| Product Name | STF-62247 |
| Description |
Autophagy inducer |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 315702-99-9 |
| Molecular Formula | C15H13N3S |
| Molecular Weight | 267.35 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inducer |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (26 mg/ml). |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Solid |
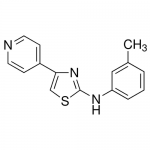
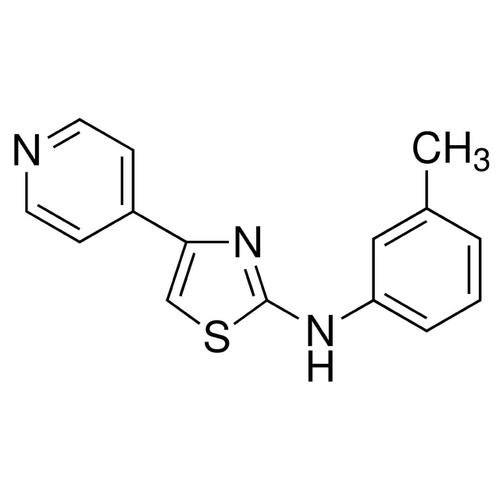
| SMILES | CC1=CC=CC(=C1)NC2=NC(=CS2)C3=CC=NC=C3 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C15H13N3S/c1-11-3-2-4-13(9-11)17-15-18-14(10-19-15)12-5-7-16-8-6-12/h2-10H,1H3,(H,17,18) |
| InChIKey | KATNUHQNJGNLPW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: D1B- Toxic Material Causing Immediate and Serious, Toxic Effects, Toxic by ingestion, D2B- Toxic Material Causing Other Toxic Effects, Moderate eye irritant Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. Hazard statements: H302- Harmful if swallowed. H319- Causes serious eye irritation. Precautionary statements: P305 + P351 + P338- IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. |
| Cite This Product | STF-62247 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-396) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | N-(3-Methylphenyl)-4-(4-pyridinyl)-2-thiazolamine |
| Research Areas | Autophagy, Cancer |
| PubChem ID | 704473 |
| Scientific Background | STF-62247 is a small molecule known for its selective cytotoxicity in cells deficient in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor protein. Although primarily studied in cancer biology, STF-62247 has emerging relevance in neuroscience due to its ability to modulate autophagy and lysosomal function. These pathways are critical in neurodegenerative diseases where impaired clearance of cellular debris contributes to pathology. STF-62247 may serve as a tool to investigate autophagy-dependent cell death and lysosomal stress in neuronal models, offering insights into mechanisms underlying diseases such as Parkinson’s and ALS. |
| References | 1. Turcotte S., et al. (2008) Autophagy, 4(7): b944-6. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.