Gamma Synuclein Aggregation in Neurodegenerative Diseases
The synuclein family of proteins consists of alpha, beta, and gamma synuclein. Gamma synuclein is encoded by the SNCG gene, which is overexpressed in breast, ovary, colon, liver, and cervix cancers.1-4 While alpha synuclein can aggregate to form Lewy bodies and has been linked to neurodegenerative disorders such Parkinson’s Disease (PD), and beta synuclein is thought to inhibit alpha synuclein aggregation, the role of gamma synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases is not as well understood.
Gamma Synuclein in CSF
Gamma synuclein can be used as a biomarker for certain cancers,5 and its concentration in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is also increased in patients with Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD).6 CSF gamma synuclein concentration is also elevated in aged patients with AD, Lewy body disease (LBD) and vascular dementia (CVD).7
Gamma Synuclein Expression in Mice
When the gamma synuclein gene is inactivated in mice, their memory capacity improves.8 Conversely, transgenic mice expressing high levels of gamma synuclein develop neurodegenerative pathology.9 This neurodegeneration is associated with gamma synuclein aggregation into spheroids and linear fibrils.9
Gamma Synuclein Oxidation and Aggregation
Gamma synuclein is thought to exist in a natively unfolded conformation, and is prone to aggregate into small, soluble oligomers in solution.10 Oxidation at methionine 38 causes gamma synuclein to aggregate into larger lesions. These inclusions are found within neurons and neurites in the amygdala and substantia nigra in human brains containing Lewy bodies.11 Gamma synuclein accumulation is also seen in some ALS cases, where it can accumulate into inclusions causing motor neuron death.12
Interactions with Alpha Synuclein
Alpha and gamma synuclein have similar structures and tendencies to aggregate.9 Both alpha and gamma synuclein lesions can be seen in brains with PD and Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB).13 Colocalization of oxidized gamma synuclein and phosphorylated alpha synuclein can also be seen in AD patients’ brains.11 Additionally, alpha and gamma synuclein are thought to interact and promote each other’s aggregation.14 The oxidation of gamma synuclein at metathionine 39 and tyrosine 39, two of the most easily oxidized residues, allows gamma synuclein to seed the aggregation of alpha synuclein.15 Gamma synuclein is thought to be secreted from neurons via exosomes, transmitted to glial cells, and promote aggregation of intracellular proteins.15 This allows it to spread in a prion-like manner and seed the aggregation of alpha synuclein seen in synucleinopathies.15
Gamma Synuclein Preformed Fibrils (PFFs)
StressMarq’s active gamma synuclein preformed fibrils (PFFs) seed the aggregation of gamma synuclein monomers, leading to the protein aggregation seen in neurodegenerative diseases. Learn more
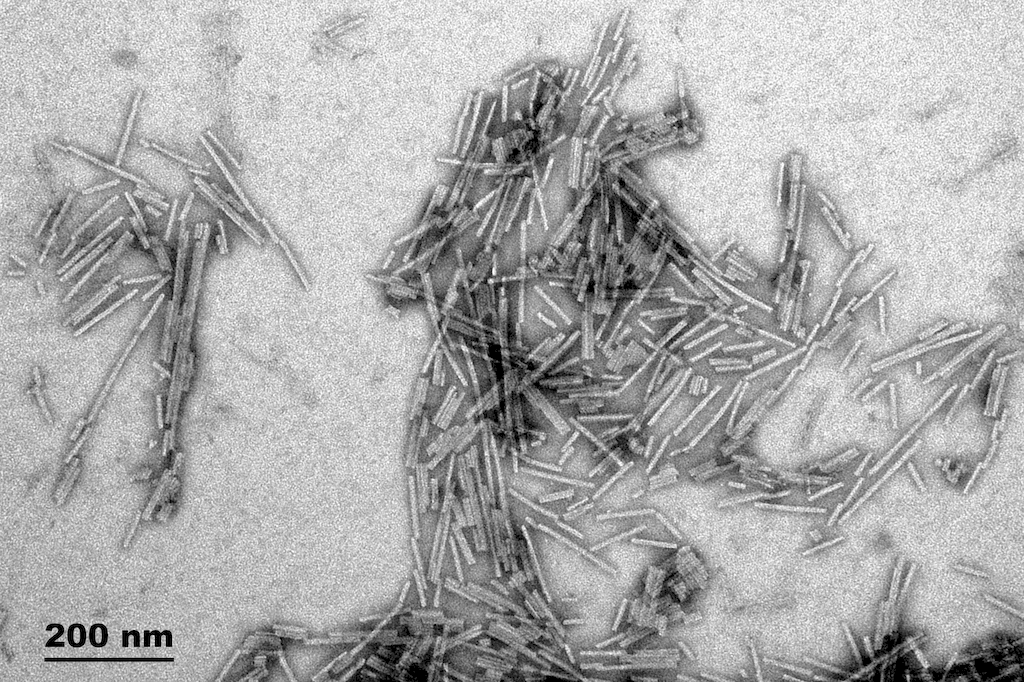
TEM of Active Human Recombinant Gamma Synuclein Protein Preformed Fibrils (Type 1) (SPR-459)
References
- Bruening, W. et al. Synucleins are expressed in the majority of breast and ovarian carcinomas and in preneoplastic lesions of the ovary. Cancer 88, 2154–2163 (2000).
- Guo, J. et al. Neuronal protein synuclein gamma predicts poor clinical outcome in breast cancer. J. Cancer 121, 1296–1305 (2007).
- Hu, H. et al. Tumor cell-microenvironment interaction models coupled with clinical validation reveal CCL2 and SNCG as two predictors of colorectal cancer hepatic metastasis. Cancer Res. 15, 5485–5493 (2009).
- Liu, H. et al. Loss of epigenetic control of synuclein-gamma gene as a molecular indicator of metastasis in a wide range of human cancers. Cancer Res. 65, 7635–7643 (2005).
- Surguchov, A. γ-Synuclein as a Cancer Biomarker: Viewpoint and New Approaches. Oncomedicine. 1,1-3 (2016).
- Oeckl, P. et al. Alpha-, Beta-, and Gamma-synuclein Quantification in Cerebrospinal Fluid by Multiple Reaction Monitoring Reveals Increased Concentrations in Alzheimer′s and Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease but No Alteration in Synucleinopathies. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Oct; 15(10): 3126–3138.
- Doherty J, McIntosh G, Milton I. Alpha- and gamma-synuclein proteins are present in cerebrospinal fluid and are increased in aged subjects with neurodegenerative and vascular changes. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2008;26(1):32-42
- Kokhan et al. Differential involvement of the gamma-synuclein in cognitive abilities on the model of knockout mice. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:53
- Ninkina N, Peters O, Millership S, Salem H, van der Putten H, Buchman VL. Gamma-synucleinopathy: neurodegeneration associated with overexpression of the mouse protein. Hum Mol Genet 2009, 18(10):1779–1794.
- Golebiewska, U. et al. Defining the Oligomerization State of γ-Synuclein in Solution and in Cells. Biochem. 2014 53(2): 293–299.
- Surgucheva et al. New α- and γ-synuclein immunopathological lesions in human brain. Acta Neuropathologica Communications 2014, 2:132
- Peters OM, Millership S, Shelkovnikova TA, et al. Selective pattern of motor system damage in gamma-synuclein transgenic mice mirrors the respective pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis 2012;48: 124–131.
- Galvin, J.E. Axon pathology in Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia hippocampus contains a-, b-, and g-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999 Nov 9; 96(23): 13450–13455.
- Surguchov A: Synucleins: are they two-edged swords? J Neurosci Res 2013, 91(2):16
- Surgucheva I, Sharov VS, Surguchov A: γ-Synuclein: seeding of α-synuclein aggregation and transmission between cells. Biochemistry 2012, 51(23):4743–4754.

Leave a Reply