| Product Name | DAPT |
| Description |
γ-secretase inhibitor |
| Purity | >99% |
| CAS No. | 208255-80-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C23H26F2N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 432.46 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
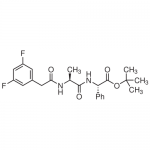
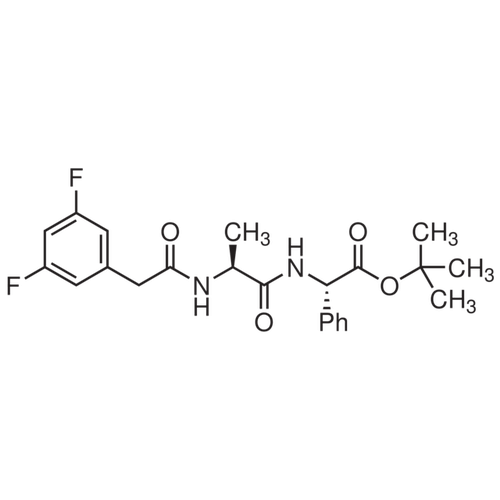
| SMILES | [C@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CC1=CC(=CC(=C1)F)F)C)(C2=CC=CC=C2)C(OC(C)(C)C)=O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C23H26F2N2O4/c1-14(26-19(28)12-15-10-17(24)13-18(25)11-15)21(29)27-20(16-8-6-5-7-9-16)22(30)31-23(2,3)4/h5-11,13-14,20H,12H2,1-4H3,(H,26,28)(H,27,29)/t14-,20-/m0/s1 |
| InChIKey | DWJXYEABWRJFSP-XOBRGWDASA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution: Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection |
| Cite This Product | DAPT (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-378) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | N-[(3,5-Difluorophenyl)acetyl]-L-alanyl-2-phenyl]glycine-1,1-dimethylethyl ester |
| Research Areas | Cell Signaling, Neuroscience |
| PubChem ID | 5311272 |
| Scientific Background | DAPT is a potent γ-secretase inhibitor widely used in neuroscience and neurodegenerative disease research. By selectively reducing the production of amyloid-β peptides Aβ40 and Aβ42—key contributors to Alzheimer’s disease pathology—DAPT serves as a critical tool for studying amyloidogenic processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP). It effectively lowers Aβ levels in human primary neuronal cultures and in vivo models, including brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma, without altering non-amyloidogenic APPα and APPβ fragments. DAPT also inhibits Notch signaling, a pathway implicated in neural development and cell fate decisions. Its ability to promote neuronal differentiation makes it valuable for exploring neurogenesis and neural stem cell biology. DAPT is frequently cited in studies investigating the molecular mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease, neuroinflammation, and synaptic dysfunction. |
| References |
1. Dovey H.F., et al. (2001) J. Neurochem. 76(1): 173-81. 2. De Smedt M., et al. (2005) Blood. 106(10): 3498-506. 3. Kanungo J., et al. (2008) J. Neurochem. 106(5): 2236-48. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.