|
Antibody Dilution |
WB (1:500), ICC/IF (1:100); optimal dilutions for assays should be determined by the user. |
|
Conjugates |
APC, ATTO 390, ATTO 488, ATTO 594, Biotin, FITC, HRP, PerCP, RPE, Unconjugated
| Dylight 488 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- High photostability
- Less pH-sensitive
- Excellent batch-to-batch reproducibility
- Stringently QC tested
- Molecular weight: 1011 g/mol
Dylight 488 Datasheet |
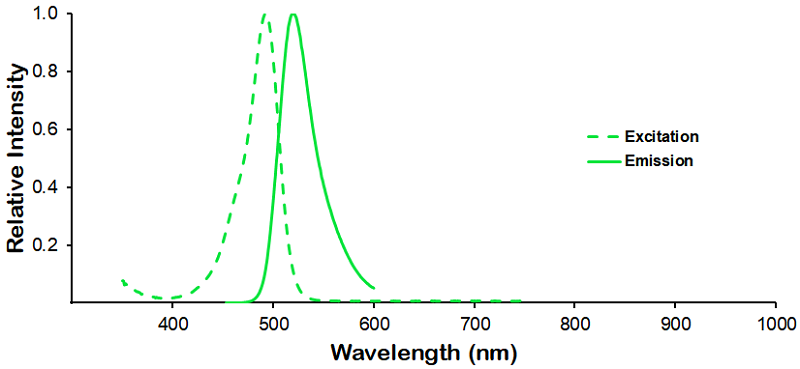 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 493 nm
λem = 518 nm
εmax = 7.0×104
Laser = 488 nm |
| APC/Cy7 |
Overview:
- High quantum yield
- Excellent batch-to-batch reproducibility
- Stringently QC tested
APC-Cy7 Datasheet
|
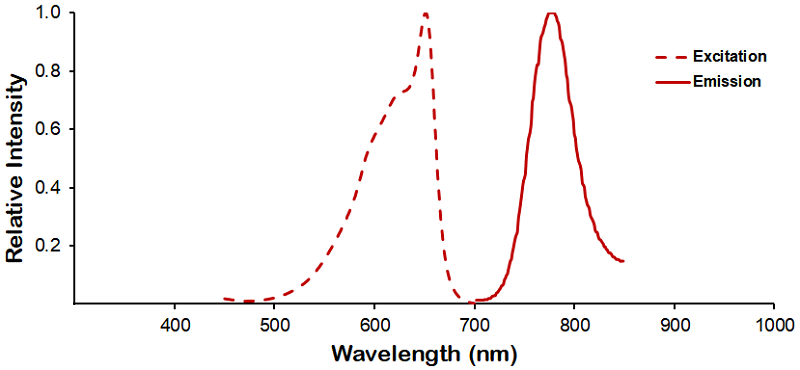 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 652 nm
λem = 790 nm
Laser = 594 or 633 nm
|
| Dylight 350 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence intensity
- High photostability
- Less pH-sensitive
- Excellent solubility in water
- Stringently QC tested
- Excellent batch-to-batch reproducibility
- Molecular weight: 874 g/mol
Dylight 350 Datasheet |
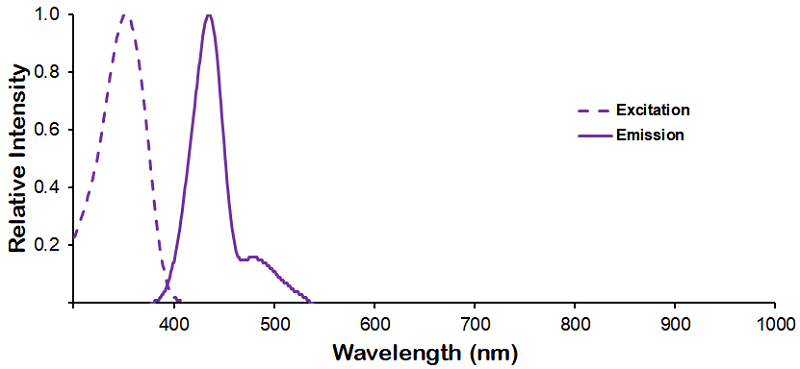 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 353 nm
λem = 432 nm
εmax = 1.5×104
|
| Dylight 405 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence intensity
- High photostability
- Less pH-sensitive
- Excellent batch-to-batch reproducibility
- Stringently QC tested
- Molecular weight: 793 g/mol
Dylight 405 Datasheet |
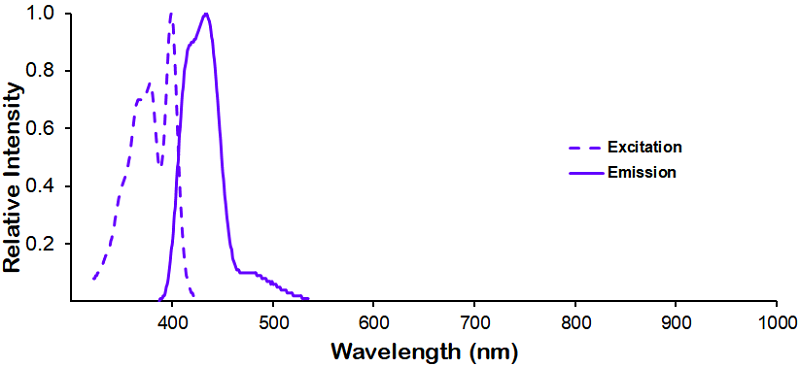 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 400 nm
λem = 420 nm
εmax = 3.0×104
Laser = 405 nm |
| Dylight 594 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- High photostability
- Less pH-sensitive
- Excellent batch-to-batch reproducibility
- Stringently QC tested
- Molecular weight: 1078 g/mol
Dylight 594 Datasheet |
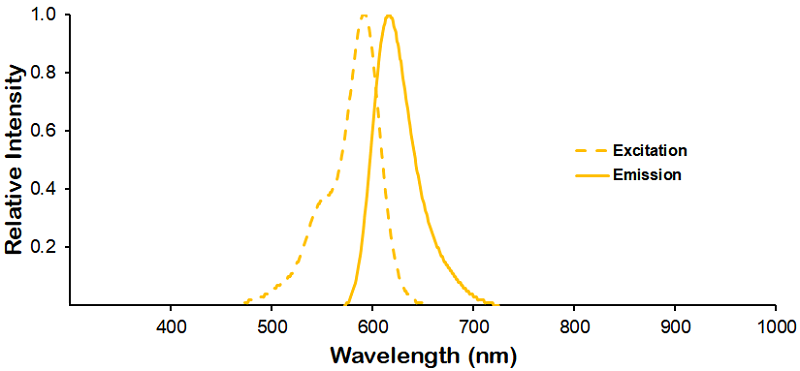 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 593 nm
λem = 618 nm
εmax = 8.0×104
Laser = 526 nm |
| Dylight 633 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- High photostability
- Less pH-sensitive
- Excellent batch-to-batch reproducibility
- Stringently QC tested
- Molecular weight: 1066 g/mol
Dylight 633 Datasheet |
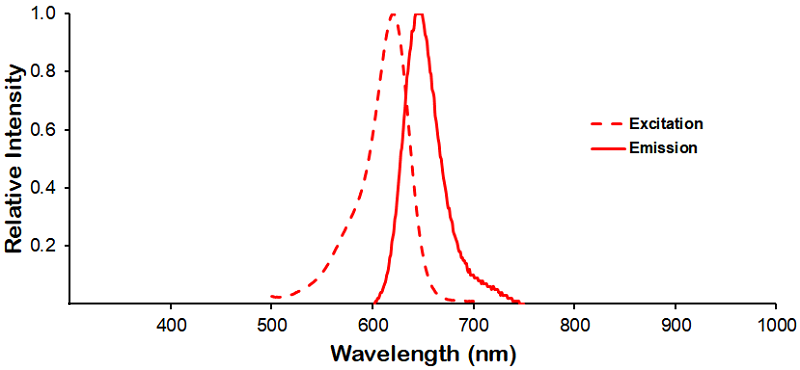 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 638 nm
λem = 658 nm
εmax = 1.7×105
Laser = 633 nm |
| PerCP |
Overview:
- Peridinin-Chlorophyll-Protein Complex
- Small phycobiliprotein
- Isolated from red algae
- Large stokes shift (195 nm)
- Molecular Weight: 35 kDa
PerCP Datasheet |
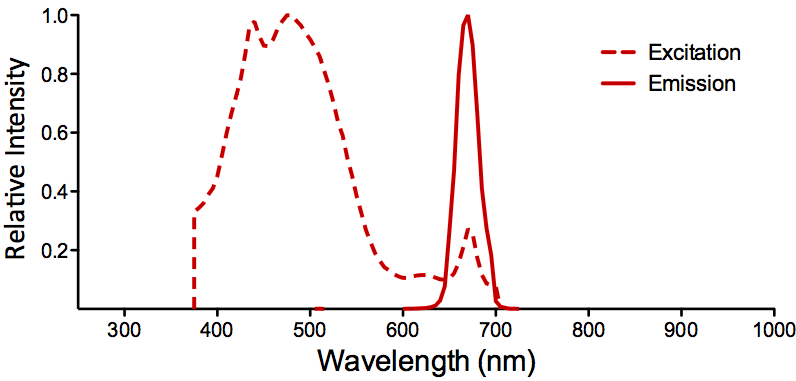 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 482 nm
λem = 677 nm
εmax = 1.96 x 106
Laser = 488 nm |
| PE/ATTO 594 |
| PE/ATTO 594 is a tandem conjugate, where PE is excited at 535 nm and transfers energy to ATTO 594 via FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer), which emits at 627 nm. |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- High photostability
- Very hydrophilic
- Excellent solubility in water
- Very little aggregation
PE/ATTO 594 Datasheet |
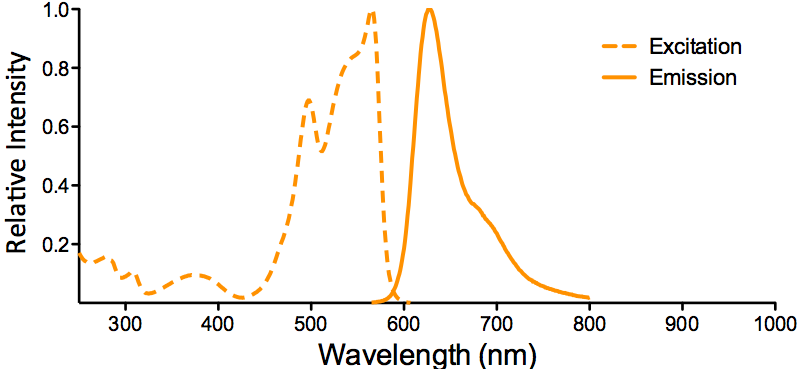 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 535 nm
λem = 627 nm
Laser = 488 to 561 nm |
| FITC (Fluorescein) |
Overview:
- Excellent fluorescence quantum yield
- High rate of photobleaching
- Good solubility in water
- Broad emission spectrum
- pH dependent spectra
- Molecular formula: C20H12O5
- Molar mass: 332.3 g/mol
FITC-Fluorescent-conjugate |
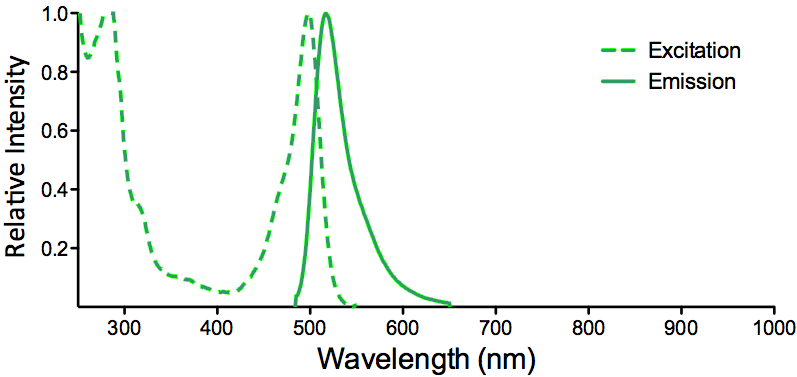 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 494 nm
λem = 520 nm
εmax = 7.3×104
Φf = 0.92
τfl = 5.0 ns
Brightness = 67.2
Laser = 488 nm
Filter set = FITC |
| ATTO 700 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- Excellent thermal and photostability
- Quenched by electron donors
- Very hydrophilic
- Good solubility in polar solvents
- Zwitterionic dye
- Molar Mass: 575 g/mol
ATTO 700 Datasheet |
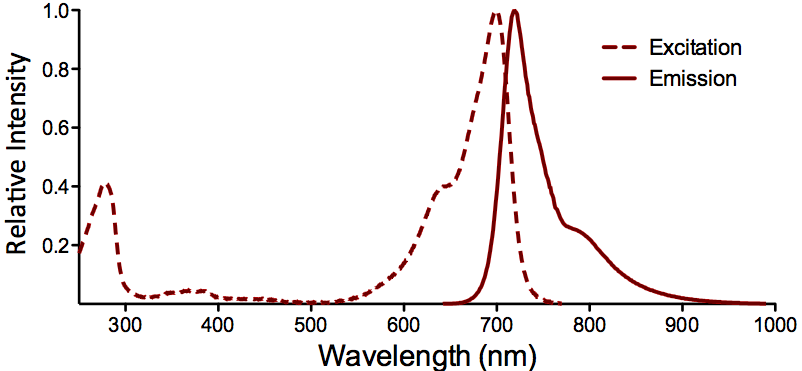 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 700 nm
λem = 719 nm
εmax = 1.25×105
Φf = 0.25
τfl = 1.6 ns
Brightness = 31.3
Laser = 676 nm
Filter set = Cy®5.5 |
| ATTO 680 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- Excellent thermal and photostability
- Quenched by electron donors
- Very hydrophilic
- Good solubility in polar solvents
- Zwitterionic dye
- Molar Mass: 631 g/mol
ATTO 680 Datasheet |
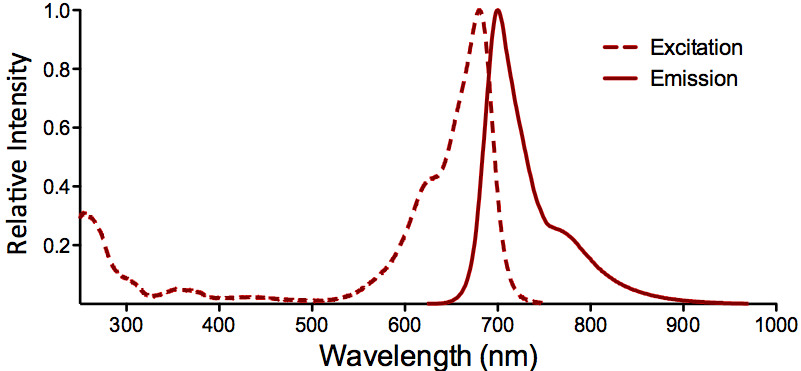 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 680 nm
λem = 700 nm
εmax = 1.25×105
Φf = 0.30
τfl = 1.7 ns
Brightness = 37.5
Laser = 633 – 676 nm
Filter set = Cy®5.5 |
| ATTO 655 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- High thermal and photostability
- Excellent ozone resistance
- Quenched by electron donors
- Very hydrophilic
- Good solubility in polar solvents
- Zwitterionic dye
- Molar Mass: 634 g/mol
ATTO 655 Datasheet |
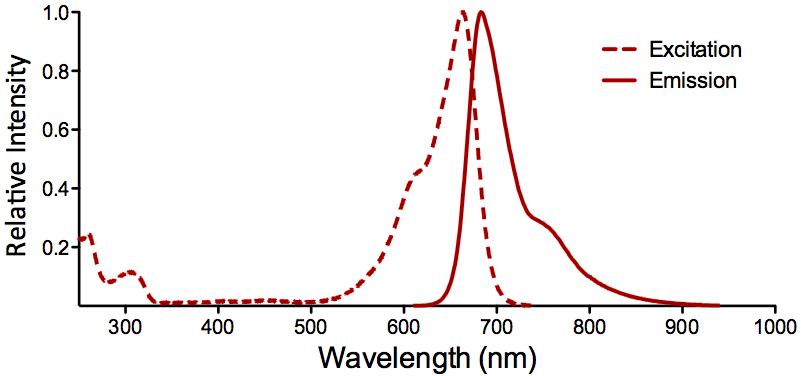 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 663 nm
λem = 684 nm
εmax = 1.25×105
Φf = 0.30
τfl = 1.8 ns
Brightness = 37.5
Laser = 633 – 647 nm
Filter set = Cy®5 |
| ATTO 633 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- High thermal and photostability
- Moderately hydrophilic
- Good solubility in polar solvents
- Stable at pH 4 – 11
- Cationic dye, perchlorate salt
- Molar Mass: 652.2 g/mol
ATTO 633 Datasheet |
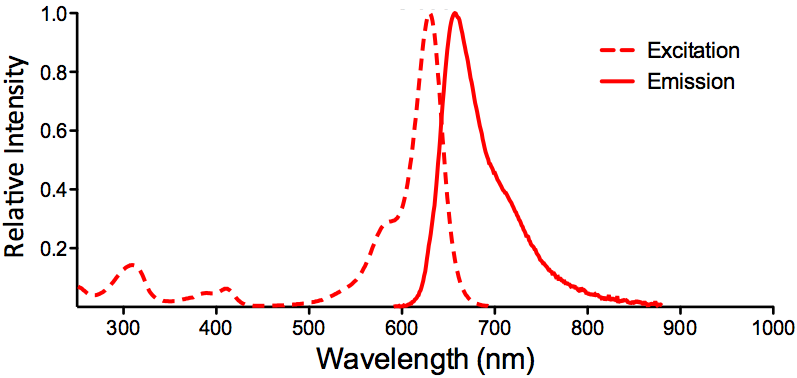 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 629 nm
λem = 657 nm
εmax = 1.3×105
Φf = 0.64
τfl = 3.2 ns
Brightness = 83.2
Laser = 633 nm
Filter set = Cy®5 |
| ATTO 594 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- High photostability
- Very hydrophilic
- Excellent solubility in water
- Very little aggregation
- New dye with net charge of -1
- Molar Mass: 1137 g/mol
ATTO 594 Datasheet |
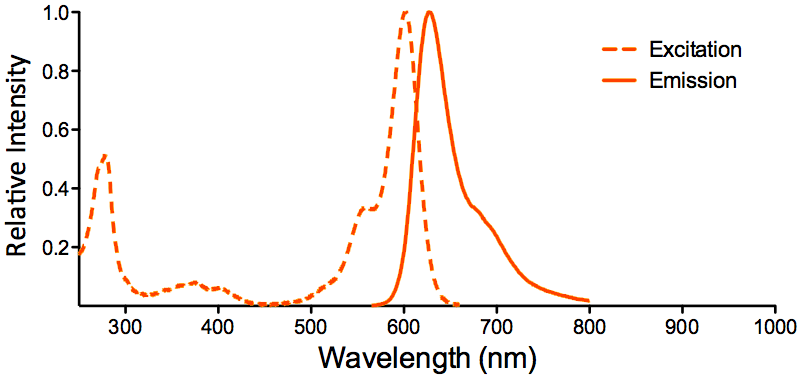 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 601 nm
λem = 627 nm
εmax = 1.2×105
Φf = 0.85
τfl = 3.5 ns
Brightness = 102
Laser = 594 nm
Filter set = Texas Red® |
| ATTO 565 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- High thermal and photostability
- Good solubility in polar solvents
- Excellent solubility in water
- Very little aggregation
- Rhodamine dye derivative
- Molar Mass: 611 g/mol
ATTO 565 Datasheet |
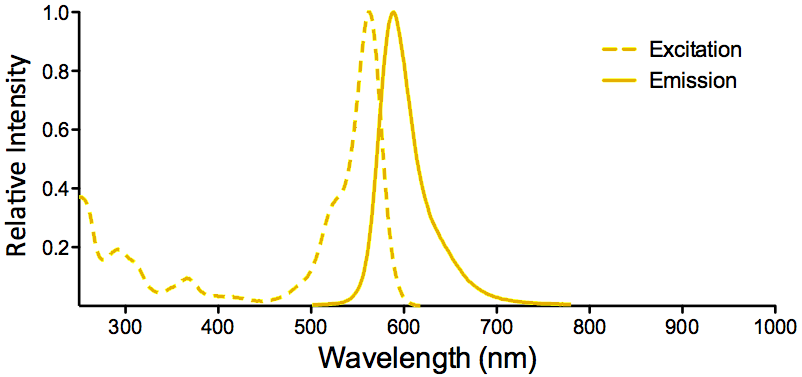 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 563 nm
λem = 592 nm
εmax = 1.2×105
Φf = 0.9
τfl = 3.4 n
Brightness = 10
Laser = 532 nm
Filter set = TRITC |
| ATTO 488 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- High photostability
- Very hydrophilic
- Excellent solubility in water
- Very little aggregation
- New dye with net charge of -1
- Molar Mass: 804 g/mol
ATTO 488 Datasheet |
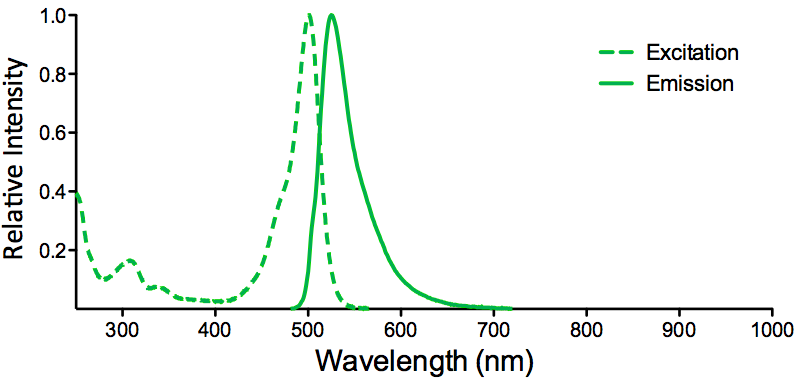 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 501 nm
λem = 523 nm
εmax = 9.0×104
Φf = 0.80
τfl = 4.1 ns
Brightness = 72
Laser = 488 nm
Filter set = FITC |
| ATTO 390 |
Overview:
- High fluorescence yield
- Large Stokes-shift (89 nm)
- Good photostability
- Moderately hydrophilic
- Good solubility in polar solvents
- Coumarin derivate, uncharged
- Low molar mass: 343.42 g/mol
ATTO 390 Datasheet |
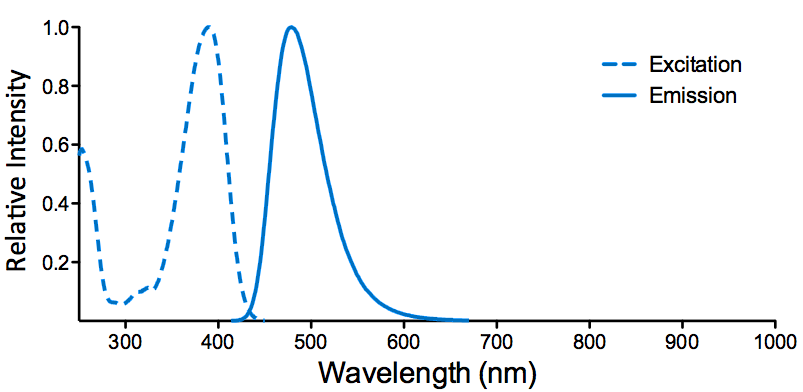 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 390 nm
λem = 479 nm
εmax = 2.4×104
Φf = 0.90
τfl = 5.0 ns
Brightness = 21.6
Laser = 365 or 405 nm |
| APC (Allophycocyanin) |
Overview:
- High quantum yield
- Large phycobiliprotein
- 6 chromophores per molecule
- Isolated from red algae
- Molecular Weight: 105 kDa
APC Datasheet |
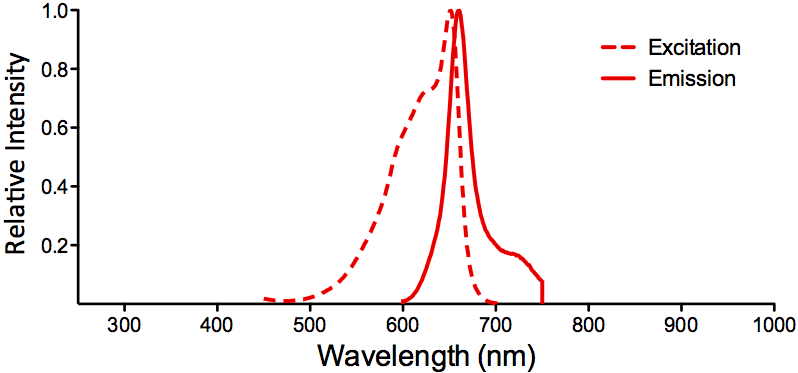 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 650 nm
λem = 660 nm
εmax = 7.0×105
Φf = 0.68
Brightness = 476
Laser = 594 or 633 nm
Filter set = Cy®5 |
Streptavidin
Properties:
- Homo-tetrameric protein purified from Streptomyces avidinii which binds four biotin molecules with extremely high affinity
- Molecular weight: 53 kDa
- Formula: C10H16N2O3S
- Applications: Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA
Streptavidin Datasheet
Biotin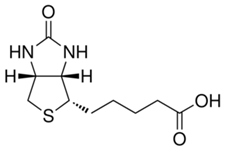
Properties:
- Binds tetrameric avidin proteins including Streptavidin and neuravidin with very high affinity
- Molar mass: 244.31 g/mol
- Formula: C10H16N2O3S
- Applications: Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA
Biotin Datasheet
HRP (Horseradish peroxidase)
Properties:
- Enzymatic activity is used to amplify weak signals and increase visibility of a target
- Readily combines with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to form HRP-H2O2 complex which can oxidize various hydrogen donors
- Catalyzes the conversion of:
- Chromogenic substrates (e.g. TMB, DAB, ABTS) into coloured products
- Chemiluminescent substrates (e.g. luminol and isoluminol) into light emitting products via enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL)
- Fluorogenic substrates (e.g. tyramine, homovanillic acid, and 4-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid) into fluorescent products
- High turnover rate enables rapid generation of a strong signal
- 44 kDa glycoprotein
- Extinction coefficient: 100 (403 nm)
- Applications: Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA
HRP Datasheet
AP (Alkaline Phosphatase)
Properties:
- Broad enzymatic activity for phosphate esters of alcohols, amines, pyrophosphate, and phenols
- Commonly used to dephosphorylate the 5’-termini of DNA and RNA to prevent self-ligation
- Catalyzes the conversion of:
- Chromogenic substrates (e.g. pNPP, naphthol AS-TR phosphate, BCIP) into coloured products
- Fluorogenic substrates (e.g. 4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate) into fluorescent products
- Molecular weight: 140 kDa
- Applications: Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA
AP Datasheet
| R-PE (R-Phycoerythrin) |
Overview:
- Broad excitation spectrum
- High quantum yield
- Photostable
- Member of the phycobiliprotein family
- Isolated from red algae
- Excellent solubility in water
- Molecular Weight: 250 kDa
R-PE Datasheet |
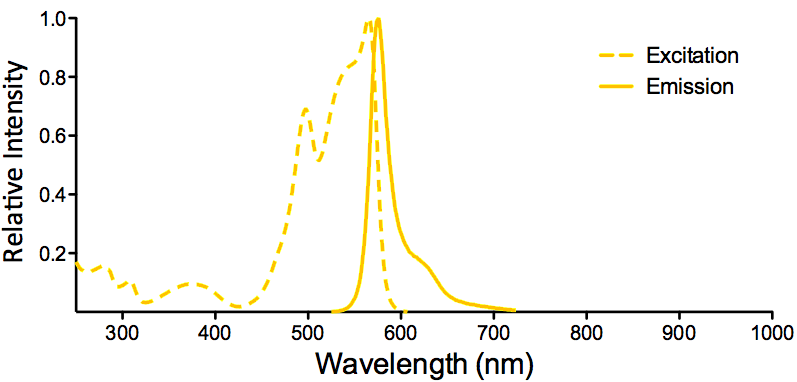 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 565 nm
λem = 575 nm
εmax = 2.0×106
Φf = 0.84
Brightness = 1.68 x 103
Laser = 488 to 561 nm
Filter set = TRITC |
|





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.