| Product Name | Doxorubicin Hydrochloride |
| Description |
Apoptosis Inducer |
| Purity | >98% (TLC); NMR (Conforms) |
| CAS No. | 25316-40-9 |
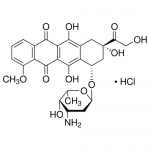
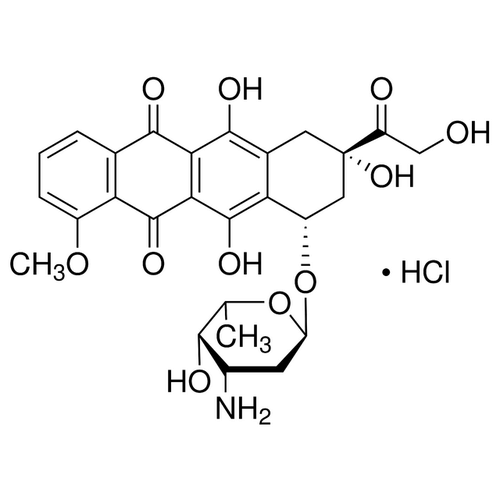
| Molecular Formula | C27H29NO11•HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 580 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inducer |
| Solubility | May be dissolved in water (25 mg/ml); or DMSO (30 mg/ml). |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Red- Orange Powder |
| SMILES | [C@H]2(OC1OC(C(O)C(N)C1)C)C[C@@](O)(CC3=C2C(=C4C(=C3O)C(=O)C5=C(C4=O)C(=CC=C5)OC)O)C(=O)CO.[H+].[Cl-] |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C27H29NO11.ClH/c1-10-22(31)13(28)6-17(38-10)39-15-8-27(36,16(30)9-29)7-12-19(15)26(35)21-20(24(12)33)23(32)11-4-3-5-14(37-2)18(11)25(21)34;/h3-5,10,13,15,17,22,29,31,33,35-36H,6-9,28H2,1-2H3 |
| InChIKey | MWWSFMDVAYGXBV-RUELKSSGSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Not WHMIS controlled. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. Hazard statements: H302- Harmful if swallowed. H350- May cause cancer. Precautionary statements: P201- Obtain special instructions before use. P308 + P313- IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/ attention. |
| Cite This Product | Doxorubicin Hydrochloride (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-390) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Adriamycin |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Apoptosis, Cancer, Cell Signaling, DNA Synthesis, DNA/RNA, Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Topoisomerases |
| PubChem ID | 443939 |
| Scientific Background | Doxorubicin Hydrochloride is a DNA-intercalating chemotherapeutic agent known for its broad-spectrum anticancer activity. In neuroscience, Doxorubicin is used to model neurotoxicity and investigate mechanisms of neuronal damage, particularly in studies of chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment ("chemo brain"). It induces apoptosis by inhibiting topoisomerase II and disrupting DNA replication and transcription. Doxorubicin also triggers oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction—key features of neurodegenerative diseases. Although its clinical use is limited by systemic toxicity, including hematologic and cardiac effects, its ability to induce autophagy and cell death pathways makes it a valuable tool for studying neuronal stress responses and neurodegeneration in vitro and in vivo. |
| References |
1. Kusayanagi, T. et al. (2012). Bioorg Med Chem. 20(21): 6248-55. 2. Chen, N. T. et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9). 3. Patel, S. et al. (1997). Mol Pharmacol. 52(4): 658-66. 4. Cutts, S. et al. (1996). J Biol Chem. 271(10): 5422-9. 5. Danesi, R. et al. (2004). Transplant Proc. 36(3): 703-4. 6. Dirks-Naylor, A. (2013). Life Sci. 93(24): 913-6. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.