Combating Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neuroinflammation is an inflammatory response in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). As a defense mechanism, it functions to protect the brain from diverse pathogens by promoting tissue repair and removing cellular debris. However, chronic neuroinflammation has harmful effects. It can lead to cellular damage, neuronal loss, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.
Two recent scientific publications each highlight the importance of steering therapeutic strategies at neuroinflammation pathways. StressMarq’s products were instrumental in each study. Here, we discuss the details of the research.
Regulating damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) suppresses cerebral inflammation
The first line of defense in neuroinflammation is the phagocytosis of pathogens and cellular debris. However, inefficient phagocytic clearance can cause problems. In this case, molecules called damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are released. DAMPs are endogenous intracellular proteins. For this reason, DAMPs remain “hidden” from the immune system when released. Once free in the extracellular environment, DAMPs can induce inflammation, which can lead to detrimental consequences.
An article published in Cell Reports describes for the first time how neuroinflammation can be regulated by targeting DAMPs with Apoptosis Inhibitor of Macrophage or AIMs1. AIMs are
circulating proteins produced by macrophages. One function of AIMs is to increase the phagocytic removal of dead cells. Dead cells have high levels of exposed phosphatidylserine, making them
highly negatively charged. AIMs binds to negatively charged dead cells using their positively charged C-terminus. This leads to the phagocytic removal of dead cells.
The researchers in the study looked at well-known DAMP proteins, including extracellular HSP70 which is known to act as a DAMP. For this reason, recombinant human full-length HSP70 (catalog# SPR-117) from StressMarq and other DAMPs were utilized. The study showed that AIMs bind directly to DAMPs in a dose-dependent manner. This results in the phagocytic internalization of DAMPs1.
The authors showed that AIMs could reduce or attenuate DAMPs and, in doing so, suppress cerebral inflammation. The study showed AIMs reduced cerebral inflammation in ischemic stroke but could also have roles in treating neurodegenerative disorders.
Pharmacological inhibition of SMOX reduces neuroinflammation
Another way to look at neuroinflammation is to focus on the downstream effects using pharmacological inhibitors. Spermine oxidase (SMOX) is an enzyme important in neuroinflammation. SMOX is overexpressed in neurons leading to oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. Excitotoxicity is caused by excessive activation of glutamate receptors. This ultimately leads to neuronal function and cell death, characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases.
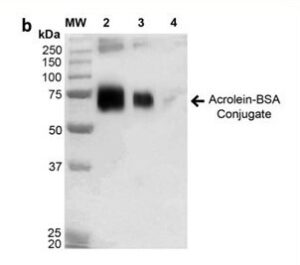
A recent study by Alfarhan et al. used a retinal model of excitotoxicity. One of the by-products of the enzymatic reaction of SMOX is acrolein. Acrolein acts as a neurotoxin and can bind to proteins causing dysfunction. The researchers assessed the effect of acrolein by using StressMarq’s Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) modified with Acrolein (catalog# SPR-206) and monitoring the formation of acrolein-containing protein complexes.
In overstimulated retina cells, there was a significant increase in acrolein-protein complexes. Treating with the SMOX inhibitor MDL 72527 markedly reduced the formation of acrolein-protein complexes of a certain molecular weight (50–60 kDa in size). Overall, the pharmacological agent decreased SMOX activation of immune cells and reduced acrolein complex formation. This study reveals the possibility of using the pharmacological inhibitor MDL 72527 to reduce neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration of the eye2.
These potential therapies may mitigate the effects of neuroinflammation or treat dangerous damage downstream.
Related StressMarq products
StressMarq’s products were vital tools to support this research. StressMarq offers a wide variety of reagents for neurodegenerative disease research, such as additional antibodies to DAMPs, including Anti-HMGB1 antibody (catalog# SPC-1259) and Anti-HO-1 Antibody (catalog# SPC-211).
Elevated levels of NRF2 are also indicators for SMOX inhibition upregulated antioxidant signaling. StressMarq produces an antibody for this protein, Anti-NRF2 Antibody (catalog# SPC-711).
References
- AIM/CD5L attenuates DAMPs in the injured brain and thereby ameliorates ischemic stroke, Maehara, N. et al. Cell Rep 36, (2021).
- Pharmacological Inhibition of Spermine Oxidase Suppresses Excitotoxicity Induced Neuroinflammation in Mouse Retina. Alfarhan, M. et al. Int J Mol Sci 23, (2022).

Leave a Reply