| Product Name | Simvastatin |
| Description |
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 79902-63-9 |
| Molecular Formula | C25H38O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 418.57 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble to 75 mM in ethanol and 50 mM in DMSO |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White solid |
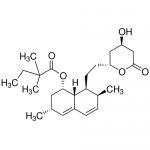
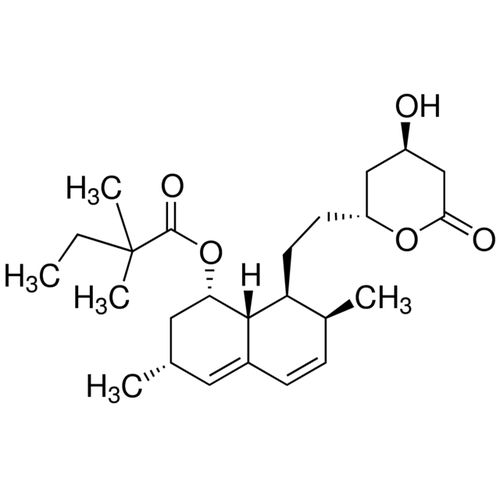
| SMILES | CCC(C)(C)C(=O)O[C@H]1C[C@H](C=C2[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](C=C2)C)CC[C@@H]3C[C@H](CC(=O)O3)O)C |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C25H38O5/c1-6-25(4,5)24(28)30-21-12-15(2)11-17-8-7-16(3)20(23(17)21)10-9-19-13-18(26)14-22(27)29-19/h7-8,11,15 |
| InChIKey | RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Harmful. May be harmful if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection Risk Phrases: R62- Possible risk of impaired fertility |
| Cite This Product | Simvastatin (StressMarq Biosciences, Canada, Cat # SIH-257) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-{2-[(2R,4R)-4-Hydroxy-6-oxotetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl}-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-1-naphthalenyl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate |
| Research Areas | Apoptosis, Cancer |
| PubChem ID | 54454 |
| Scientific Background | Simvastatin is a lipid-lowering agent belonging to the statin class, primarily used to reduce cholesterol levels and prevent cardiovascular disease. In neuroscience, simvastatin has garnered interest for its potential neuroprotective effects. It inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, thereby reducing the synthesis of cholesterol and isoprenoids—molecules involved in protein prenylation and cellular signaling. This mechanism may influence neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and amyloid-beta accumulation, all of which are implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's. Simvastatin's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier further supports its potential as a therapeutic agent in neurological disorders. |
| References | 1. Alberts A.W. (1998) Am J Cardio. 62(15): 10J-15J. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.