| Product Name | U0126 |
| Description |
MEK inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 109511-58-2 |
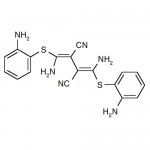
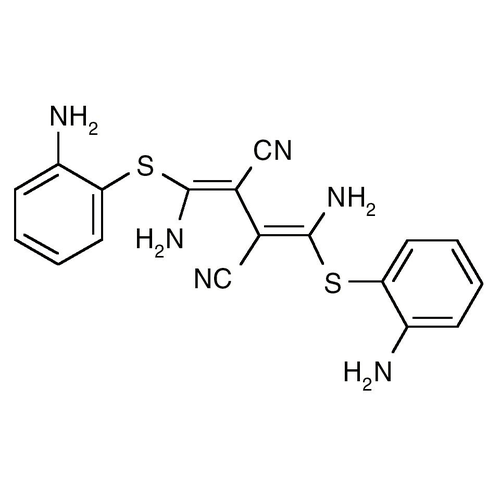
| Molecular Formula | C18H16N6S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 380.5 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (>10 mg/ml), 100% ethanol (2 mg/ml) |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White solid |
| SMILES | C2=C(SC(/N)=C(/C(=C(SC1=CC=CC=C1N)N)C#N)C#N)C(=CC=C2)N |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C18H16N6S2/c19-9-11(17(23)25-15-7-3-1-5-13(15)21)12(10-20)18(24)26-16-8-4-2-6-14(16)22/h1-8H,21-24H2/b17-11+,18-12+ |
| InChIKey | DVEXZJFMOKTQEZ-JYFOCSDGSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution: Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection |
| Cite This Product | U-0126 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-380) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 1,4-Diamino-2,3-dicyano-1,4-bis[2-aminophenylthio]butadiene |
| Research Areas | Cell Signaling |
| PubChem ID | 3006531 |
| Scientific Background | U-0126 is a selective and non-competitive inhibitor of MEK1 and MEK2 (IC50 = 72 nM and 58 nM, respectively), key kinases in the MAPK/ERK signaling cascade. This pathway regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival—processes often dysregulated in neurodegenerative diseases. U-0126 is widely used in neuroscience to investigate ERK-dependent mechanisms of synaptic plasticity, memory formation, and neuronal survival. It also inhibits AP-1 transcriptional activity and suppresses the production of inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases, linking it to studies on neuroinflammation and glial activation. U-0126’s ability to induce apoptosis under growth factor deprivation conditions further supports its use in modeling neurodegenerative stress responses. Its fluorescence properties in cell culture also make it a useful marker in imaging-based assays. |
| References |
1. Duncia J.V., et a.l (1998) Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 8(20): 2839-44. 2. Favata M.F., et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273(29): 18623-32. 3. Davies S.P., et al. (2000) Biochem. J. 351(Pt1): 95-105. 4. Namura S., et al. (2001) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98(20): 11569-74. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.