Properties
| Storage Buffer | 20mM Phosphate Buffer, 150mM NaCl, 10% glycerol |
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Purification | Affinity Purified |
| Cite This Product | Human Recombinant HSP60 Protein (StressMarq Biosciences | Victoria, BC CANADA | Catalog# SPR-104) |
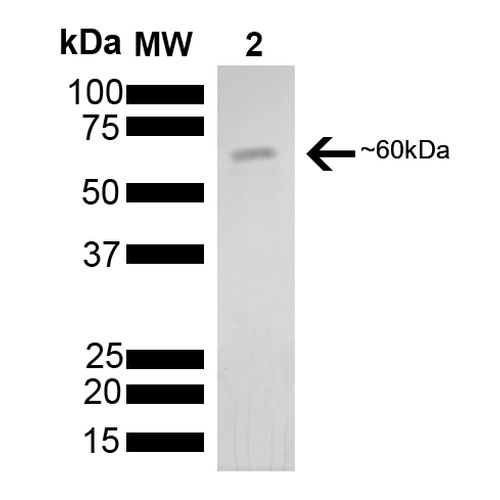
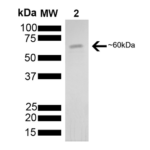
| Certificate of Analysis | This product has been certified >90% pure using SDS-PAGE analysis. The protein has ATPase activity at the time of manufacture of 3.6µM phosphate liberated/hr/µg protein in a 200µl reaction at 37°C (pH7.5) in the presence of 20ul of 1mM ATP using a Malachite Green assay. |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | HSPD1, HSP60, 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial, Chaperonin 60, CPN60, HuCHA60, Heat shock protein family D member 1, GroEL homolog, mitochondrial, GROEL, HLD4, HSP 60, HSP65, SPG 13 |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Heat Shock |
| Cellular Localization | Mitochondrion Matrix |
| Accession Number | BC003030 |
| Gene ID | 3329 |
| Swiss Prot | P10809 |
| Scientific Background |
HSP60 is a mitochondrial chaperonin essential for the proper folding and assembly of proteins within the mitochondrial matrix. It plays a critical role in maintaining mitochondrial proteostasis, especially under conditions of cellular stress. HSP60 is highly conserved across species and is constitutively expressed, with levels increasing in response to heat shock and other stressors. In neuroscience, HSP60 has gained attention for its involvement in neurodegenerative diseases characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction and protein misfolding, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis. Disruptions in HSP60 expression or function can impair mitochondrial protein folding, leading to oxidative stress, energy deficits, and neuronal apoptosis. Beyond its mitochondrial role, HSP60 has been implicated in immune signaling and inflammation, processes that are increasingly recognized as contributors to neurodegeneration. Its presence in extracellular compartments and association with autoimmune responses further suggest a role in neuroinflammatory conditions. HSP60’s ability to form oligomeric complexes, its ATPase activity, and its interaction with co-chaperonin HSP10 are essential for its chaperone function. These properties make it a valuable target for studying mitochondrial resilience and neuroprotection in degenerative brain disorders. |
| References |
1. Hartl F.U. (1996) Nature. 381: 571-579. 2. Bukau B. and Horwich A.L. (1998) Cell. 92: 351-366. 3.Hartl F.U. and Hayer-Hartl M. (2002) Science. 295: 1852-1858. 4. Jindal S., et al. (1989) Molecular and Cellular Biol. 9: 2279-2283. 5. La Verda D., et al (1999) Infect Dis. Obstet. Gynecol. 7: 64-71. 6. Itoh H., et al. (2002) Eur. J. Biochem. 269: 5931-5938. 7.Gupta S. and Knowlton A.A. J. Cell Mol Med. 9: 51-58. 8. Deocaris C.C. et al. (2006) Cell Stress Chaperones. 11: 116-128. 9. Lai H.C., et al. (2007) Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 292: E292-E297. |

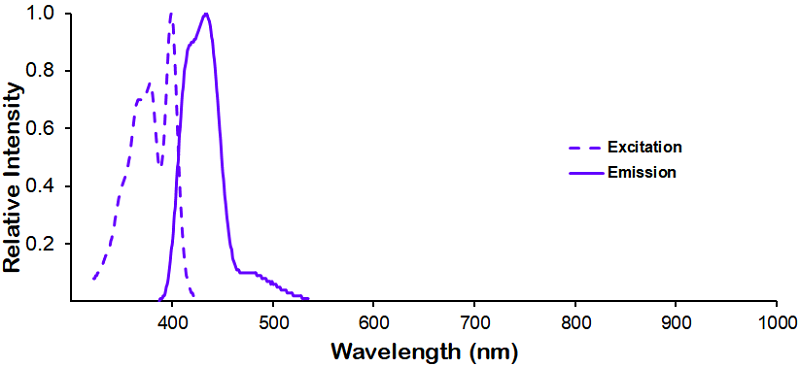
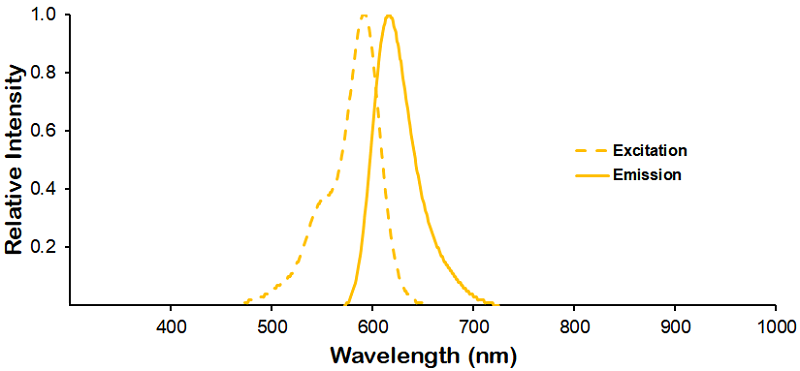
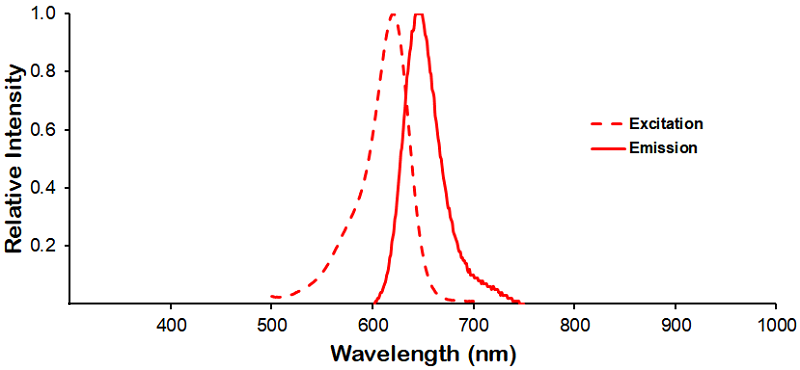
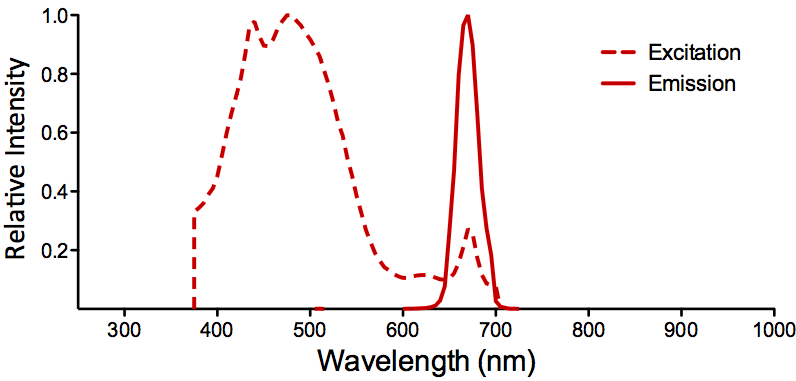
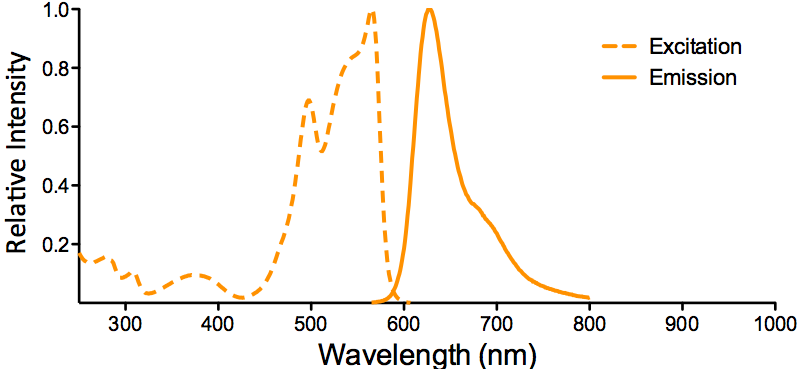
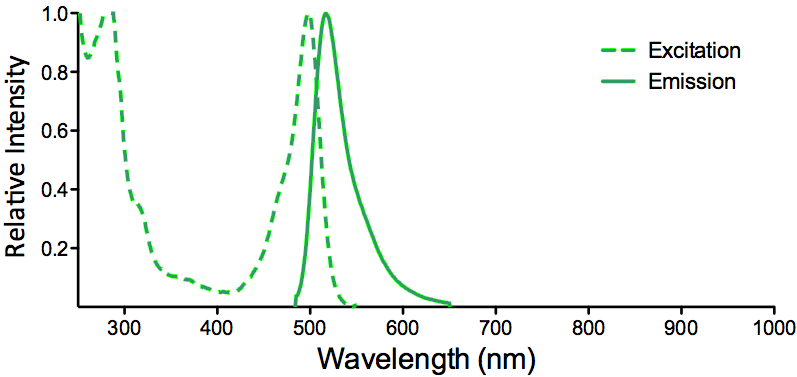
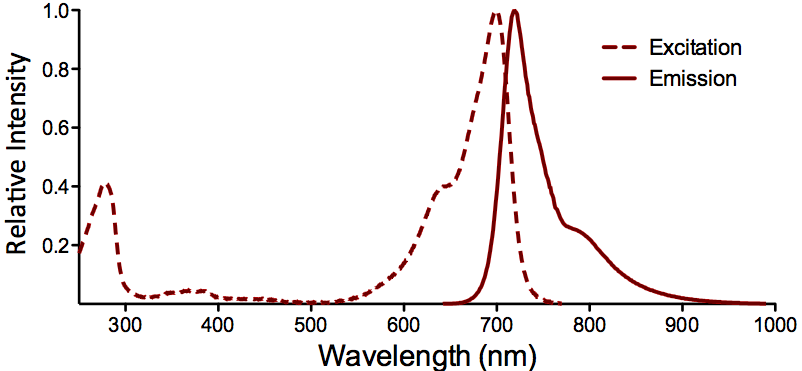
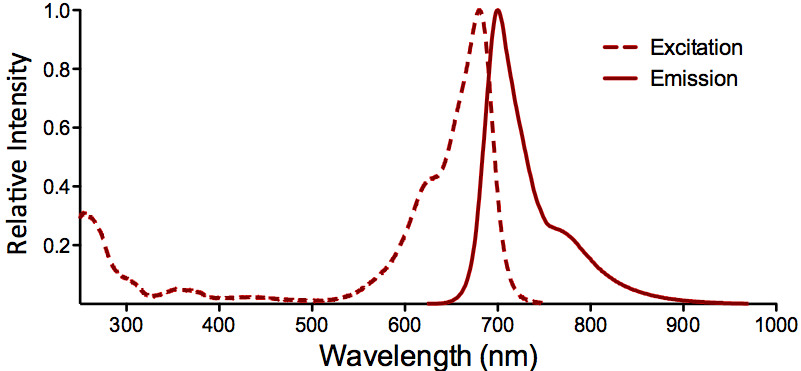
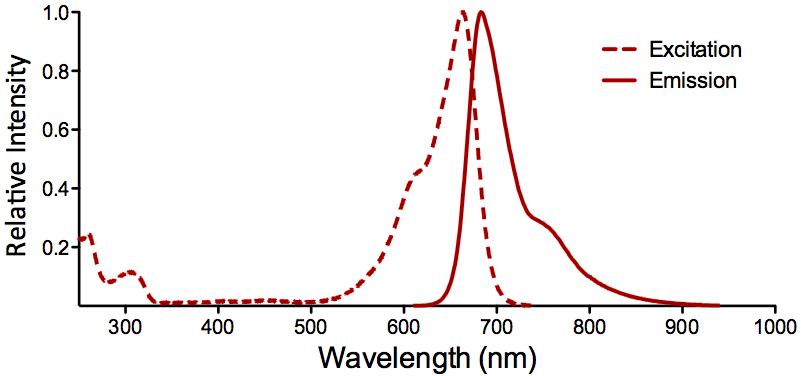
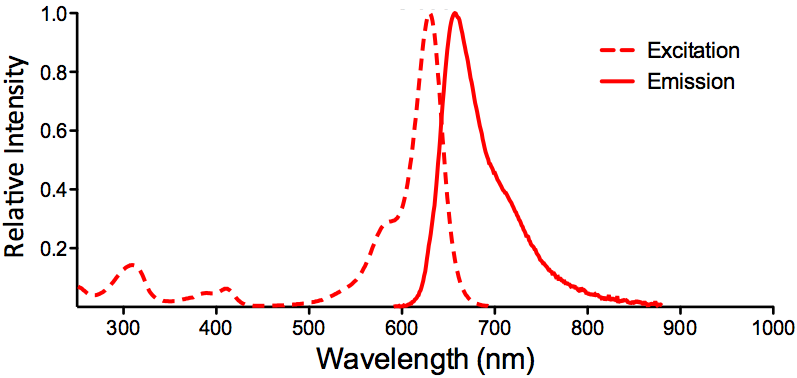
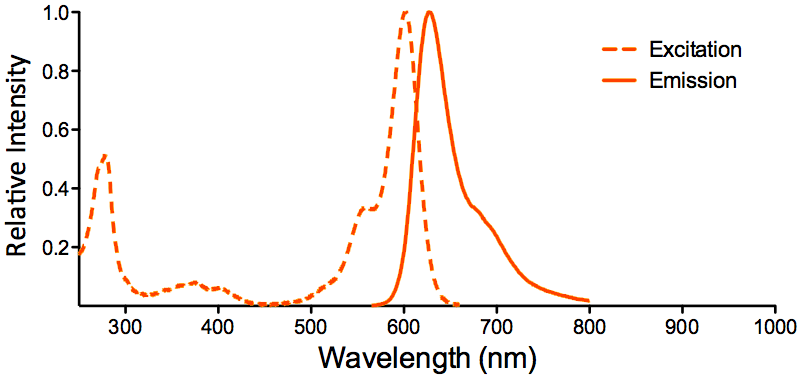
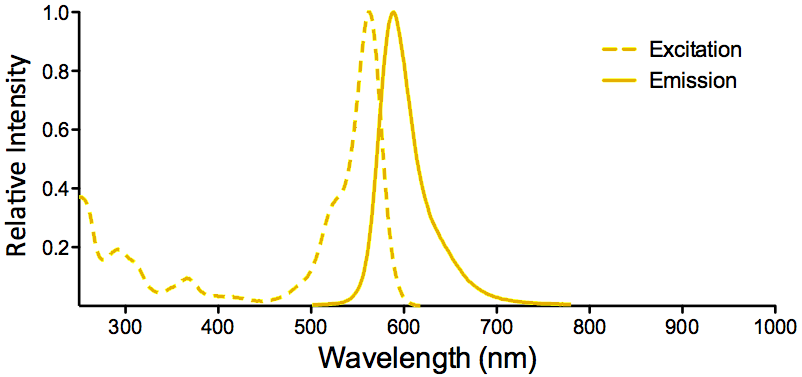
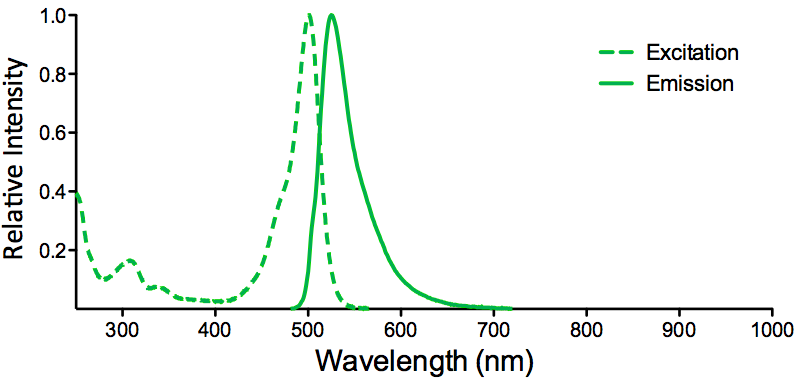
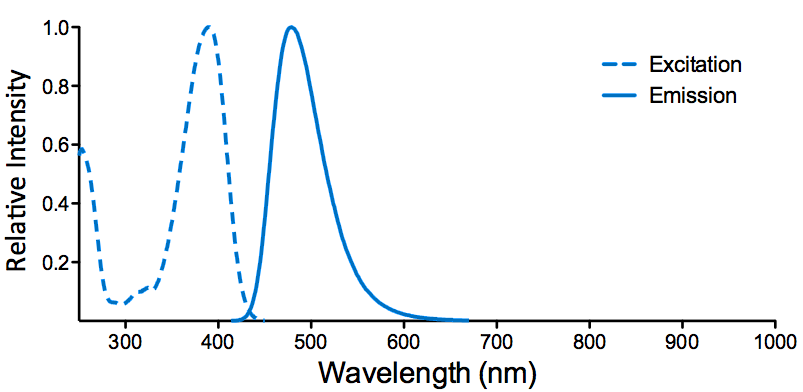
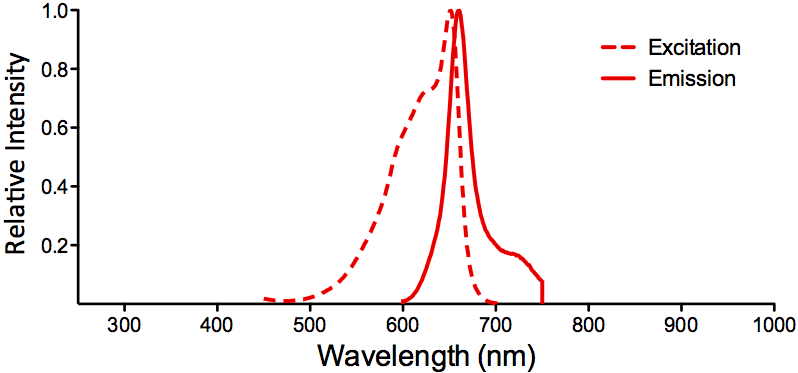
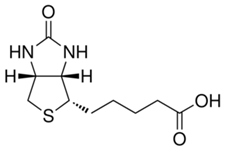

StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.