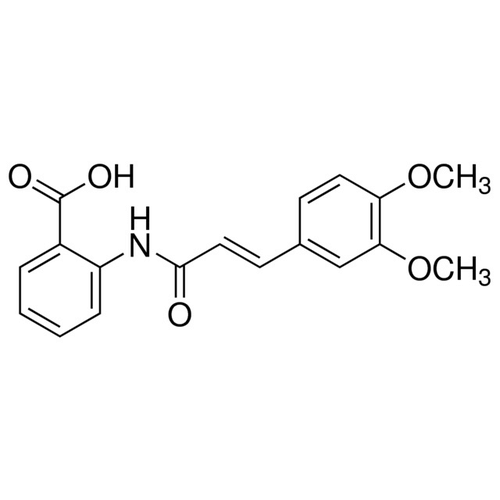
| Molecular Formula | C18H17NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 327.33 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO. |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Off-white to yellow powder. |
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)/C=C/C(=O)NC2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)O)OC |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C18H17NO5/c1-23-15-9-7-12(11-16(15)24-2)8-10-17(20)19-14-6-4-3-5-13(14)18(21)22/h3-11H,1-2H3,(H,19,20)(H,21,22)/b10-8+ |
| InChIKey | NZHGWWWHIYHZNX-CSKARUKUSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution: Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection Hazard Phrases: H302 – Harmful if swallowed. H312 – Harmful in contact with skin. H332 – Harmful if inhaled. Precautionary Phrases: P261 – Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray P280 – Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+ P312 IF SWALLOWED: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell. P304+P340 – IF INHALED: remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P501 – Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local/regional/national/ international regulations. |
| Cite This Product | Tranilast (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-369) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 2-{[(2E)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2- enoyl]amino}benzoic acid |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cardiovascular System, Cell Signaling, Neuroscience |
| PubChem ID | 5282230 |
| Scientific Background | Tranilast is an antiallergic and antifibrotic compound increasingly explored in neurodegenerative disease research for its ability to modulate inflammatory and fibrotic pathways. It inhibits collagen synthesis in a dose-dependent manner and suppresses transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a cytokine implicated in neuroinflammation and glial scarring. These properties suggest potential therapeutic relevance in conditions such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease, where fibrosis and chronic inflammation contribute to disease progression. While traditionally used in allergy and oncology research, Tranilast’s emerging role in modulating neuroimmune responses positions it as a candidate for repurposing in neuroprotective strategies. |
| References |
1. Yamada H., Tajima S., Nishikawa T., Murad S., and Pinnell S., (1999) The Journal of Biochemistrystry. 116(4): 892-897. 2. Chakrabarti R., Subramanian V., Abadalla J., Jothy S., Predhomme GJ. (2009) Anticancer Drugs. 20(5): 334-45. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.