Therapeutic Approaches to Target Pathogenic Alpha-Synuclein
Parkinson’s disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and multiple system atrophy (MSA) belong to a group of progressive neurodegenerative disorders called synucleinopathies. Synucleinopathies are defined by the presence of misfolded and aggregated forms of alpha-synuclein. The molecular state of alpha-synuclein is critically important to its function. In a physiological state, alpha-synuclein is abundantly expressed in the blood, brain interstitial fluid and cerebrospinal fluid as monomers and have important roles in synaptic vesicle trafficking and neurotransmitter release.
In a pathological state, however, oligomers and soluble fibrillar/pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) are neurotoxic and spread between cells to disrupt cellular functions and promote inflammation. They can recruit monomeric alpha-synuclein to fibrils by acting as templates or “seeds”. In addition, insoluble fibrils of alpha-synuclein do not appear to be toxic and may even protect cells by sequestering toxic forms of alpha-synuclein.
A recent study by Gibbs et al., develops antibodies to specifically target pathogenic alpha-synuclein. The study authors describe the protective role the antibodies play in preventing cell-to-cell spread and neurotoxicity of pathogenic alpha-synuclein[1].
Modelling identifies structures in pathogenic alpha-synuclein
First, the study authors wanted to ensure that antibodies only targeted pathogenic forms of alpha-synuclein and not physiological forms. To achieve this, the authors used computational modelling to design an immunizing peptide only present in the three-dimensional structure of alpha-synuclein oligomeric and soluble fibrillar/PFFs, and not monomeric or insoluble fibrillar forms. The authors successfully identified a small cyclic peptide uniquely present on the surface of oligomers and small soluble fibrils.
Studying pathogenic alpha-synuclein
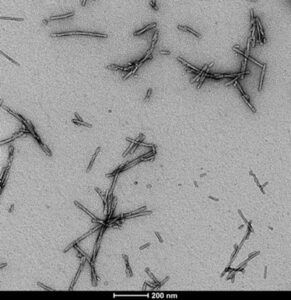
Figure 1. Pre-formed fibrils of alpha-synuclein (SPR-322) from StressMarq provide key tools for neurodegenerative disease research
The authors went on to determine the biological effect of the small cyclic peptide. For this, the authors compared the cyclic peptide with a pathogenic fibrillar form of alpha-synuclein, StressMarq’s human recombinant alpha-synuclein pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) (catalog# SPR-322).
Before use, StressMarq’s PFFs are sonicated to produce small soluble fibrils/protofibrils, as the shorter fibril size is critical for the aggregation of monomeric alpha-synuclein. StressMarq’s alpha-synuclein PFFs, like endogenous fibrillar alpha-synuclein, exert a pathogenic effect by inducing the formation of alpha-synuclein aggregates. The authors showed that the cyclic peptide could replicate the effect of StressMarq’s alpha-synuclein PFFs in causing the aggregation of intracellular alpha-synuclein monomers.
Visual analysis using negative stain electron microscopy showed that the shape and width of cyclic peptides resembled StressMarq’s sonicated alpha-synuclein PFFs. The authors also showed that the cyclic peptide exhibited toxicity in neuronal cultures.
Generating antibodies against pathogenic alpha-synuclein
Next, the cyclic peptide was used to generate antibodies against pathogenic alpha-synuclein. The study authors used surface plasmon resonance for binding studies to check whether the antibodies only targeted pathogenic alpha-synuclein and not other forms of alpha-synuclein. They found the antibodies bound small soluble fibrils/protofibrils of alpha-synuclein but not monomeric alpha-synuclein. In addition, the antibodies could recognize pathogenic alpha-synuclein species in brain extracts from patients with DLB and MSA.
Monoclonal antibodies play a protective role
The study authors then assessed whether the antibodies abrogated the pathogenic effects of alpha-synuclein oligomers and small soluble fibrils. Antibody treatment stopped soluble fibrillar PFFs from aggregating monomeric alpha-synuclein, as well as reducing their recruitment into pathogenic aggregates.
Overall, the study produced selective monoclonal antibodies targeting pathogenic alpha-synuclein forms. The antibodies did not interfere with physiologically important alpha-synuclein and non-toxic forms of alpha-synuclein. This therapeutic strategy could provide an improved efficacy and safety profile compared to pan alpha-synuclein-directed antibodies currently assessed in clinical trials.
StressMarq’s products support neurodegenerative disease research
StressMarq has a range of monomeric, fibrilized and oligomeric protein preparations for neurodegenerative disease research. Gibbs et al., designed selective antibodies that targeted pathogenic forms of alpha-synuclein. This study could have important applications in alpha-synuclein targeting therapeutics for synucleinopathies.
Article references
[1] E. Gibbs et al., ‘Selective for Pathogenic Forms of Alpha-Synuclein Rational Generation of Monoclonal Antibodies’, Biomedicines ., vol. 10, no. 9, p. 2168, 2022, doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092168.


Leave a Reply