| Product Name | Rottlerin |
| Description |
Autophagy inducer |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 82-08-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C30H28O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 516.55 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inducer |
| Solubility | Soluble to 2 mM in ethanol and to 20 mM in DMSO. |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Orange to brown solid. |
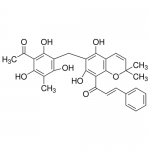
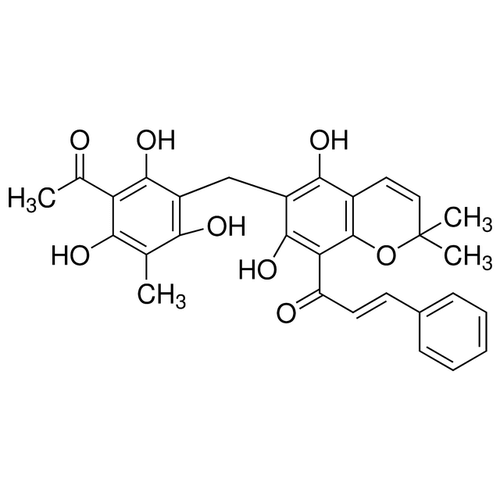
| SMILES | C1=CC=CC=C1/C=C/C(C2=C(C(=C(C3=C2OC(C)(C)C=C3)O)CC4=C(C(=C(C(=C4O)C(C)=O)O)C)O)O)=O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C30H28O8/c1-15-24(33)19(27(36)22(16(2)31)25(15)34)14-20-26(35)18-12-13-30(3,4)38-29(18)23(28(20)37)21(32)11-10-17-8-6-5-7-9-17/h5-13,33-37H,14H2,1-4H3/b11-10+ |
| InChIKey | DEZFNHCVIZBHBI-ZHACJKMWSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Not WHMIS controlled. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. |
| Cite This Product | Rottlerin (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-394) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 3'-[(8-Cinnamoyl-5,7-dihydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-2H-1-benzopyran-6-yl)methyl]-2',4',6'-trihydroxy-5'-methylacetophenone |
| Research Areas | Autophagy, Cancer |
| PubChem ID | 5281847 |
| Scientific Background | Rottlerin is a natural polyphenol known for its inhibitory effects on protein kinase C (PKC) and Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent kinase III. In neuroscience, Rottlerin is recognized for its neuroprotective properties, particularly in models of Parkinson’s disease. It acts as a mitochondrial uncoupler, depolarizing membrane potential and influencing energy metabolism. Rottlerin also induces autophagy by inhibiting mTORC1 signaling, a pathway critical for neuronal survival and protein clearance. Its ability to modulate potassium channels and reduce oxidative stress further supports its application in neurodegenerative disease research. Rottlerin is frequently used to explore the interplay between mitochondrial function, autophagy, and neuronal health. |
| References |
1. Gschwendt M. et al. (1994) Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 199(1): 93-8. 2. Wu S., et al. (2007) J Cell Physiol. 210(3): 655-66. 3. Soltoff S. (2001) J Biol Chem. 276(41): 37986-92. 4. Balgi A., et al. (2009) PLoS One. 4(9): e7124. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.