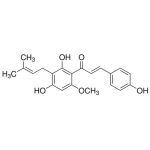
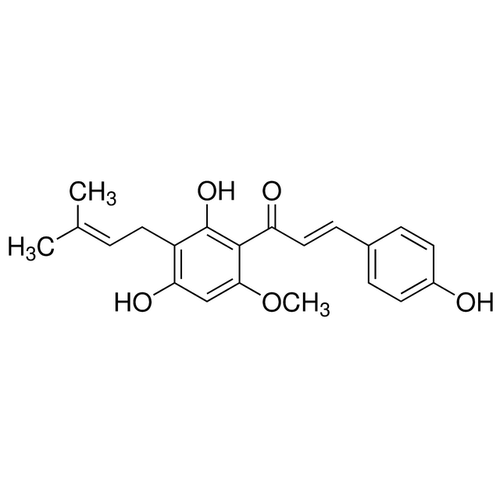
| Product Name | Xanthohumol |
| Description |
Autophagy inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% (TLC); NMR (Conforms) |
| CAS No. | 6754-58-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C21H22O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 354.4 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | May be dissolved in DMSO (35 mg/ml) or Ethanol (35 mg/ml) |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| SMILES | CC(=CCC1=C(C(=C(C=C1O)OC)C(=O)/C=C/C2=CC=C(C=C2)O)O)C |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C21H22O5/c1-13(2)4-10-16-18(24)12-19(26-3)20(21(16)25)17(23)11-7-14-5-8-15(22)9-6-14/h4-9,11-12,22,24-25H,10H2,1-3H3/b11-7+ |
| InChIKey | ORXQGKIUCDPEAJ-YRNVUSSQSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Toxic Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection Hazard Phrases: H317 May cause an allergic skin reaction. H400 Very toxic to aquatic life. Precautionary Phrases: P273 Avoid release to the environment. P280 Wear protective gloves. |
| Cite This Product | Xanthohumol (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-370) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | (2E)-1-[2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methoxy-3-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)phenyl]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propen-1-one |
| Research Areas | Autophagy, Cancer |
| PubChem ID | 639665 |
| Scientific Background | Xanthohumol is a prenylated flavonoid and valosin-containing protein (VCP) inhibitor that has shown promise in neurodegenerative disease research. By binding to the N-domain of VCP, it disrupts autophagosome maturation, a process critical for cellular waste clearance in neurons. Impaired autophagy is a hallmark of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Xanthohumol also exhibits potent anticancer activity by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis. Its dual role in modulating proteostasis and cell survival pathways makes it a valuable tool for investigating therapeutic interventions in neurodegeneration. |
| References |
1. Sasazawa Y., et al. (2012) ACS Chem Biol. 7(5): 892-900. 2. Vene R., et al. (2012) Mol. Med. 18: 1292. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.