| Product Name | Aripiprazole |
| Description |
Dopamine D2 receptor antagonist. |
| Purity | 98% (TLC); NMR (Conforms) |
| CAS No. | 129722-12-9 |
| Molecular Formula | C23H27Cl2N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 448.4 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Antagonist |
| Solubility | May be dissolved in DMSO (30 mg/ml); or ethanol (5 mg/ml, warm) |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White powder |
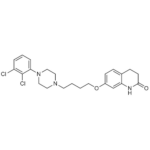
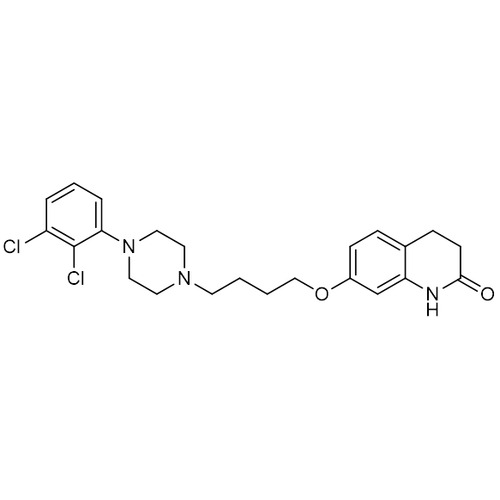
| SMILES | C1CC(=O)NC2=C1C=CC(=C2)OCCCCN3CCN(CC3)C4=C(C(=CC=C4)Cl)Cl |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C23H27Cl2N3O2/c24-19-4-3-5-21(23(19)25)28-13-11-27(12-14-28)10-1-2-15-30-18-8-6-17-7-9-22(29)26-20(17)16-18/h3-6,8,16H,1-2,7,9-15H2,(H,26,29) |
| InChIKey | CEUORZQYGODEFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Danger GHS Hazard Statements, H301 (62.7%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H302 (35.3%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H361 (15.7%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity] H413 (13.7%): May cause long lasting harmful effects to aquatic life [Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard] Precautionary Statement Codes,: P203, P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+P316, P301+P317, P318, P321, P330, P405, and P501 |
| Cite This Product | Aripiprazole (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-630) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 7-[4-[4-(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone; OPC-14597 |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience |
| PubChem ID | 60795 |
| Scientific Background | Aripiprazole is an atypical antipsychotic with a unique pharmacological profile, acting as a partial agonist at dopamine D2 receptors and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors, and as an antagonist at 5-HT2A receptors. It is clinically used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder and has shown efficacy in managing psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Aripiprazole also modulates reward pathways and has been shown to reduce drug-seeking behavior in animal models. Its dopaminergic and serotonergic modulation makes it relevant in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative research. |
| References |
1.,B Green Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004 20:207 2.,T Kikuchi et al. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995 274:329 3.,S Madhusoodanan et al. Clin. Interv. Aging. 2008 3:491 4.,MW Feltenstein et al. Biol. Psychiatry 2007 61:582 |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.