Properties
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH 7.4 |
| Storage Temperature | -80ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Dry Ice. Shipping note: Product will be shipped separately from other products purchased in the same order. |
| Purification | Ion-exchange Purified |
| Cite This Product | Human Recombinant Alpha Synuclein Protein (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SPR-331) |
| Certificate of Analysis | Acetylation cofirmed via ESI mass spectrometry. Low endotoxin <5 EU/mL @ 2mg/mL. |
| Other Relevant Information | For corresponding PFFs, see catalog# SPR-332 |
Biological Description
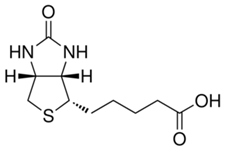
| Alternative Names | N-acetylated Alpha synuclein monomer, N-terminal acetylated Alpha-synuclein monomer, Alpha synuclein protein monomer, Alpha synuclein monomer, Alpha-synuclein protein, Non-A beta component of AD amyloid protein, Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor protein, NACP protein, SNCA protein, NACP protein, PARK1 protein, Alpha synuclein monomers, SYN protein, Parkinson's disease familial 1 Protein, N‐terminal Ac‐αsyn |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Parkinson's Disease, Synuclein, Tangles & Tau, Multiple System Atrophy |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm, Membrane, Nucleus |
| Accession Number | NP_000336.1 |
| Gene ID | 6622 |
| Swiss Prot | P37840 |
| Scientific Background | Alpha-Synuclein (SNCA) is expressed predominantly in the brain, where it is concentrated in presynaptic nerve terminals (1). Alpha-synuclein is highly expressed in the mitochondria of the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, striatum and thalamus (2). Functionally, it has been shown to significantly interact with tubulin (3), and may serve as a potential microtubule-associated protein. It has also been found to be essential for normal development of the cognitive functions; inactivation may lead to impaired spatial learning and working memory (4). SNCA fibrillar aggregates represent the major non A-beta component of Alzheimers disease amyloid plaque, and a major component of Lewy body inclusions, and Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive accumulation in selected neurons of protein inclusions containing alpha-synuclein and ubiquitin (5, 6). Alpha synuclein purified from both normal and pathological brain tissue is N-acetylated (7) and this post-translational modification affects affect alpha-synuclein stability and toxicity (8). |
| References |
1. “Genetics Home Reference: SNCA”. US National Library of Medicine. (2013). 2. Zhang L., et al. (2008) Brain Res. 1244: 40-52. 3. Alim M.A., et al. (2002) J Biol Chem. 277(3): 2112-2117. 4. Kokhan V.S., Afanasyeva M.A., Van'kin G. (2012) Behav. Brain. Res. 231(1): 226-230. 5. Spillantini M.G., et al. (1997) Nature. 388(6645): 839-840. 6. Mezey E., et al. (1998) Nat Med. 4(7): 755-757. 7. Anderson, J.P. et al. (2006) J Biol Chem. 2006;281:29739–29752. 8. Vinueza-Gavilanes, R. et al. (2020) Neurobiol Dis. 137, 2020, Article 104783 |
Product Images
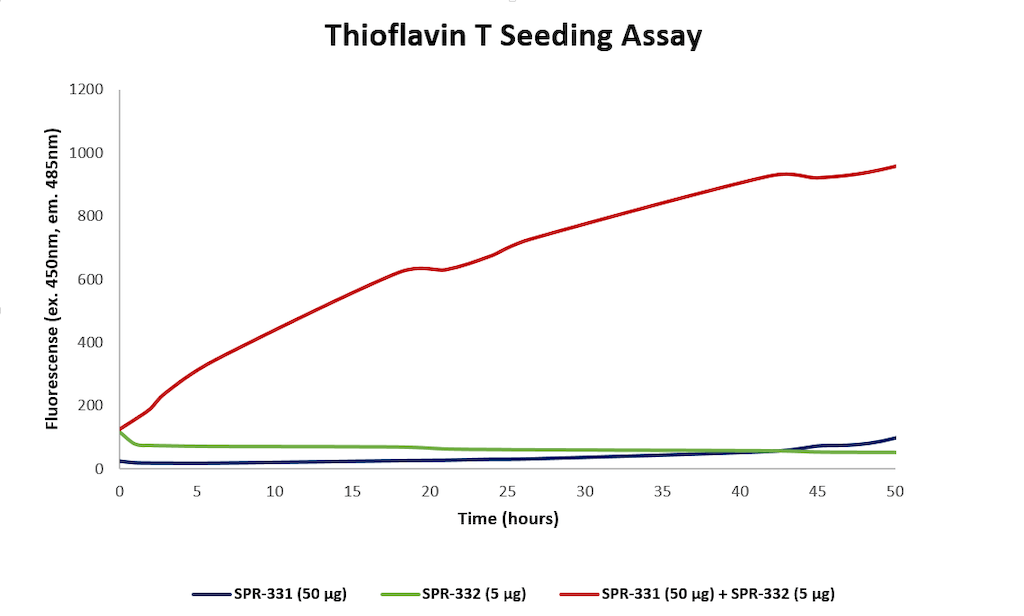
Thioflavin T assay for N-terminal acetylated alpha synuclein monomers (SPR-331) and pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) (SPR-332). Increased fluorescence, indicative of beta-sheet formation, was seen when 50 ug N-acetylated monomer and 5 ug N-acetylated fibril were combined, compared to monomer or fibril alone.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.