| Product Name | Vorinostat (SAHA) |
| Description |
HDAC inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% (TLC); NMR (Conforms) |
| CAS No. | 149647-78-9 |
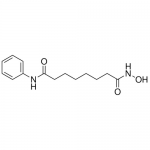
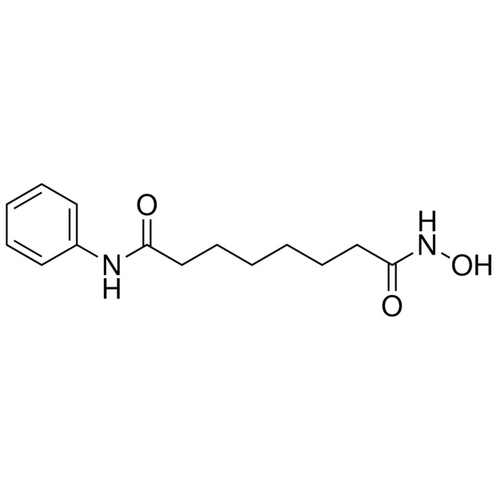
| Molecular Formula | C14H20N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 264.3 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in 50 mg/ml DMSO, or 2 mg/ml Ethanol |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White Solid |
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)NC(=O)CCCCCCC(=O)NO |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C14H20N2O3/c17-13(15-12-8-4-3-5-9-12)10-6-1-2-7-11-14(18)16-19/h3-5,8-9,19H,1-2,6-7,10-11H2,(H,15,17)(H,16,18) |
| InChIKey | WAEXFXRVDQXREF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Harmful- May be harmful if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection S24/25- Avoid contact with skin and eyes Hazard Statements: H341-H360 (Suspected of causing genetic defects) Precautionary Statements: P201-P281-P308 + P313 |
| Cite This Product | SAHA (Vorinostat) (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-359) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | Suberoylanilide-hydroxamic acid; Vorinostat; N-Hydroxy-N'-phenyloctanediamide |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cell Signaling |
| PubChem ID | 5311 |
| Scientific Background |
SAHA (Vorinostat) is a potent, cell-permeable HDAC inhibitor with significant implications in neurodegenerative disease research and neuro-oncology. By altering chromatin structure and gene expression, SAHA promotes neuronal differentiation, reduces neuroinflammation, and enhances synaptic function. Its ability to synergize with kinase inhibitors to target CNS tumors also positions it as a promising agent in glioblastoma therapy. Widely cited in oncology for its pro-apoptotic effects, SAHA is increasingly recognized in neuroscience for its role in epigenetic modulation and neuroprotection, making it a valuable compound in translational research. |
| References |
1. Vrana J.A., et al., (1999) Oncogene. 18: 7016. 2. Butler L.M., et al., (2002) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99: 11700. 3. Tang Y., et al., (2012) Cancer Biol. Ther. 2012 13(7): 567-574. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.