| Product Name | Anisomycin |
| Description |
p38 MAP kinase activator |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Toxic. May be harmful or fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through skin. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection S45 - In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label where possible) Risk Phrases: R23/24/25 - Toxic by inhilation, in contact with skin and if swallowed Hazard Phrases: H301 Precautionary Phrases: P301 + P310 |
| Cite This Product | Anisomycin (StressMarq Biosciences, Canada, Cat # SIH-266) |
Biological Description
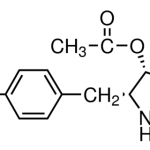
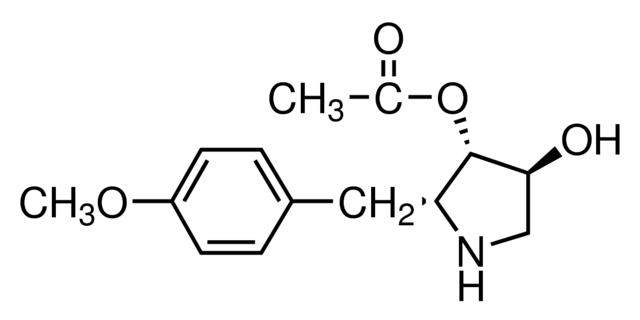
| Alternative Names | (2S,3R,4R)-4-Hydroxy-2-(4-methoxybenzyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl acetate |
| Scientific Background | Anisomycin is an antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis by targeting peptidyl transferase activity on the 80S ribosome. It disrupts both protein and DNA synthesis and is widely used in neuroscience research to activate stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs), MAP kinases, and other signal transduction pathways. These pathways are critical in studying cellular stress responses, synaptic plasticity, and memory formation. Anisomycin has been instrumental in elucidating mechanisms of long-term potentiation and memory consolidation in the brain. |
| References | 1. Grollman A.P. (1967) J Biol Chem. 242(13): 3226-3233. |

StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.