Cell Culture Media Influences Alpha Synuclein Aggregation
Neurodegenerative diseases affect the lives of millions of people worldwide. Parkinson’s disease (PD) is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases. Neuronal cell culture has been imperative in uncovering the neuronal molecular mechanisms underlying disease pathology. Microscopically, PD shows the build-up of intraneuronal inclusions called Lewy bodies (LBs). Alpha synuclein is a major component of aggregates in LBs. PD also causes the loss of neurons that synthesize the neurotransmitter dopamine (dopaminergic neurons) found in the midbrain.
A study by Hlushchuk et al. was designed to analyze the effects of insulin signaling on abnormal alpha synuclein accumulation. However, their findings shed light on the importance of cell culture media in these models. They found that changing culture media, independent of insulin, causes differences in alpha synuclein aggregation in dopaminergic neurons1.
Insulin signaling does not affect alpha synuclein aggregation
Insulin enters the brain via the blood-brain barrier, and some think it is produced locally in the brain itself. Insulin enhances the growth and survival of neurons, and several links have been drawn between insulin resistance and neurodegenerative diseases.
For this reason, the researchers first investigated whether insulin signaling influenced alpha synuclein aggregates. Exogenous alpha synuclein preformed fibrils (PFFs) (catalog# SPR-324) from StressMarq were employed to measure the effect on alpha synuclein. PFFs recruit endogenous soluble alpha synuclein, causing aggregation and promoting insoluble LB-like inclusions.
In this model, the researchers used inhibitors targeting insulin signaling at points in the signaling cascade. The insulin receptors were blocked with an inhibitor called GSK1904529A. The study added VO-OHpic and AS1949490 to block downstream insulin signaling via PTEN and SHIP2, respectively. Interestingly, none of the inhibitors affected alpha synuclein aggregation. Alpha synuclein aggregation could however be reduced using glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF).
The effect of cell culture media
Next, the researchers wanted to check if the presence of insulin made a difference in alpha synuclein aggregation. The researchers had already used DPM media (containing a DMEM base) with an N2 supplement. N2 supplement contains recombinant insulin. So, the researchers needed media without insulin. They chose a neurobasal medium (NB) using a B27 supplement which can be purchased without insulin.
But surprisingly, the presence of insulin did not affect alpha synuclein. Instead, the type of media, regardless of insulin, affected alpha synuclein aggregation. The effect was so great that there was more than a two-fold reduction in PFF-induced alpha-synuclein aggregation.
The cell culture media could effectively lower the signal of assay readout. This has knock-on effects when pharmacological inhibitors are added to test further effects. Therefore, the choice of cell culture could reduce the sensitivity of the assay of dopaminergic neurons.
Finally, the researchers wanted to know if alpha synuclein aggregation in other neurons was affected by cell culture media. They found hippocampal or cortical neurons did not show the same effect.
StressMarq’s alpha synuclein pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) help define neuronal culture conditions
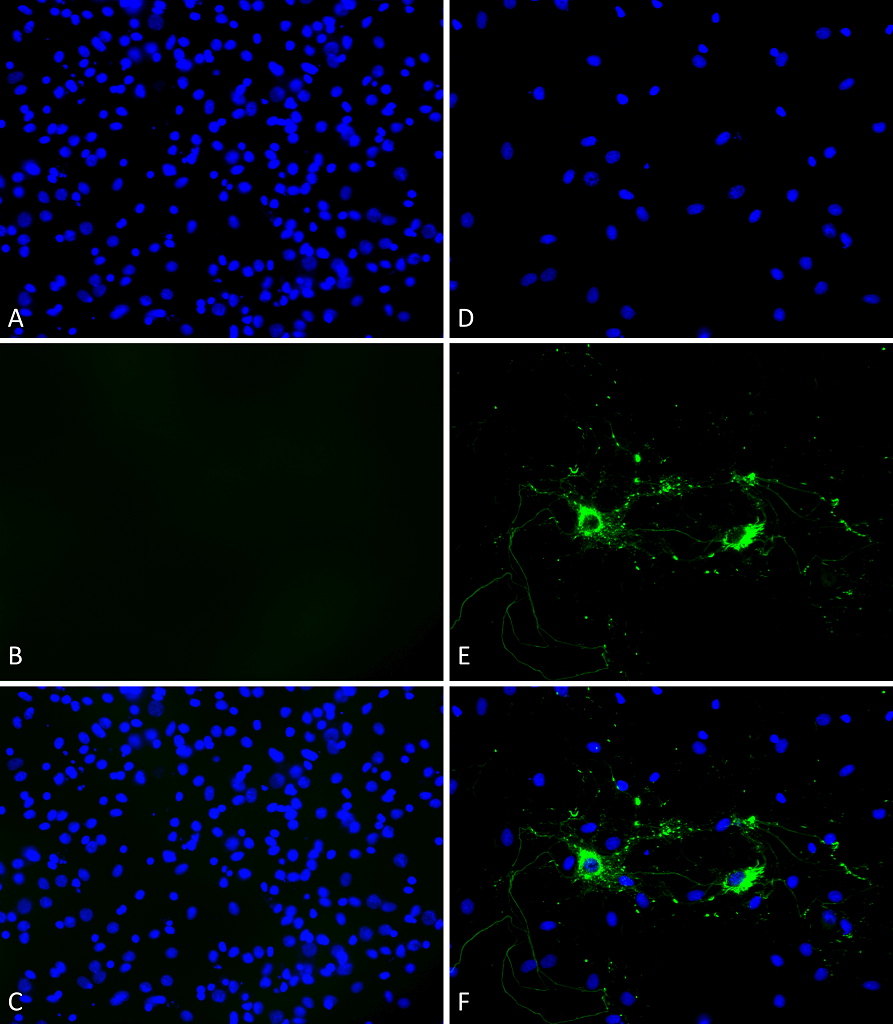
Figure 1. Mouse Recombinant Alpha Synuclein Preformed Fibrils (Type 1) (catalog# SPR-324)
Cellular models have greatly benefited neuroscience research. Cheaper than animal models, cell models can also quickly screen chemical compounds in a short time frame. The study shows the importance of carefully selecting cell culture media. This choice can ultimately have an unintended affect on subsequent phenomena like alpha synuclein aggregation induced by alpha synuclein PFFs.
These findings have implications for the neurodegenerative research landscape; it highlights the need for more cooperative efforts, potentially establishing a consortium. This can help define validated methods for assay development.
Related StressMarq products
Rabbit anti-human insulin polyclonal (catalog# SPC-1296) from StressMarq detects endogenous levels of total insulin. Tested in western blot (WB) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
StressMarq’s rabbit anti-human IGF-1 polyclonal antibody (catalog# SPC-699) detects human IGF-1. Tested in western blot (WB), immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunofluorescence applications. WB, ICC/IF, IHC
To detect GDNF, use StressMarq’s anti-GDNF antibody (catalog# SPC-710). Tested in western blot (WB) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
References
- Cell Culture Media, Unlike the Presence of Insulin, Affect α-Synuclein Aggregation in Dopaminergic Neurons. Hlushchuk, I. et al., Biomolecules. 2022; 12.


Leave a Reply