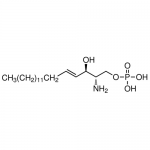
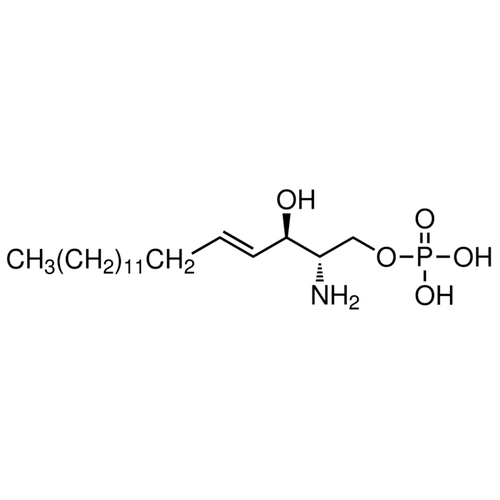
| Product Name | Sphingosine-1-phosphate, D-erythro |
| Description |
Signaling molecule |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 26993-30-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C18H38NO5P |
| Molecular Weight | 379.5 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Second Messenger |
| Solubility | Sparingly soluble in 1:1 ethanol:water. Addition of small amounts of acetic acid may help dissolve this product. Soluble in warm methanol. |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White solid |
| SMILES | [C@@H](N)([C@H](O)C=CCCCCCCCCCCCCC)CO[P](=O)(O)O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C18H38NO5P/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-18(20)17(19)16-24-25(21,22)23/h14-15,17-18,20H,2-13,16,19H2,1H3,(H2,21,22,23)/b15-14+/t17-,18+/m0/s1 |
| InChIKey | DUYSYHSSBDVJSM-KRWOKUGFSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution. Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes Hazard Phrases: H315 - Causes skin irritation. H319 - Causes serious eye irritation. H335 - May cause respiratory irritation. Precautionary Phrases: P261 Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280 Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing P321 Specific treatment (see on this label). P405 Store locked up. P501 Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local/regional/national/international regulations |
| Cite This Product | Sphingosine-1-phosphate, D-erythro (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-386) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | [(E,2S,3R)-2-Amino-3-hydroxyoctadec-4-enyl] dihydrogen phosphate |
| Research Areas | Cell Signaling |
| PubChem ID | 5283560 |
| Scientific Background | Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a bioactive sphingolipid metabolite that signals through a family of G-protein-coupled receptors (S1PR1–S1PR5) to regulate cell survival, migration, and immune responses. In the nervous system, S1P plays a critical role in neurogenesis, synaptic transmission, and neuroinflammation. Dysregulation of S1P signaling has been implicated in multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and stroke. Therapeutic agents targeting S1P receptors, such as fingolimod, have demonstrated efficacy in modulating neuroimmune interactions. S1P is also involved in maintaining blood-brain barrier integrity and neuronal-glial communication, making it a key molecule in neurodegenerative disease research. |
| References |
1. Van Veldhoven P.P., et al. (1989). J. Lipid Res. 30(4): 611-6. 2. Desai N.N., et al. (1992). J. Biol. Chem. 267(32): 23122-8. 3. Sadahira Y., et al. (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89(20): 9686-90. 4. Olivera A. and Spiegel, S. (1993). Nature. 365(6446): 557-60. 5. Mattie M., et al. (1994). J. Biol. Chem. 269(5): 3181-8. 6. Wu J., et al. (1995). J. Biol. Chem. 270(19): 11484-8. 7. Choi O.H., et al. (1996). Nature. 380(6575): 634-6. 8. Cuvillier O., et al. (1996). Nature. 381(6585): 800-3. 9. Spiegel S., et al. (2000). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1484(2-3): 107-16. 10. Spiegel S. and Milstien, S. (2000). FEBS Lett. 476(1-2): 55-57. 11. Shida, D., et al. (2004). FEBS Lett. 577(3): 333-8. 12. Watterson, K.R., et al. (2005). Cell. Signal. 17(3): 289-98. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.