| Product Name | Cordycepin |
| Description |
Nucleoside Antagonist |
| Purity | >98% (HPLC); NMR (conforms) |
| CAS No. | 73-03-0 |
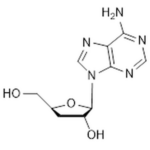
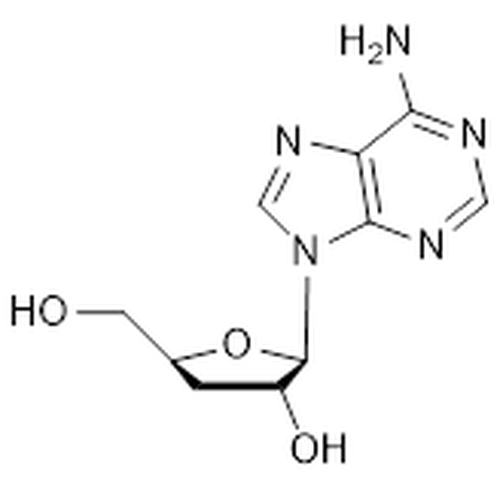
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 251.2 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Antagonist |
| Solubility | May be dissolved in DMSO (25 mg/ml) |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White powder |
| SMILES | NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]3O[C@H](CO)C[C@H]3O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C10H13N5O3/c11-8-7-9(13-3-12-8)15(4-14-7)10-6(17)1-5(2-16)18-10/h3-6,10,16-17H,1-2H2,(H2,11,12,13)/t5-,6+,10+/m0/s1 |
| InChIKey | OFEZSBMBBKLLBJ-BAJZRUMYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Not a hazardous substance or mixture. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. |
| Cite This Product | Cordycepin (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-576) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | (2R,3R,5S)-2-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-ol; 3-deoxyadenosine; NSC 63984 |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Cardiovascular System, Cell Signaling, Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling, Heart, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, NFkB Pathway, Nuclear Signaling Pathways |
| PubChem ID | 6303 |
| Scientific Background |
Cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) is a naturally occurring adenosine analog that lacks a hydroxyl group at the 3′ position of its ribose moiety. This structural modification allows Cordycepin to interfere with RNA synthesis, polyadenylation, and cellular signaling pathways, making it a versatile molecule in biomedical research. In neuroscience, Cordycepin has garnered attention for its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. Cordycepin has been shown to inhibit poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1), a key enzyme involved in DNA repair and cell death pathways. Overactivation of PARP1 is associated with neuronal damage in conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. By modulating PARP1 activity, Cordycepin may help preserve neuronal integrity and reduce oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. Additionally, Cordycepin exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and signaling pathways, contributing to a reduction in neuroinflammation—a hallmark of many neurodegenerative disorders. It has also demonstrated the ability to inhibit beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis in hippocampal neurons, suggesting a direct protective effect against Alzheimer’s-related toxicity. Beyond its neurological applications, Cordycepin has shown anti-cancer and anti-obesity activities, highlighting its broad therapeutic potential. However, its emerging role in modulating neuronal survival, inflammation, and protein aggregation positions it as a promising candidate for further exploration in neurodegenerative disease research. |
| References | 1. Siev M., Weignberg R., Penman S., (1969) J Cell Biol. 41(2): 510-520. 2. Zhang Y., et al. (2018) Onco Targets Ther. 11: 4479. 3. Hardeeps S., Sardul S., Sharma A.K. (2014) 3 Biotech. 4(1): 1-12. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.