Troubleshooting | Western Blot
Follow our western blot troubleshooting guide to quickly identify and get solutions for common protocol issues.
First identify the problem with your western blot from the options below:
| Weak or No Signal | High Background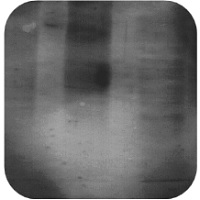 |
Non-Specific Bands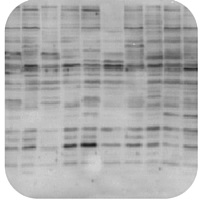 |
Smile effect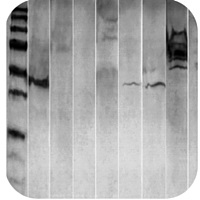 |
Band is smaller than expected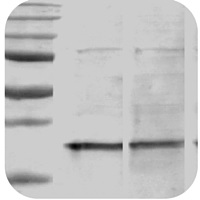 |
Band is larger than expected |
| Ran too far, or not enough | Patchy background | Black Dots |
Weak or No Signal
Antibody Concentrations:
- Too low- use a higher concentration of antibody, or try incubating longer.
- Too high- this is indicated with ghost/hollow bands. Decrease the concentrations.
- Always optimize both primary and secondary antibodies with every experiment.
Primary antibody does not recognize the antigen:
- Check the datasheet/reference materials or perform a BLAST alignment to see whether the antibody should react with the target protein. Use a positive control with all experiments.
Primary and secondary antibodies are incompatible:
- The secondary antibody should be raised against the host species of the primary antibody. For example, if the primary was raised in mouse (ie. Mouse Anti-HSP70) use an anti-mouse secondary (ie. Goat Anti-Mouse).
Detection agent inhibited:
- HRP should not be used in conjunction with sodium azide (1% or greater) or hemoglobin.
- Biotinylated antibodies should not be used with milk or casein.
Storage issues:
- Freeze/thaw cycles are detrimental and can cause degradation. It is best to create aliquots of smaller amounts as soon as the product arrives at your location.
- Antibody was not stored as recommended. Unfortunately this might require a new vial to be used instead.
Protein is undetectable:
- Load sufficient protein onto the gel (~20-30 µg).
- It also may be necessary to induce cells before harvest.
- Ensure protein is not degraded.
The protein of interest in not abundantly present in the tissue:
- Use an enrichment step to maximize the signal.
- Concentrate your protein lysates by isolating the cellular compartment containing your protein of interest (ie. mitochondria or cellular membrane).
- Try using ECL western blot rather than the colorimetric western blot.
Epitope is masked by the blocker:
- Use a different blocker agent.
- Optimize the concentration of the blocker.
Protein did not transfer:
- Optimize transfer protocol for specific protein either by increasing the transfer time or increasing the voltage.
Secondary antibody tag not visible:
- Ensure that the secondary antibody tag has not been exposed to excessive light.
- Use a longer incubation time.
- Decrease the number of washing steps and/or the duration of washes.
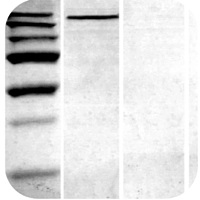
High Background Staining
High Concentration of Antibody:
- Reduce the concentration of primary and/or secondary antibodies.
- Always optimize both primary and secondary antibodies with every experiment.
Insufficient Blocking:
- Increase blocker incubation time and/or temperature.
- Increase concentration of blocker.
- Try a different blocker such as BSA, casein, or milk.
- We recommend 5% w/v non-fat dry milk in Tris buffered saline with 0.05% TritonX100, TBST overnight at 4oC or 1 hour at RT.
Insufficient Washing:
- Increase the volume and number of washes.
- Add or increase concentration of detergent in wash buffer (ie. 0.05% Tween-20).
Contaminated Solutions:
- Be aware of potential contaminants. Always use clean equipment, fresh solutions and wear gloves.
Cross-reaction between the blocking agent and the primary and secondary antibodies:
- Add a mild detergent (Tween 20) to the incubation and washing buffer. For phospho-specific antibodies, always use BSA rather than milk. Milk contains casein which is a phospho-protein.
Overexposure of Membrane:
- Reduce film exposure times to less than 30 seconds.
Membrane dried out:
- Ensure membranes are thoroughly covered in buffer at all times.
- We recommend using a nitrocellulose membrane with a pore size of 0.2 µm. PVDF membranes tend to have a higher background.
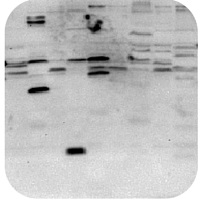
Non-Specific Bands
Lysates preparation is old:
- Use freshly prepared sample lysates as they will have less degradation and therefore less non-specific bands.
Antibody concentration is too high:
- Decrease the concentration of the primary antibody, and run a secondary antibody control.
- Refer back to the product datasheet/ product page for recommended starting dilutions.
Protein is overloaded:
- Load less protein into each well.
Unpurified antibodies can produce non-specific bands:
- Try switching to an affinity purified product instead.
Nonspecific sites were not blocked:
- Increase the concentration of the blocker from 5% to 7%.
- Increase the blocker incubation time.
- Increase the blocker incubation temperature.
- Add blocker to antibody dilution buffers.
Smile effect
Migration of protein was too fast due to low resistance:
- Decrease the voltage while running your gel.
- Run the gel immersed in ice-cold buffer, on ice, or in a cold space.
Band size is smaller than expected
Protein sample is degraded:
- Ensure that there is sufficient protease inhibitors in the sample buffer.
- Use a fresh sample and keep on ice.
Band size is larger than expected
Protein may form multimers:
- Try boiling in Laemmli buffer for extra time to break down the quaternary structure.
Protein sample has multiple modified forms such (acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation etc.):
- Use a modifying agent to remove post-translational modifications, or review the literature for expected band size of modified forms.
Band ran too far, or not far enough
Proteins were not adequately separated:
- Change the percentage of the gel, either by increasing it for smaller proteins, or by decreasing it for larger proteins.
- Change the run time of the gel, either by increasing it for larger proteins, or decreasing it for smaller proteins.
Patchy Background or Black Dots
Uneven transfer of proteins to membrane:
- Roll out any air bubbles between the gel and the membrane to ensure even transfer of proteins.
Secondary antibody aggregates:
- Spin down the secondary antibody or remove aggregates through filtration.
Antibodies are binding to the blocking agent:
- Filter the blocker to remove aggregates and contamination.
Uneven coverage of membrane during incubation:
- Use a shaker to ensure that the membrane is evenly covered with solution.