Targeting Alpha Synuclein Aggregation with CBP/p300 Inhibitors: A Novel Approach in Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutics
Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies are characterized by the accumulation of abnormal fibrillary aggregates of alpha synuclein protein that form inclusion structures known as Lewy Bodies. Alpha synuclein aggregation has been the subject of several studies that investigate new compounds to reduce or inhibit this process. Targeting alpha synuclein aggregation with small molecule inhibitors has been a new approach in Parkinson’s disease therapeutics. A recent study investigated selective lysine acetyltransferase (KAT) and bromodomain inhibitors on alpha synuclein aggregation induced by StressMarq’s mouse alpha synuclein preformed fibrils1.
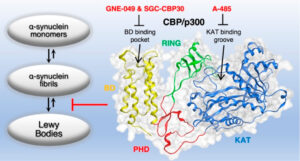
“Domain-Independent Inhibition of CBP/p300 Attenuates α-Synuclein Aggregation” Hlushchuk I., et al. 2021 ACS Chemical Neuroscience 12 (13), 2273-2279
Protein lysine acetylation by CBP/p300 and human disease
Lysine acetylation is one of the major post translational modifications (PTMs) of proteins involved in several biological processes including transcription, protein translation and degradation. This reversible PTM is highly regulated by the histone (lysine) acetyltransferases (HATs or KATs), which add the acetyl group to lysine residues and histone (lysine) deacetylases (HDACs or KDACs), which remove the acetyl group from proteins2. The CREB-binding (CBP) and the p300 proteins or CBP/p300 coactivator family are closely related transcriptional lysine acetyltransferases that have been studied extensively as they are involved in a variety of human diseases. Lysine acetyltransferases (KATs) catalyse the transfer of acetyl groups on substrate proteins. Each one of those proteins contains a KAT domain and a bromodomain. Bromodomains recognize and bind specifically to acetylated lysine residues and play a significant role in transcription and DNA repair5.
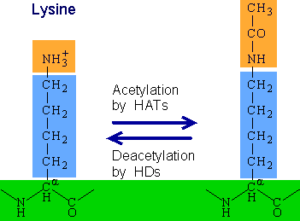
Lysine acetylation mechanism
Abnormal lysine acetylation activity has been linked to the development of different human diseases like cancer, inflammation and neurodegeneration3. It can affect protein structure and function leading to misfolding and aggregation, a pathological mechanism in neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s4. Bromodomain-containing proteins have received great attention as they are implicated in various diseases. Small molecules inhibitors that target bromodomains have been developed and used in preclinical and clinical studies for cancer therapy6,7. Recent studies showed that bromodomain proteins are also involved in protein aggregation. Chemical probes that specifically bind the CBP/p300 bromodomains can inhibit the formation of amyloid-like aggregates and reduce cytotoxicity4,5.
The impact of CBP/p300 inhibitors on alpha synuclein aggregation induced by StressMarq’s alpha synuclein PFFs
A research group from University of Helsinki recently published a study in the ACS Chemical Neuroscience journal1. The researchers used StressMarq’s mouse alpha synuclein preformed fibrils (catalog# SPR-324) to induce alpha synuclein aggregation in mouse embryonic dopaminergic neurons. The goal of this study was to investigate the effect of certain lysine acetyltransferase (KAT) and bromodomain inhibitors on alpha synuclein aggregation. Different inhibitors of specific multidomain proteins like CBP/p300, SMARCA2/4, TATA-box binding associated protein 1 (TAF1) and bromodomains and extraterminal domain (BET) family proteins were tested.
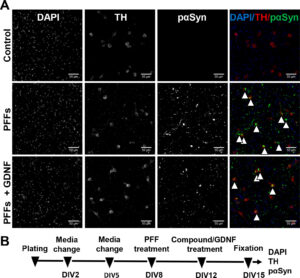
Accumulation of phosphorylated α-synuclein at Ser129 (pαSyn) in mouse embryonic dopaminergic neurons. (A) Treatment with preformed fibrils (PFFs) for 7 days induced formation of large intrasomal Lewy-body-like pαSyn-positive aggregates (indicated by arrowheads) in tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive dopaminergic neurons, as assessed by immunofluorescent staining with corresponding antibodies. GDNF, added 4 days after PFFs, reduced the pαSyn aggregation and was used as a positive control in the experiments. (B) Treatment timeline. Scale bar, 50 μm.
Specifically, primary neuronal cell cultures were treated with mouse alpha synuclein PFFs to induce Lewy body pathology and after 4 days of incubation KAT and bromodomain inhibitors were administered. GDNF (glial-cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor) was used as a positive control as it has been shown that it efficiently reduces phosphorylated α-synuclein accumulation in dopaminergic neurons. The results showed that specific KAT/bromodomain inhibitors of CBP/p300 (GNE-049, A-485, SGC-CBP30) significantly decreased alpha synuclein aggregation and they could be a promising therapeutic approach for Parkinson’s disease.
REFERENCES
- Domain-Independent Inhibition of CBP/p300 Attenuates α-Synuclein Aggregation. Hlushchuk I., et al. 2021 ACS Chemical Neuroscience12 (13), 2273-2279.
- Lysine Acetylation Goes Global: From Epigenetics to Metabolism and Therapeutics. Ali I., et al. 2018 Chem Rev. 118(3):1216-1252.
- Correction to Protein Lysine Acetylation by p300/CBP. Dancy BM., et al. 2016 Chem Rev. 116(14):8314.
- CBP/p300 Bromodomains Regulate Amyloid-like Protein Aggregation upon Aberrant Lysine Acetylation. Olzscha H. et al 2016 Cell Chemical Biology 24: 1–15.
- CBP/p300 Bromodomain Mediates Amyloid Formation. Liao D. 2017 Cell Chemical Biology 24(2): 128-129.
- Functions of bromodomain-containing proteins and their roles in homeostasis and cancer. Fujisawa T., et al. 2017 Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol18, 246–262.
- Bromodomain inhibitors and cancer therapy: From structures to applications. Pérez-Salvia M., et al. 2017 Epigenetics 12(5):323-339.


Leave a Reply