| Product Name | ml167 |
| Description |
Clk4 kinase inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% (HPLC) |
| CAS No. | 1285702-20-6 |
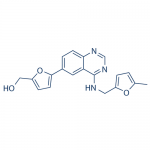
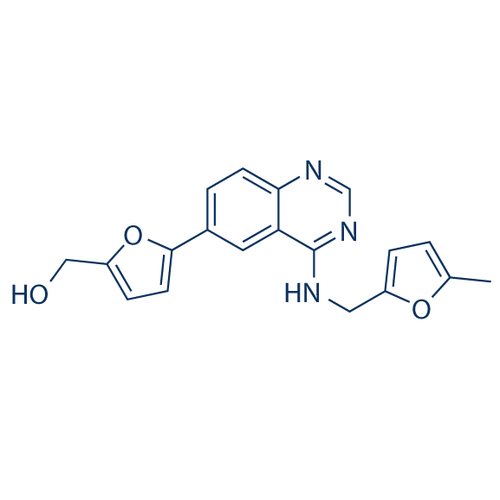
| Molecular Formula | C19H17N3O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 335.4 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO 10 mg/ml, clear |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Off-white to gray to brown |
| SMILES | CC1=CC=C(O1)CNC2=NC=NC3=C2C=C(C=C3)C4=CC=C(O4)CO |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C19H17N3O3/c1-12-3-8-18(24-12)22(2)19-15-9-13(4-6-16(15)20-11-21-19)17-7-5-14(10-23)25-17/h3-9,11,23H,10H2,1-2H3 |
| InChIKey | STBPLRTXXJJXLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Acute toxicity, Oral (Category 4), H302 Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. Hazard statements: H302 Harmful if swallowed. Precautionary statements: P264 Wash skin thoroughly after handling. P270 Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301 + P312 IF SWALLOWED: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/ physician if you feel unwell. P330 Rinse mouth. P501 Dispose of contents/ container to an approved waste disposal plant. |
| Cite This Product | ml167 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-505) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | ml-167, 5-[4-[[(5-Methyl-2-furanyl)methyl]amino]-6-quinazolinyl]-2-furanmethanol, CID 44968231, NCGC00188654 |
| Research Areas | Apoptosis, Cancer, Cancer Growth Inhibitors, Cell Signaling, Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors |
| PubChem ID | 51347463 |
| Scientific Background | ml167 is a highly selective inhibitor of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4), a member of the Clk family involved in alternative mRNA splicing. Aberrant splicing is increasingly recognized as a contributor to neurodegenerative diseases, including ALS and frontotemporal dementia. By modulating Clk4 activity, ml167 enables the study of splicing regulation in neuronal systems and may inform therapeutic approaches targeting RNA metabolism in neurodegeneration. |
| References | 1. Rosenthal A.S., et al. (2010). In Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.