| Product Name | Etoposide |
| Description |
Topoisomerase II inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 33419-42-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C29H32O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 588.56 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inducer |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White solid |
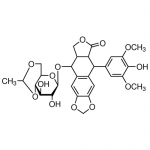
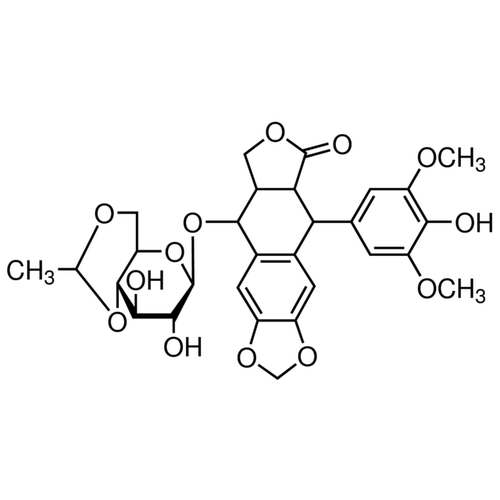
| SMILES | C[C@@H]1OC[C@@H]2[C@@H](O1)[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O2)O[C@H]3[C@H]4COC(=O)[C@@H]4[C@@H](C5=CC6=C(C=C35)OCO6)C7=CC(=C(C(=C7)OC)O)OC)O)O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C29H32O13/c1-11-36-9-20-27(40-11)24(31)25(32)29(41-20)42-26-14-7-17-16(38-10-39-17)6-13(14)21(22-15(26)8-37-28(22)33)12-4-18(34-2)23(30)1 |
| InChIKey | VJJPUSNTGOMMGY-MRAJQDPKSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Toxic. May be harmful or fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through skin. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection S53 - Avoid exposure - obtain special instruction before use Risk Phrases: R20/21/22 - Harmful by inhilation, in contact with skin and if swallowed R45 - May cause cancer R62 - Possible risk of impaired fertility R68 - Possible risk of irreversible effects Hazard Phrases: H302-H350 Precautionary Phrases: P201-P308 + P313 |
| Cite This Product | Etoposide (StressMarq Biosciences, Canada, Cat # SIH-244) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | (5S,5aR,8aR,9R)-9-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-8-oxo-5,5a,6,8,8a,9-hexahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4,6-O-[(1R)-ethylidene]-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| Research Areas | Apoptosis, Cancer |
| PubChem ID | 36462 |
| Scientific Background | Etoposide is a topoisomerase II inhibitor that induces DNA strand breaks by preventing the re-ligation of cleaved DNA. This mechanism leads to apoptosis, making etoposide a useful tool in studying DNA damage pathways in neurons. It is also used in models of neurotoxicity and to investigate the role of DNA repair in neurodegenerative conditions. |
| References | 1. Gordaliza M., et al. (2004) Toxicon. 44(4): 441-459. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.