| Product Name | Erlotinib Hydrochloride |
| Description |
EGFR Kinase inhibitor |
| Purity | >99% |
| CAS No. | 183319-69-9 |
| Molecular Formula | C22H24ClN3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 429.9 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO at 18 mg/ml with warming; very poorly soluble in ethanol; very poorly soluble in water; maximum solubility in plain water is estimated to be about 5-20 µM; buffers, serum, or other additives may increase or decrease the aqueous solubility |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
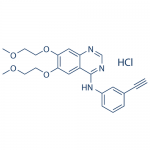
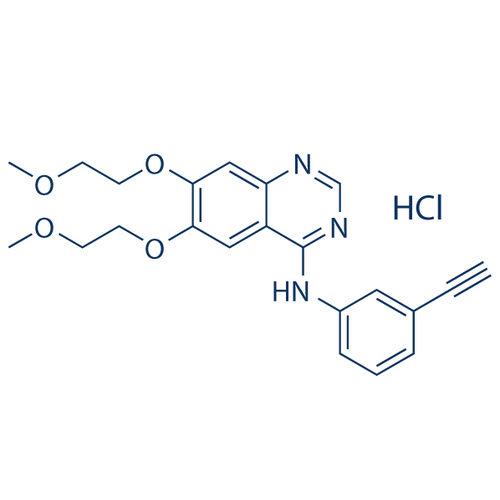
| SMILES | [H+].C1=C(OCCOC)C(=CC2=NC=NC(=C12)NC3=CC(=CC=C3)C#C)OCCOC.[Cl-] |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C22H23N3O4.ClH/c1-4-16-6-5-7-17(12-16)25-22-18-13-20(28-10-8-26-2)21(29-11-9-27-3)14-19(18)23-15-24-22;/h1,5-7,12-15H,8-11H2,2-3H3,(H,23,24,25);1H |
| InChIKey | GTTBEUCJPZQMDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Not a hazardous substance or mixture. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. |
| Cite This Product | Erlotinib Hydrochloride (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-444) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine hydrochloride |
| Research Areas | Apoptosis, Cancer, Cancer Growth Inhibitors, Cell Signaling, Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors |
| PubChem ID | 176871 |
| Scientific Background | Erlotinib Hydrochloride is a selective inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR/HER-1) tyrosine kinase. In neuroscience, EGFR signaling has been implicated in neuroinflammation, gliogenesis, and blood-brain barrier integrity. Erlotinib is used to explore the role of EGFR in neural cell proliferation, survival, and response to injury. Its ability to modulate receptor tyrosine kinase activity makes it a useful compound in studying neurovascular remodeling and neurodegenerative disease mechanisms involving aberrant EGFR signaling. |
| References | 1. Ali S., et al. (2008) Mol. Cancer Ther. 7(6): 1708–1719. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.